Abstract
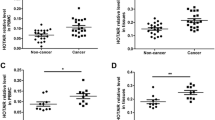
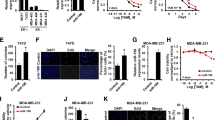
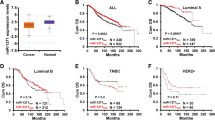
Metastasis has become the main challenge for treatment of estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) negative breast cancer. Here, we found a negative correlation between miR-497 and estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRα), a nuclear receptor overexpressed in ERα negative breast cancer. Targeted inhibition of ERRα by si-RNA increased miR-497 expression while overexpression of ERRα inhibited miR-497 expression. Further investigation showed that miR-497 targeted ERRα by binding to the 3′UTR region of ERRα. Luciferase assay and ChIP assay confirmed that ERα directly regulated the transcription of miR-497, suggesting that loss of ERα lowered miR-497 level in ERα negative breast cancer. Further, overexpression of miR-497 not only inhibited ERRα expression but also reduced MIF level and MMP9 activity, which led to significant decreases in cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of ERα negative breast cancer. Taken together, our findings suggested that, in ERα negative breast cancer, the low level of ERα reduced miR-497 expression, which promoted ERRα expression that enhanced cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by increasing MIF expression and MMP9 activity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2012;490:61–70.
Yager JD, Davidson NE. Estrogen carcinogenesis in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:270–82.
Musgrove EA, Sutherland RL. Biological determinants of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9:631–43.
D’Amato NC, Rogers TJ, Gordon MA, Greene LI, Cochrane DR, Spoelstra NS, Nemkov TG, D’Alessandro A, Hansen KC, Richer JK. A TDO2-AhR signaling axis facilitates anoikis resistance and metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2015;75:4651–64.
Qu Q, Mao Y, Xiao G, Fei X, Wang J, Zhang Y, Liu J, Cheng G, Chen X, Wang J, Shen K. USP2 promotes cell migration and invasion in triple negative breast cancer cell lines. Tumour Biol. 2015;36:5415–23.
Giguere V, Yang N, Segui P, Evans RM. Identification of a new class of steroid hormone receptors. Nature. 1988;331:91–4.
Barry JB, Laganiere J, Giguere V. A single nucleotide in an estrogen-related receptor alpha site can dictate mode of binding and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1alpha activation of target promoters. Mol Endocrinol. 2006;20:302–10.
Deblois G, Giguère V. Oestrogen-related receptors in breast cancer: control of cellular metabolism and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:27–36.
Kammerer M, Gutzwiller S, Stauffer D, Delhon I, Seltenmeyer Y, Fournier B. Estrogen receptor α (ERα) and estrogen related receptor α (ERRα) are both transcriptional regulators of the Runx2-I isoform. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2013;369:150–60.
Kraus RJ, Ariazi EA, Farrell ML, Mertz JE. Estrogen-related receptor alpha 1 actively antagonizes estrogen receptor-regulated transcription in MCF-7 mammary cells. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:24826–34.
Vanacker JM, Pettersson K, Gustafsson JA, Laudet V. Transcriptional targets shared by estrogen receptor- related receptors (ERRs) and estrogen receptor (ER) alpha, but not by ERbeta. EMBO J. 1999;18:4270–9.
Suzuki T, Miki Y, Moriya T, Shimada N, Ishida T, Hirakawa H, Ohuchi N, Sasano H. Estrogen-related receptor alpha in human breast carcinoma as a potent prognostic factor. Cancer Res. 2004;64:4670–6.
Ariazi EA, Clark GM, Mertz JE. Estrogen-related receptor α and estrogen-related receptor γ associate with unfavorable and favorable biomarkers, respectively, in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2002;62:6510–8.
Manna S, Bostner J, Sun Y, Miller LD, Alayev A, Schwartz NS, Lager E, Fornander T, Nordenskjöld B, JJ Y, Stål O, Holz MK. ERRα is a marker of tamoxifen response and survival in triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22:1421–31.
Fradet A, Sorel H, Bouazza L, Goehrig D, Dépalle B, Bellahcène A, Castronovo V, Follet H, Descotes F, Aubin JE, Clézardin P, Bonnelye E. Dual function of ERRα in breast cancer and bone metastasis formation: implication of VEGF and osteoprotegerin. Cancer Res. 2011;71:5728–38.
YM W, Chen ZJ, Liu H, Wei WD, LL L, Yang XL, Liang WT, Liu T, Liu HL, Du J, Wang HS. Inhibition of ERRα suppresses epithelial mesenchymal transition of triple negative breast cancer cells by directly targeting fibronectin. Oncotarget. 2015;6:25588–601.
Stein RA, Chang CY, Kazmin DA, Way J, Schroeder T, Wergin M, Dewhirst MW, McDonnell DP. Estrogen-related receptor alpha is critical for the growth of estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2008;68:8805–12.
Thewes V, Simon R, Schroeter P, Schlotter M, Anzeneder T, Büttner R, Benes V, Sauter G, Burwinkel B, Nicholson RI, Sinn HP, Schneeweiss A, Deuschle U, Zapatka M, Heck S, Lichter P. Reprogramming of the ERRα and ERα target gene landscape triggers tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2015;75:720–31.
Xu J, Wang T, Cao Z, Huang H, Li J, Liu W, Liu S, You L, Zhou L, Zhang T, Zhao Y. MiR-497 downregulation contributes to the malignancy of pancreatic cancer and associates with a poor prognosis. Oncotarget. 2014;5:6983–93.
Qiu YY, Hu Q, Tang QF, Feng W, SJ H, Liang B, Peng W, Yin PH. MicroRNA-497 and bufalin act synergistically to inhibit colorectal cancer metastasis. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:2599–606.
Li D, Zhao Y, Liu C, Chen X, Qi Y, Jiang Y, Zou C, Zhang X, Liu S, Wang X, Zhao D, Sun Q, Zeng Z, Dress A, Lin MC, Kung HF, Rui H, Liu LZ, Mao F, Jiang BH, Lai L. Analysis of MiR-195 and MiR-497 expression, regulation and role in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:1722–30.
Luo M, Shen D, Zhou X, Chen X, Wang W. MicroRNA-497 is a potential prognostic marker in human cervical cancer and functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. Surgery. 2013;153:836–47.
Li W, Jin X, Deng X, Zhang G, Zhang B, Ma L. The putative tumor suppressor microRNA-497 modulates gastric cancer cell proliferation and invasion by repressing eIF4E. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;449:235–40.
Wu Z, Cai X, Huang C, Xu J, Liu A. miR-497 suppresses angiogenesis in breast carcinoma by targeting HIF-1α. Oncol Rep. 2016;35:1696–702.
Wu Z, Li X, Cai X, Huang C, Zheng M. miR-497 inhibits epithelial mesenchymal transition in breast carcinoma by targeting Slug. Tumour Biology 2015.
Tu Y, Liu L, Zhao D, Liu Y, Ma X, Fan Y, Wan L, Huang T, Cheng Z, Shen B. Overexpression of miRNA-497 inhibits tumor angiogenesis by targeting VEGFR2. Scientific Reports. 2016. doi:10.1038/srep21221.
Wei C, Luo Q, Sun X, Li D, Song H, Li X, Song J, Hua K, Fang L. MicroRNA-497 induces cell apoptosis by negatively regulating Bcl-2 protein expression at the posttranscriptional level in human breast cancer. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology. 2015;8:7729–39.
Hu P, Kinyamu HK, Wang L, Martin J, Archer TK, Teng C. Estrogen induces estrogen-related receptor α gene expression and chromatin structural changes in estrogen receptor (ER)-positive and ER-negative breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2008;283:6752–63.
Liu Y, Zhao L, Ju Y, Li W, Zhang M, Jiao Y, Zhang J, Wang S, Wang Y, Zhao M, Zhang B, Zhao Y. A novel androstenedione derivative induces autophagy and attenuates drug resistance in osteosarcoma by inhibiting macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF). Cell Death Dis. 2014. doi:10.1038/cddis.2014.300.
Liu J, Xian G, Li M, Zhang Y, Yang M, Yu Y, Lv H, Xuan S, Lin Y, Gao L. Cholesterol oxidase from Bordetella species promotes irreversible cell apoptosis in lung adenocarcinoma by cholesterol oxidation. Cell Death Dis. 2014. doi:10.1038/cddis.2014.324.
Zou J, Xu L, Ju Y, Zhang P, Wang Y, Zhang B. Cholesterol depletion induces ANTXR2-dependent activation of MMP-2 via ERK1/2 phosphorylation in neuroglioma U251 cell. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;452:186–90.
Guo ST, Jiang CC, Wang GP, Li YP, Wang CY, Guo XY, Yang RH, Feng Y, Wang FH, Tseng HY, Thorne RF, Jin L, Zhang XD. MicroRNA-497 targets insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor and has a tumour suppressive role in human colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 2013;32:1910–20.
Wang L, Jiang CF, Li DM, Ge X, Shi ZM, Li CY, Liu X, Yin Y, Zhen L, Liu LZ, Jiang BH. MicroRNA-497 inhibits tumor growth and increases chemosensitivity to 5-fluorouracil treatment by targeting KSR1. Oncotarget. 2016;7:2660–71.
Qiu Y, Yu H, Shi X, Xu K, Tang Q, Liang B, Hu S, Bao Y, Xu J, Cai J, Peng W, Cao Q, Yin. micro RNA-497 inhibits invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells by targeting vascular endothelial growth factor-a. Cell Prolif. 2016;49:69–78.
Wei W, Zhang WY, Bai JB, Zhang HX, Zhao YY, Li XY, Zhao SH. The NF-κB-modulated microRNAs miR-195 and miR-497 inhibit myoblast proliferation by targeting Igf1r, Insr and cyclin genes. J Cell Sci. 2016;129:39–50.
Lan J, Xue Y, Chen H, Zhao S, Wu Z, Fang J, Han C, Lou M. Hypoxia-induced miR-497 decreases glioma cell sensitivity to TMZ by inhibiting apoptosis. FEBS Lett. 2014;588:3333–9.
Yang J, AlTahan A, Jones DT, Buffa FM, Bridges E, Interiano RB, Qu C, Vogt N, Li JL, Baban D, Ragoussis J, Nicholson R, Davidoff AM, Harris AL. Estrogen receptor-α directly regulates the hypoxia-inducible factor 1 pathway associated with antiestrogen response in breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112:15172–7.
Lam SS, Mak AS, Yam JW, Cheung AN, Ngan HY, Wong AS. Targeting estrogen-related receptor alpha inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stem cell properties of ovarian cancer cells. Mol Ther. 2014;22:743–51.
Sailland J, Tribollet V, Forcet C, Billon C, Barenton B, Carnesecchi J, Bachmann A, Gauthier KC, Yu S, Giguère V, Chan FL, Vanacker JM. Estrogen-related receptor α decreases RHOA stability to induce orientated cell migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111:15108–13.
Dwyer MA, Joseph JD, Wade HE, Eaton ML, Kunder RS, Kazmin D, Chang CY, McDonnell DP. WNT11 expression is induced by estrogen-related receptor alpha and beta-catenin and acts in an Autocrine manner to increase cancer cell migration. Cancer Res. 2010;70:9298–308.
Jarzabek K, Koda M, Kozlowski L, Sulkowski S, Kottler ML, Wolczynski S. The significance of the expression of ERR alpha as a potential biomarker in breast cancer. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2009;113:127–33.
Chang CY, Kazmin D, Jasper JS, Kunder R, Zuercher WJ, McDonnell DP. The metabolic regulator ERRalpha, a downstream target of HER2/IGF-1R, as a therapeutic target in breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 2011;20:500–10.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Yanliang Lin (Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University) for careful technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 13 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, L., Liu, B., Jiang, L. et al. MicroRNA-497 downregulation contributes to cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of estrogen receptor alpha negative breast cancer by targeting estrogen-related receptor alpha. Tumor Biol. 37, 13205–13214 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5200-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5200-1