Abstract
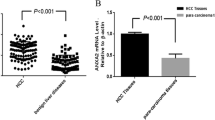
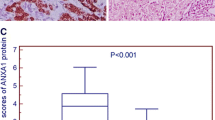
The prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after surgical resection remains unsatisfactory for the majority of HCC patients who developed early recurrence or metastasis. There is still a lack of reliable biomarkers that can be used to predict the possibility of recurrence/metastasis in HCC patients after operation. In the current study, annexin A4, a calcium-dependent phospholipid-binding protein, has been found to be significantly elevated in HCC patients with early recurrence/metastasis, and had a strong correlation with portal vein tumor thrombosis (p = 0.03) and advanced BCLC stage (p = 0.002). Cox proportional hazards regression analysis revealed that annexin A4 was an independent prognostic predictor for both early recurrence/metastasis (HR = 1.519, p = 0.032) and overall survival (HR = 1.827, p = 0.009) after surgical resection. Meanwhile, Kaplan–Meier analysis showed that Patients with high-expression levels of annexin A4 had higher recurrence rate and shorter overall survival than those with low expression (log-rank test, p < 0.001). Furthermore, in vitro studies have demonstrated that overexpression of annexin A4 facilitated HCC cell migration and invasion via regulating epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT). In conclusion, annexin A4 has played important roles in the progression of HCC, and might act as a potential prognostic biomarker for HCC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
El–Serag HB, Rudolph KL. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2007;132(7):2557–76.
El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(12):1118–27.
W-q C, Zheng R-s, S-w Z, Li N, Zhao P, G-l L, et al. Report of incidence and mortality in China cancer registries, 2008. Chin J Cancer Res. 2012;24(3):171–80.
Poon RT. Prevention of recurrence after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: a daunting challenge. Hepatology. 2011;54(3):757–9.
Portolani N, Coniglio A, Ghidoni S, Giovanelli M, Benetti A, Tiberio GAM, et al. Early and late recurrence after liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: prognostic and therapeutic implications. Ann Surg. 2006;243(2):229–35.
Imamura H, Matsuyama Y, Tanaka E, Ohkubo T, Hasegawa K, Miyagawa S, et al. Risk factors contributing to early and late phase intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. J Hepatol. 2003;38(2):200–7.
Gerke V, Moss SE. Annexins: from structure to function. Physiol Rev. 2002;82(2):331–71.
Gerke V, Creutz CE, Moss SE. Annexins: linking Ca2+ signalling to membrane dynamics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6(6):449–61.
Ortiz-Zapater E, Peiró S, Roda O, Corominas JM, Aguilar S, Ampurdanés C, et al. Tissue plasminogen activator induces pancreatic cancer cell proliferation by a non-catalytic mechanism that requires extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 activation through epidermal growth factor receptor and annexin A2. Am J Pathol. 2007;170(5):1573–84.
Babbin BA, Lee WY, Parkos CA, Winfree LM, Akyildiz A, Perretti M, et al. Annexin I regulates SKCO-15 cell invasion by signaling through formyl peptide receptors. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(28):19588–99.
Zhao P, Zhang W, Tang J, Ma XK, Dai JY, Li Y, et al. Annexin II promotes invasion and migration of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro via its interaction with HAb18G/CD147. Cancer Sci. 2010;101(2):387–95.
de Graauw M, van Miltenburg MH, Schmidt MK, Pont C, Lalai R, Kartopawiro J, et al. Annexin A1 regulates TGF-β signaling and promotes metastasis formation of basal-like breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(14):6340–5.
Masaki T, Tokuda M, Ohnishi M, Watanabe S, Fujimura T, Miyamoto K, et al. Enhanced expression of the protein kinase substrate annexin I in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 1996;24(1):72–81.
Mohammad HS, Kurokohchi K, Yoneyama H, Tokuda M, Morishita A, Jian G, et al. Annexin A2 expression and phosphorylation are up-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 2008;33(6):1157–63.
Pan QZ, Pan K, Weng DS, Zhao JJ, Zhang XF, Wang DD, et al. Annexin A3 promotes tumorigenesis and resistance to chemotherapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 2013;54(8):598–607.
Guo W, Man X, Yuan H, Shi J, Xue J, Wu M, et al. Proteomic analysis on portal vein tumor thrombus-associated proteins for hepatocellular carcinoma. Zhonghua yi xue za zhi. 2007;87(30):2094–7.
Liu S, Sun MZ, Tang JW, Wang Z, Sun C, Greenaway FT. High-performance liquid chromatography/nano-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry, two-dimensional difference in-gel electrophoresis and gene microarray identification of lymphatic metastasis-associated biomarkers. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2008;22(20):3172–8.
Liu S-H, Lin C-Y, Peng S-Y, Jeng Y-M, Pan H-W, Lai P-L, et al. Down-regulation of annexin A10 in hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with vascular invasion, early recurrence, and poor prognosis in synergy with p53 mutation. Am J Pathol. 2002;160(5):1831–7.
Mussunoor S, Murray G. The role of annexins in tumour development and progression. J Pathol. 2008;216(2):131–40.
Dreier R, Schmid KW, Gerke V, Riehemann K. Differential expression of annexins I, II and IV in human tissues: an immunohistochemical study. Histochem Cell Biol. 1998;110(2):137–48.
Lin LL, Chen CN, Lin WC, Lee PH, Chang KJ, Lai YP, et al. Annexin A4: A novel molecular marker for gastric cancer with Helicobacter pylori infection using proteomics approach. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2008;2(4):619–34.
Duncan R, Carpenter B, Main L, Telfer C, Murray G. Characterisation and protein expression profiling of annexins in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2008;98(2):426–33.
Shen J, Person MD, Zhu J, Abbruzzese JL, Li D. Protein expression profiles in pancreatic adenocarcinoma compared with normal pancreatic tissue and tissue affected by pancreatitis as detected by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. Cancer Res. 2004;64(24):9018–26.
Deng S, Wang J, Hou L, Li J, Chen G, Jing B, et al. Annexin A1, A2, A4 and A5 play important roles in breast cancer, pancreatic cancer and laryngeal carcinoma, alone and/or synergistically. Oncol Lett. 2013;5(1):107–12.
Kim A, Enomoto T, Serada S, Ueda Y, Takahashi T, Ripley B, et al. Enhanced expression of annexin A4 in clear cell carcinoma of the ovary and its association with chemoresistance to carboplatin. Int J Cancer. 2009;125(10):2316–22.
Han EK-H, Tahir S, Cherian S, Collins N, Ng S. Modulation of paclitaxel resistance by annexin IV in human cancer cell lines. Br J Cancer. 2000;83(1):83–8.
Yamashita T, Nagano K, Kanasaki S-I, Maeda Y, Furuya T, Inoue M. Annexin A4 is a possible biomarker for cisplatin susceptibility of malignant mesothelioma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2012;421(1):140–4.
Matsuzaki S, Enomoto T, Serada S, Yoshino K, Nagamori S, Morimoto A, et al. Annexin A4-conferred platinum resistance is mediated by the copper transporter ATP7A. Int J Cancer. 2014;134(8):1796–809.
Choi CH, Sung CO, Kim H-J, Lee Y-Y, Song SY, Song T, et al. Overexpression of annexin A4 is associated with chemoresistance in papillary serous adenocarcinoma of the ovary. Hum Pathol. 2013;44(6):1017–23.
Zimmermann U, Balabanov S, Giebel J, Teller S, Junker H, Schmoll D, et al. Increased expression and altered location of annexin IV in renal clear cell carcinoma: a possible role in tumour dissemination. Cancer Lett. 2004;209(1):111–8.
Mogami T, Yokota N, Asai-Sato M, Yamada R, Koizume S, Sakuma Y, et al. Annexin A4 is involved in proliferation, chemo-resistance and migration and invasion in ovarian clear cell adenocarcinoma cells. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(11):e80359.
Lu ZJ, Liu SY, Yao YQ, Zhou YJ, Zhang S, Dai L, et al. The effect of miR-7 on behavior and global protein expression in glioma cell lines. Electrophoresis. 2011;32(24):3612–20.
Lin L-L, Huang H-C, Juan H-F. Revealing the molecular mechanism of gastric cancer marker annexin A4 in cancer cell proliferation using exon arrays. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(9):e44615.
Xin W, Rhodes DR, Ingold C, Chinnaiyan AM, Rubin MA. Dysregulation of the annexin family protein family is associated with prostate cancer progression. Am J Pathol. 2003;162(1):255–61.
Mozos A, Sole M, Miquel R, Petit A, Nadal A, Fernández PL. Usefulness and limitations of alpha-methylacyl-CoA racemase expression in the hepatobiliary system and pancreas: a wide tissue microarray analysis of normal and neoplastic epithelia. Anal Quant Cytol Histol. 2010;32(5):261–8.
Toyama A, Suzuki A, Shimada T, Aoki C, Aoki Y, Umino Y, et al. Proteomic characterization of ovarian cancers identifying annexin-A4, phosphoserine aminotransferase, cellular retinoic acid-binding protein 2, and serpin B5 as histology-specific biomarkers. Cancer Sci. 2012;103(4):747–55.
Fromowitz FB, Viola MV, Chao S, Oravez S, Mishriki Y, Finkel G, et al. Ras p21 expression in the progression of breast cancer. Hum Pathol. 1987;18(12):1268–75.
Kalluri R, Weinberg RA. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 2009;119(6):1420–8.
Huang X, Zeng Y, Xing X, Zeng J, Gao Y, Cai Z, et al. Quantitative proteomics analysis of early recurrence/metastasis of huge hepatocellular carcinoma following radical resection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;12:22.
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY, Nieto MA. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell. 2009;139(5):871–90.
Yang J, Weinberg RA. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: at the crossroads of development and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 2008;14(6):818–29.
Kan H, Guo W, Huang Y, Liu D. MicroRNA-520g induces epithelial–mesenchymal transition and promotes metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting SMAD7. FEBS Lett. 2015;589(1):102–9.
Wong T-S, Gao W, Chan JY-W. Transcription regulation of E-cadherin by zinc finger E-box binding homeobox proteins in solid tumors. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:921564.
Zhang W, Shi X, Peng Y, Wu M, Zhang P, Xie R, et al. HIF-1α promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis through direct regulation of ZEB1 in colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(6):e0129603.
Yuan D, Xia H, Zhang Y, Chen L, Leng W, Chen T, et al. P-Akt/miR-200 signaling regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition, migration and invasion in circulating gastric tumor cells. Int J Oncol. 2014;45(6):2430–8.
Yun E, Baek S, Xie D, Tseng S, Dobin T, Hernandez E, et al. DAB2IP regulates cancer stem cell phenotypes through modulating stem cell factor receptor and ZEB1. Oncogene. 2014;34(21):2741–52.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the key clinical specialty discipline construction program of Fujian, People’s Republic of China; the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31201008, Grant No. 31400634); the specialized Science and Technology Key Project of Fujian Province (Grant No. 2013YZ0002-3); the Science and Technology Infrastructure Construction Program of Fujian Province (Grant No. 2014Y2005); the scientific innovation project of Fujian provincial Health and Family Planning Commission (Grant No. 2014-CXB-24); the Scientific Foundation of Fuzhou City (Grant No. 2015-S-143-20).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None
Additional information
Wenwei Chen and Lihong Chen contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, W., Chen, L., Cai, Z. et al. Overexpression of annexin A4 indicates poor prognosis and promotes tumor metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 37, 9343–9355 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-4823-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-4823-6