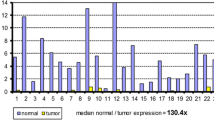
Abstract
Colorectal adenomatous polyp (CRAP) is a major risk factor for the development of sporadic colorectal cancer (CRC). Histone modifications are one of the epigenetic mechanisms that may have key roles in the carcinogenesis of CRC. The objective of the present study is to investigate the alternations in the defined histone modification gene expression profiles in patients with CRAP and CRC. Histone modification enzyme key gene expressions of the CRC, CRAP, and control groups were evaluated and compared using the reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) array method. Gene expression analysis was performed in the CRAP group after dividing the patients into subgroups according to the polyp diameter, pathological results, and morphological parameters which are risk factors for developing CRC in patients with CRAP. PAK1, NEK6, AURKA, AURKB, HDAC1, and HDAC7 were significantly more overexpressed in CRC subjects compared to the controls (p < 0.05). PAK1, NEK6, AURKA, AURKB, and HDAC1 were significantly more overexpressed in the CRAP group compared to the controls (p < 0.005). There were no significant differences between the CRAP and CRC groups with regards to PAK1, NEK6, AURKA, or AURKB gene overexpression. PAK1, NEK6, AURKA, and AURKB were significantly in correlation with the polyp diameter as they were more overexpressed in polyps with larger diameters. In conclusion, overexpressions of NEK6, AURKA, AURKB, and PAK1 genes can be used as predictive markers to decide the colonoscopic surveillance intervals after the polypectomy procedure especially in polyps with larger diameters.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–917.
Shussman N, Wexner SD. Colorectal polyps and polyposis syndromes. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2014;2:1–15.
Leslie A, Carey FA, Pratt NR, Steele RJ. The colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence. Br J Surg. 2002;89:845–60.
Imperiale TF, Juluri R, Sherer EA, Glowinski EA, Johnson CS, Morelli MS. A risk index for advanced neoplasia on the second surveillance colonoscopy in patients with previous adenomatous polyps. Gastrointest Endosc 2014.
Jawad N, Direkze N, Leedham SJ. Inflammatory bowel disease and colon cancer. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2011;185:99–115.
Kulaylat MN, Dayton MT. Ulcerative colitis and cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2010;101:706–12.
Migheli F, Migliore L. Epigenetics of colorectal cancer. Clin Genet. 2012;81:312–8.
Stypula-Cyrus Y, Damania D, Kunte DP, Cruz MD, Subramanian H, Roy HK, et al. HDAC up-regulation in early colon field carcinogenesis is involved in cell tumorigenicity through regulation of chromatin structure. PLoS ONE. 2013;8, e64600.
Higashijima J, Kurita N, Miyatani T, Yoshikawa K, Morimoto S, Nishioka M, et al. Expression of histone deacetylase 1 and metastasis-associated protein 1 as prognostic factors in colon cancer. Oncol Rep. 2011;26:343–8.
Wilson AJ, Byun DS, Popova N, Murray LB, L’Italien K, Sowa Y, et al. Histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) and other class I HDACs regulate colon cell maturation and p21 expression and are deregulated in human colon cancer. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:13548–58.
Witt O, Deubzer HE, Milde T, Oehme I. HDAC family: what are the cancer relevant targets? Cancer Lett. 2009;277:8–21.
Belt EJ, Brosens RP, Delis-van Diemen PM, Bril H, Tijssen M, van Essen DF, et al. Cell cycle proteins predict recurrence in stage II and III colon cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19 Suppl 3:S682–692.
Glauben R, Sonnenberg E, Zeitz M, Siegmund B. HDAC inhibitors in models of inflammation-related tumorigenesis. Cancer Lett. 2009;280:154–9.
Khare V, Lyakhovich A, Dammann K, Lang M, Borgmann M, Tichy B, et al. Mesalamine modulates intercellular adhesion through inhibition of p-21 activated kinase-1. Biochem Pharmacol. 2013;85:234–44.
He H, Huynh N, Liu KH, Malcontenti-Wilson C, Zhu J, Christophi C, et al. P-21 activated kinase 1 knockdown inhibits beta-catenin signalling and blocks colorectal cancer growth. Cancer Lett. 2012;317:65–71.
Nassirpour R, Shao L, Flanagan P, Abrams T, Jallal B, Smeal T, et al. Nek6 mediates human cancer cell transformation and is a potential cancer therapeutic target. Mol Cancer Res. 2010;8:717–28.
Feinberg AP, Ohlsson R, Henikoff S. The epigenetic progenitor origin of human cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:21–33.
Lao VV, Grady WM. Epigenetics and colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;8:686–700.
Yi JM, Dhir M, Guzzetta AA, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Heo K, Yang KM, et al. DNA methylation biomarker candidates for early detection of colon cancer. Tumour Biol. 2012;33:363–72.
Yoo CB, Jones PA. Epigenetic therapy of cancer: past, present and future. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2006;5:37–50.
He TC, Sparks AB, Rago C, Hermeking H, Zawel L, da Costa LT, et al. Identification of c-MYC as a target of the APC pathway. Science. 1998;281:1509–12.
Polakis P. The many ways of Wnt in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2007;17:45–51.
Vogelstein B, Fearon ER, Hamilton SR, Kern SE, Preisinger AC, Leppert M, et al. Genetic alterations during colorectal-tumor development. N Engl J Med. 1988;319:525–32.
Marumoto T, Zhang D, Saya H. Aurora-A—a guardian of poles. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5:42–50.
Bischoff JR, Anderson L, Zhu Y, Mossie K, Ng L, Souza B, et al. A homologue of Drosophila aurora kinase is oncogenic and amplified in human colorectal cancers. EMBO J. 1998;17:3052–65.
Carvalho B, Postma C, Mongera S, Hopmans E, Diskin S, van de Wiel MA, et al. Multiple putative oncogenes at the chromosome 20q amplicon contribute to colorectal adenoma to carcinoma progression. Gut. 2009;58:79–89.
Jee HJ, Kim AJ, Song N, Kim HJ, Kim M, Koh H, et al. Nek6 overexpression antagonizes p53-induced senescence in human cancer cells. Cell Cycle. 2010;9:4703–10.
Belham C, Roig J, Caldwell JA, Aoyama Y, Kemp BE, Comb M, et al. A mitotic cascade of NIMA family kinases. Nercc1/Nek9 activates the Nek6 and Nek7 kinases. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:34897–909.
O’Regan L, Fry AM. The Nek6 and Nek7 protein kinases are required for robust mitotic spindle formation and cytokinesis. Mol Cell Biol. 2009;29:3975–90.
Cao X, Xia Y, Yang J, Jiang J, Chen L, Ni R, et al. Clinical and biological significance of never in mitosis gene A-related kinase 6 (NEK6) expression in hepatic cell cancer. Pathol Oncol Res. 2012;18:201–7.
Kasap E, Boyacioglu SO, Korkmaz M, Yuksel ES, Unsal B, Kahraman E, et al. Aurora kinase A (AURKA) and never in mitosis gene A-related kinase 6 (NEK6) genes are upregulated in erosive esophagitis and esophageal adenocarcinoma. Exp Ther Med. 2012;4:33–42.
Rugge M, Fassan M, Zaninotto G, Pizzi M, Giacomelli L, Battaglia G, et al. Aurora kinase A in Barrett’s carcinogenesis. Hum Pathol. 2010;41:1380–6.
Katsha A, Soutto M, Sehdev V, Peng D, Washington MK, Piazuelo MB, et al. Aurora kinase A promotes inflammation and tumorigenesis in mice and human gastric neoplasia. Gastroenterology. 2013;145:1312–22. e1311-1318.
Mariadason JM. HDACs and HDAC inhibitors in colon cancer. Epigenetics. 2008;3:28–37.
Winawer SJ, Zauber AG, Gerdes H, O’Brien MJ, Gottlieb LS, Sternberg SS, et al. Risk of colorectal cancer in the families of patients with adenomatous polyps. National Polyp Study Workgroup. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:82–7.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Celal Bayar University Coordinator of the Scientific Research Projects (2013-10) Manisa, Turkey.
Compliance with ethical standards
ᅟ
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kasap, E., Gerceker, E., Boyacıoglu, S.Ö. et al. The potential role of the NEK6, AURKA, AURKB, and PAK1 genes in adenomatous colorectal polyps and colorectal adenocarcinoma. Tumor Biol. 37, 3071–3080 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4131-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4131-6