Abstract
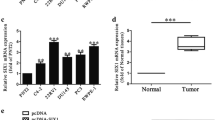
Prostate cancer is one of the biggest health problems for the aging male. To the present, the roles of dysregulated microRNAs in prostate cancer are still unclear. Here, we evaluated the anti-proliferative role of miR-378 in prostate cancer. And, we found that the expression of miR-378 was significantly downregulated in clinical prostate cancer tissues. In vitro assay suggested that overexpression of miR-378-suppressed prostate cancer cell migration and invasion promoted cell apoptosis. Furthermore, we identified and validated MAPK1 as a direct target of miR-378. Ectopic expression of MAPK1 rescues miR-378-suppressed cell migration and invasion. In vivo assay demonstrated that the stably miR-378-overexpressed prostate cancer cells displayed a significantly reduction in tumor growth. Taken together, our data suggested that miR-378 may act as a potential therapeutic target against human prostate cancer.






Similar content being viewed by others

References
Shaikhibrahim Z, Lindstrot A, Ellinger J, Rogenhofer S, Buettner R, Wernert N. Identification of immunity-related genes in prostate cancer and potential role of the ets family of transcription factors in their regulation. Int J Mol Med. 2011;28:799–807.
Chen WQ, Zheng RS, Zhang SW, Li N, Zhao P, Li GL, et al. Report of incidence and mortality in china cancer registries, 2008. Chin J Cancer Res. 2012;24:171–80.
Zhang W, Mao YQ, Wang H, Yin WJ, Zhu SX, Wang WC. Mir-124 suppresses cell motility and adhesion by targeting talin 1 in prostate cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2015;15:49.
Zhang GM, Bao CY, Wan FN, Cao DL, Qin XJ, Zhang HL, et al. Microrna-302a suppresses tumor cell proliferation by inhibiting akt in prostate cancer. PloS One. 2015;10:e0124410.
Wei Y, Yang J, Yi L, Wang Y, Dong Z, Liu Z, et al. Mir-223-3p targeting sept6 promotes the biological behavior of prostate cancer. Sci Rep. 2014;4:7546.
Ambros V, Chen X. The regulation of genes and genomes by small rnas. Development. 2007;134:1635–41.
Stegeman S, Moya L, Selth LA, Spurdle AB, Clements JA, Batra J. A genetic variant of mdm4 influences regulation by multiple micrornas in prostate cancer. Endoc Relat Cancer. 2015;22:265–76.
Li J, Wan X, Qiang W, Li T, Huang W, Huang S, et al. Mir-29a suppresses prostate cell proliferation and induces apoptosis via kdm5b protein regulation. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8:5329–39.
Goto Y, Kurozumi A, Enokida H, Ichikawa T, Seki N. Functional significance of aberrantly expressed micrornas in prostate cancer. Int J Urol. 2015;22:242–52.
Yun SJ, Jeong P, Kang HW, Kim YH, Kim EA, Yan C, et al. Urinary micrornas of prostate cancer: virus-encoded hsv1-mirh18 and hsv2-mir-h9-5p could be valuable diagnostic markers. Int Neurourol J. 2015;19:74–84.
Xu WT, Jia YJ, Li XJ, Chen J. Micrornas and prostate cancer. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2015;21:458–62.
Song C, Chen H, Wang T, Zhang W, Ru G, Lang J. Expression profile analysis of micrornas in prostate cancer by next-generation sequencing. Prostate. 2015;75:500–16.
Nguyen HC, Xie W, Yang M, Hsieh CL, Drouin S, Lee GS, et al. Expression differences of circulating micrornas in metastatic castration resistant prostate cancer and low-risk, localized prostate cancer. Prostate. 2013;73:346–54.
Avgeris M, Stravodimos K, Scorilas A. Loss of mir-378 in prostate cancer, a common regulator of klk2 and klk4, correlates with aggressive disease phenotype and predicts the short-term relapse of the patients. Biol Chem. 2014;395:1095–104.
Mishra S, Deng JJ, Gowda PS, Rao MK, Lin CL, Chen CL, et al. Androgen receptor and microrna-21 axis downregulates transforming growth factor beta receptor ii (tgfbr2) expression in prostate cancer. Oncogene. 2014;33:4097–106.
Avgeris M, Stravodimos K, Fragoulis EG, Scorilas A. The loss of the tumour-suppressor mir-145 results in the shorter disease-free survival of prostate cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 2013;108:2573–81.
Sun D, Li X, Ma M, Liu J, Xu Y, Ye L, et al. The predictive value and potential mechanisms of mirna-328 and mirna-378 for brain metastases in operable and advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2015;45:464–73.
Li LH, Gao Q, Wang XY, Guo ZJ. mir-378 suppresses hbv-related hepatocellular carcinoma tumor growth by directly targeting the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2013;21:609–13.
Zhang GJ, Zhou H, Xiao HX, Li Y, Zhou T. Mir-378 is an independent prognostic factor and inhibits cell growth and invasion in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:109.
Fei B, Wu H. Mir-378 inhibits progression of human gastric cancer mgc-803 cells by targeting mapk1 in vitro. Oncol Res. 2012;20:557–64.
Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T, Xu BE, Karandikar M, Berman K, et al. Mitogen-activated protein (map) kinase pathways: regulation and physiological functions. Endocr Rev. 2001;22:153–83.
Ganesan J, Ramanujam D, Sassi Y, Ahles A, Jentzsch C, Werfel S, et al. Mir-378 controls cardiac hypertrophy by combined repression of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway factors. Circulation. 2013;127:2097–106.
Zhang L, Ge Y, Fuchs E. Mir-125b can enhance skin tumor initiation and promote malignant progression by repressing differentiation and prolonging cell survival. Genes Dev. 2014;28:2532–46.
Huang N, Wang J, Xie W, Lyu Q, Wu J, He J, et al. Mir-378a-3p enhances adipogenesis by targeting mitogen-activated protein kinase 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;457:37–42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Qg., Zhou, W., Han, T. et al. MiR-378 suppresses prostate cancer cell growth through downregulation of MAPK1 in vitro and in vivo. Tumor Biol. 37, 2095–2103 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3996-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3996-8