Abstract
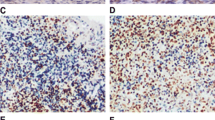
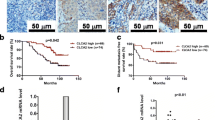
The chemokine CXCL12 and its receptors CXCR4 and CXCR7 might play important roles in the occurrence and development of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). While CXCR4 expression is associated to initiation and progression of OSCC, the role of CXCR7, the recently founded second CXCL12 receptor, has not yet been elucidated in OSCC. In this study, CXCR4 and CXCR7 expressions were evaluated using western blot and quantitative RT-PCR in OSCC cells. AMD3100 (CXCR4 antagonist) was used to inhibit the activation of CXCR4. In contrast to CXCR4, effective CXCR7 small interfering RNA (siRNA) segments were used to silence CXCR7 in OSCC cells. The biological effects of CXCL12-CXCR4/CXCR7 axis on OSCC cell lines were studied by CCK-8 and transwell assay. As determined by RT-PCR and Western blot, CXCR7 expression was significantly downregulated after siRNA transfection in OSCC cells, and thus significantly promoted OSCC cell migration and invasion in vitro. The relative roles of the two CXCL12 receptors were further assessed by CXCR7 knockdown or deactivate CXCR4 receptor alone, or in combination, in the OSCC cells. In vitro functional analyses indicated that, in response to their common ligand (CXCL12), both receptors induced inhibition of proliferation and migration in OSCC cells in a dose-dependent manner. Exogenous CXCL12 could promote cell migration and invasion. In conclusion, our results indicated that CXCL12 which combined its receptor CXCR4 and CXCR7 together could promote cell motilities of OSCC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh RK, Sudhakar A, Lokeshwar BL. Role of chemokines and chemokine receptors in prostate cancer development and progression. J Cancer Sci Ther. 2010;2:89–94.
Lazennec G, Richmond A. Chemokines and chemokine receptors: new insights into cancer-related inflammation. Trends Mol Med. 2010;16:133–44.
Salomonnson E, Stacer AC, Ehrlich A, Luker KE, Luker GD. Imaging CXCL12-CXCR4 signaling in ovarian cancer therapy. PLoS One. 2013;8:e51500.
Ehtesham M, Winston JA, Kabos P, Thompson RC. CXCR4 expression mediates glioma cell invasiveness. Oncogene. 2006;25:2801–6.
Zhang R, Pan X, Huang Z, Weber GF, Zhang G. Osteopontin enhances the expression and activity of MMP-2 via the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. PLoS One. 2011;6:e23831.
Jin J, Zhao WC, Yuan F. CXCR7/CXCR4/CXCL12 axis regulates the proliferation, migration, survival and tube formation of choroid-retinal endothelial cells. Ophthalmic Res. 2013;50:6–12.
Burns JM, Summers BC, Wang Y, Melikian A, Berahovich R, Miao Z, et al. A novel chemokine receptor for SDF-1 and I-TAC involved in cell survival, cell adhesion, and tumor development. J Exp Med. 2006;203:2201–13.
Gahan JC, Gosalbez M, Yates T, Young EE, Escudero DO, Chi A, et al. Chemokine and chemokine receptor expression in kidney tumors: molecular profiling of histological subtypes and association with metastasis. J Urol. 2012;187:827–33.
Imai H, Sunaga N, Shimizu Y, Kakegawa S, Shimizu K, Sano T, et al. Clinicopathological and therapeutic significance of CXCL12 expression in lung cancer. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2010;23:153–64.
Yao X, Zhou L, Han S, Chen Y. High expression of CXCR4 and CXCR7 predicts poor survival in gallbladder cancer. J Int Med Res. 2011;39:1253–64.
Monnier J, Boissan M, L’Helgoualc’h A, Lacombe ML, Turlin B, Zucman-Rossi J, et al. CXCR7 is up-regulated in human and murine hepatocellular carcinoma and is specifically expressed by endothelial cells. Eur J Cancer. 2012;48:138–48.
Gebauer F, Tachezy M, Effenberger K, von Loga K, Zander H, Marx A, et al. Prognostic impact of CXCR4 and CXCR7 expression in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 2011;104:140–5.
Xia J, Wang J, Chen N, Dai Y, Hong Y, Chen X, et al. Expressions of CXCR7/ligands may be involved in oral carcinogenesis. J Mol Histol. 2011;42:175–80.
Xia J, Chen N, Hong Y, Chen X, Tao X, Cheng B, et al. Expressions of CXCL12/CXCR4 in oral premalignant and malignant lesions. Mediat Inflamm. 2012;2012:516395.
Sanchez-Martin L, Sanchez-Mateos P, Cabanas C. CXCR7 impact on CXCL12 biology and disease. Trends Mol Med. 2013;19:12–22.
Zhu S, Hong J, Tripathi MK, Sehdev V, Belkhiri A, El-Rifai W. Regulation of CXCR4-mediated invasion by DARPP-32 in gastric cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2013;11:86–94.
Hattermann K, Mentlein R. An infernal trio: the chemokine CXCL12 and its receptors CXCR4 and CXCR7 in tumor biology. Ann Anat. 2013;195:103–10.
Burger JA, Stewart DJ, Wald O, Peled A. Potential of CXCR4 antagonists for the treatment of metastatic lung cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2011;11:621–30.
Weekes CD, Song D, Arcaroli J, Wilson LA, Rubio-Viqueira B, Cusatis G, et al. Stromal cell-derived factor 1alpha mediates resistance to mTOR-directed therapy in pancreatic cancer. Neoplasia. 2012;14:690–701.
de Nigris F, Schiano C, Infante T, Napoli C. CXCR4 inhibitors: tumor vasculature and therapeutic challenges. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2012;7:251–64.
Kriechbaumer V, Nabok A, Widdowson R, Smith DP, Abell BM. Quantification of ligand binding to G-protein coupled receptors on cell membranes by ellipsometry. PLoS One. 2012;7:e46221.
Li KC, Huang YH, Ho CY, Chu CY, Cha ST, Tsai HH, et al. The role of IL-8 in the SDF-1alpha/CXCR4-induced angiogenesis of laryngeal and hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2012;48:507–15.
Uchida D, Onoue T, Kuribayashi N, Tomizuka Y, Tamatani T, Nagai H, et al. Blockade of CXCR4 in oral squamous cell carcinoma inhibits lymph node metastases. Eur J Cancer. 2011;47:452–9.
Hong JS, Pai HK, Hong KO, Kim MA, Kim JH, Lee JI, et al. CXCR-4 knockdown by small interfering RNA inhibits cell proliferation and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. J Oral Pathol Med. 2009;38:214–9.
Hernandez L, Magalhaes MA, Coniglio SJ, Condeelis JS, Segall JE. Opposing roles of CXCR4 and CXCR7 in breast cancer metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. 2011;13:R128.
Hattermann K, Held-Feindt J, Lucius R, Muerkoster SS, Penfold ME, Schall TJ, et al. The chemokine receptor CXCR7 is highly expressed in human glioma cells and mediates antiapoptotic effects. Cancer Res. 2010;70:3299–308.
Luker KE, Gupta M, Steele JM, Foerster BR, Luker GD. Imaging ligand-dependent activation of CXCR7. Neoplasia. 2009;11:1022–35.
Zhu B, Xu D, Deng X, Chen Q, Huang Y, Peng H, et al. CXCL12 enhances human neural progenitor cell survival through a CXCR7- and CXCR4-mediated endocytotic signaling pathway. Stem Cells. 2012;30:2571–83.
Boudot A, Kerdivel G, Habauzit D, Eeckhoute J, Le Dily F, Flouriot G, et al. Differential estrogen-regulation of CXCL12 chemokine receptors, CXCR4 and CXCR7, contributes to the growth effect of estrogens in breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 2011;6:e20898.
Rehman AO, Wang CY. CXCL12/SDF-1 alpha activates NF-kappaB and promotes oral cancer invasion through the Carma3/Bcl10/Malt1 complex. Int J Oral Sci. 2009;1:105–18.
Levoye A, Balabanian K, Baleux F, Bachelerie F, Lagane B. CXCR7 heterodimerizes with CXCR4 and regulates CXCL12-mediated G protein signaling. Blood. 2009;113:6085–93.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81070841 and 81371148) and the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University from Ministry of Education (MOE), People’s Republic of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Na Chen and Xiao Jiang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, N., Jiang, X., Wang, J. et al. CXCL12-CXCR4/CXCR7 axis contributes to cell motilities of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 37, 567–575 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3803-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3803-6