Abstract
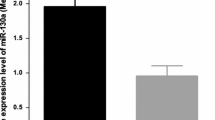
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have a large number of various target genes in different cancer types, which may result in many biological functions. Thus, identifying the molecular mechanisms of miRNAs may effect on the complexity of cancer progression via regulation of gene. In the current study, we utilized real-time PCR to quantify the diction of miR-148b in trail hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) specimen and normal tissues. Furthermore, we evaluated the relationship of miR-148b and clinicopathological features with survival of HCC patients. Therefore, we evaluated the level of miR-148b expression in 101 HCC patients and also in 40 normal control cases. The result suggested lower expression in tumor tissues than normal control tissues (0.96 ± 0.14; 1.84 ± 0.20, P < 0.05). Our findings suggest that the declined expression of miR-148b can considerably be linked to tumor node metastasis (TNM) stage (stages III and IV; P = 0.021) and vein invasion (P = 0.029). Nevertheless, miR-148b expression was not related to sex (P = 0.674), age (P = 0. 523), size of tumor (P = 0.507), liver cirrhosis, and histologic grade (P = 0.734). Survival analysis showed that low expression was remarkably related to overall survival (P = 0.012). Furthermore, multivariate survival test suggested that decline of miR-148b diction was linked to poor survival in HCC patients. Our results suggested that miR-148b is decreased in HCC. Therefore, we concluded that miR-148b may play its role in the prognosis of HCC.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97.
Zheng B, Liang L, Wang C, Huang S, Cao X, Zha R, et al. MicroRNA-148a suppresses tumor cell invasion and metastasis by downregulating ROCK1 in gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:7574–83.
Wu XJ, Li Y, Liu D, Zhao LD, Bai B, Xue MH. MiR-27a as an oncogenic microRNA of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14:885–9.
Ling H, Fabbri M, Calin GA. MicroRNAs and other non-coding RNAs as targets for anticancer drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013;12:847–65.
Krol J, Loedige I, Filipowicz W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11:597–610.
Calin GA, Croce CM. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6(11):857–66.
Ueda T, Volinia S, Okumura H, Shimizu M, Taccioli C, Rossi S, et al. Relation between microRNA expression and progression and prognosis of gastric cancer: a microRNA expression analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:136–46.
Zhao G, Zhang JG, Liu Y, Qin Q, Wang B, Tian K, et al. MiR-148b functions as a tumor suppressor in pancreatic cancer by targeting AMPKalpha1. Mol Cancer Ther. 2013;12:83–93.
Azizi M, Teimoori-Toolabi L, Arzanani MK, Azadmanesh K, Fard-Esfahani P, Zeinali S. MicroRNA-148b and microRNA-152 reactivate tumor suppressor genes through suppression of DNA methyltransferase-1 gene in pancreatic cancer cell lines. Cancer Biol Ther. 2014;15(4):419–27.
Yang JD, Roberts LR. Epidemiology and management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Infect Dis Clin N Am. 2010;24(4):899–919.
Zhang Z, Zheng W, Hai J. MicroRNA-148b expression is decreased in hepatocellular carcinoma and associated with prognosis. Med Oncol. 2014;31(6):984.
Cimino D, De Pitta C, Orso F, Zampini M, Casara S, Penna E, et al. MiR148b is a major coordinator of breast cancer progression in a relapseassociated microRNA signature by targeting ITGA5, ROCK1, PIK3CA, NRAS, and CSF1. FASEB J. 2013;27:1223–35.
Song YX, Yue ZY, Wang ZN, Xu YY, Luo Y, Xu HM. MicroRNA-148b is frequently down-regulated in gastric cancer and acts as a tumor suppressor by inhibiting cell proliferation. Mol Cancer. 2011;10:1.
Liu GL, Liu X, Lv XB, Wang XP, Fang XS, Sang Y. miR-148b functions as a tumor suppressor in non-small cell lung cancer by targeting carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA). Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014;7:1990–9.
Song Y, Xu Y, Wang Z, Chen Y, Yue Z, Gao P. MicroRNA-148b suppresses cell growth by targeting cholecystokinin-2 receptor in colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 2012;131(5):1042–51.
Cuk K, Zucknick M, Heil J, Madhavan D, Schott S, Turchinovich A, et al. Circulating microRNAs in plasma as early detection markers for breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 2013;132(7):1602–12.
Chang H, Zhou X, Wang ZN, Song YX, Zhao F, Gao P, et al. Increased expression of miR-148b in ovarian carcinoma and its clinical significance. Mol Med Rep. 2012;5(5):1277–80.
Li L, Chen YY, Li SQ, Huang C, Qin YZ. Expression of miR-148/152 family as potential biomarkers in non-small-cell lung cancer. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21:1155–61.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Javad Javanbakht for his help with this manuscript.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article has been retracted at the request of the Editor-in-Chief, the International Society of Oncology and BioMarkers (ISOBM) and the Publisher per the Committee on Publication Ethics guidelines. The article shows evidence of irregularities in authorship during the submission process, there is strong reason to believe that the peer review process was compromised and there are similarities with the following articles which were all submitted within a close timeframe:
Naeemeh Ghasemkhani, Sahar Shadvar, Yasamin Masoudi, Amir Jouya Talaei, Emad Yahaghi, Peyman Karimi Goudarzi, Ebrahim Shakiba, Down-regulated MicroRNA 148b expression as predictive biomarker and its prognostic significance associated with clinicopathological features in non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Diagnostic Pathology 2015, 10:164 DOI: 10.1186/s13000-015-0393-y Date received: 18 June 2015
Yasan Sadeghian, Zahra Kamyabi-Moghaddam, Seyed Mohamad Hossein Tabatabaei Nodushan, Samaneh Khoshbakht, Behnam Pedram, Emad Yahaghi, Aram Mokarizadeh, Mahdi Mohebbi, Profiles of tissue microRNAs; miR-148b and miR-25 serve as potential prognostic biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol. First Online: 25 July 2015 DOI: 10.1007/s13277-015-3799-y Date received: 1 July 2015
The retracted article was received: 16 June 2015
As such the validity of the content of this article cannot be verified.
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5477-0.
About this article
Cite this article
Ziari, K., Zarea, M., Gity, M. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Downregulation of miR-148b as biomarker for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma and may serve as a prognostic marker. Tumor Biol. 37, 5765–5768 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3777-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3777-4