Abstract
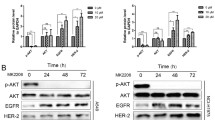
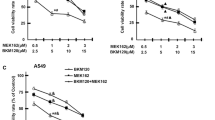
KRAS mutations are found in 15–25 % of patients with lung adenocarcinoma, and they lead to constitutive activation of KRAS signaling pathway that results in sustained cell proliferation. Currently, there are no direct anti-KRAS therapies available. Therefore, it is rational to target the downstream molecules of KRAS signaling pathway, which are mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway (RAF-MEK-ERK) and PI3K pathway (PI3K-AKT-mTOR). Here, we examined the inhibition of both these pathways alone and in combination and analyzed the anti-proliferative and apoptotic events in KRAS mutant NSCLC cell lines, A549 and Calu-1. Cytotoxicity was determined by MTT assay after the cells were treated with LY294002 (PI3K inhibitor), U0126 (MEK inhibitor), and RAD001 (mTOR inhibitor) for 24 and 48 h. The expression levels of p-ERK, ERK, AKT, p-AKT, p53, cyclinD1, c-myc, p27kip1, BAX, BIM, and GAPDH were detected by western blot after 6 and 24 h treatment. Although PI3K/mTOR inhibition is more effective in cytotoxicity in A549 and Calu-1 cells, MEK/mTOR inhibition markedly decreases cell proliferation protein marker expressions. Our data show that combined targeting of MEK and PI3K-AKT with mTOR is a better option than single agents alone for KRAS mutant NSCLC, thus opening the possibility of a beneficial treatment strategy in the future.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- SCLC:
-
Small cell lung cancer
- PIP3:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3, 4, 5-triphosphate
- PIP2:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-diphosphate
- mTORC1:
-
mTOR1 complex
- TSC2:
-
Tuberous sclerosis protein 2
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MEK1/2:
-
MAP-ERK kinases 1 and 2
- BEZ235:
-
Dual PI3K and mTOR inhibitor
References
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29.
Beasley MB, Brambilla E, Travis WD. The 2004 world health organization classification of lung tumors. Semin Roentgenol. 2005;40:90–7.
A genomics-based classification of human lung tumors. Sci Transl Med 5: 209ra153. 2013.
Steelman LS, Pohnert SC, Shelton JG, Franklin RA, Bertrand FE, et al. JAK/STAT, Raf/MEK/ERK, PI3K/Akt and BCR-ABL in cell cycle progression and leukemogenesis. Leukemia. 2004;18:189–218.
Diaz-Flores E, Shannon K. Targeting oncogenic Ras. Genes Dev. 2007;21:1989–92.
Pylayeva-Gupta Y, Grabocka E, Bar-Sagi D. RAS oncogenes: weaving a tumorigenic web. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011;11:761–74.
Mascaux C, Iannino N, Martin B, Paesmans M, Berghmans T, et al. The role of RAS oncogene in survival of patients with lung cancer: a systematic review of the literature with meta-analysis. Br J Cancer. 2005;92:131–9.
Sekido Y, Fong KM, Minna JD. Molecular genetics of lung cancer. Annu Rev Med. 2003;54:73–87.
Sable CL, Filippa N, Filloux C, Hemmings BA, Van Obberghen E. Involvement of the pleckstrin homology domain in the insulin-stimulated activation of protein kinase B. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:29600–6.
Liang J, Slingerland JM. Multiple roles of the PI3K/PKB (Akt) pathway in cell cycle progression. Cell Cycle. 2003;2:339–45.
Testa JR, Bellacosa A. AKT plays a central role in tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:10983–5.
Bondar VM, Sweeney-Gotsch B, Andreeff M, Mills GB, Mcconkey DJ. Inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase-AKT pathway induces apoptosis in pancreatic carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther. 2002;1:989–97.
Tsurutani J, Fukuoka J, Tsurutani H, Shih JH, Hewitt SM, et al. Evaluation of two phosphorylation sites improves the prognostic significance of Akt activation in non-small-cell lung cancer tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:306–14.
Boulay A, Lane HA. The mammalian target of rapamycin kinase and tumor growth inhibition. Recent Results Cancer Res Fortschritte der Krebsforschung Progres dans les Recherches sur le Cancer. 2007;172:99–124.
O’donnell A, Faivre S, Burris 3rd HA, Rea D, Papadimitrakopoulou V, et al. Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the oral mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor everolimus in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:1588–95.
Tabernero J, Rojo F, Calvo E, Burris H, Judson I, et al. Dose- and schedule-dependent inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway with everolimus: a phase I tumor pharmacodynamic study in patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:1603–10.
O’reilly KE, Rojo F, She QB, Solit D, Mills GB, et al. mTOR inhibition induces upstream receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and activates Akt. Cancer Res. 2006;66:1500–8.
Rodrik-Outmezguine VS, Chandarlapaty S, Pagano NC, Poulikakos PI, Scaltriti M, et al. mTOR kinase inhibition causes feedback-dependent biphasic regulation of AKT signaling. Cancer Discov. 2011;1:248–59.
Mccubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH, Abrams SL, Wong EW, et al. Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth, malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1773:1263–84.
Papin C, Eychene A, Brunet A, Pages G, Pouyssegur J, et al. B-Raf protein isoforms interact with and phosphorylate Mek-1 on serine residues 218 and 222. Oncogene. 1995;10:1647–51.
Adjei AA. Signal transduction pathway targets for anticancer drug discovery. Curr Pharm Des. 2000;6:361–78.
Favata MF, Horiuchi KY, Manos EJ, Daulerio AJ, Stradley DA, et al. Identification of a novel inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:18623–32.
Shaul YD, Seger R. The MEK/ERK cascade: from signaling specificity to diverse functions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1773:1213–26.
Carracedo A, Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, Rojo F, Salmena L, et al. Inhibition of mTORC1 leads to MAPK pathway activation through a PI3K-dependent feedback loop in human cancer. J Clin Invest. 2008;118:3065–74.
Yu CF, Liu ZX, Cantley LG. ERK negatively regulates the epidermal growth factor-mediated interaction of Gab1 and the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:19382–8.
Zimmermann S, Moelling K. Phosphorylation and regulation of Raf by Akt (protein kinase B). Science. 1999;286:1741–4.
Guan KL, Figueroa C, Brtva TR, Zhu T, Taylor J, et al. Negative regulation of the serine/threonine kinase B-Raf by Akt. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:27354–9.
Carriere A, Romeo Y, Acosta-Jaquez HA, Moreau J, Bonneil E, et al. ERK1/2 phosphorylate raptor to promote Ras-dependent activation of mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1). J Biol Chem. 2011;286:567–77.
Iida S, Miki Y, Ono K, Akahira J, Nakamura Y, et al. Synergistic anti-tumor effects of RAD001 with MEK inhibitors in neuroendocrine tumors: a potential mechanism of therapeutic limitation of mTOR inhibitor. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012;350:99–106.
Wan X, Harkavy B, Shen N, Grohar P, Helman LJ. Rapamycin induces feedback activation of Akt signaling through an IGF-1R-dependent mechanism. Oncogene. 2007;26:1932–40.
Chen X, Zhao M, Hao M, Sun X, Wang J, et al. Dual inhibition of PI3K and mTOR mitigates compensatory AKT activation and improves tamoxifen response in breast cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2013;11:1269–78.
Ishibe S, Haydu JE, Togawa A, Marlier A, Cantley LG. Cell confluence regulates hepatocyte growth factor-stimulated cell morphogenesis in a beta-catenin-dependent manner. Mol Cell Biol. 2006;26:9232–43.
Swat A, Dolado I, Rojas JM, Nebreda AR. Cell density-dependent inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling by p38alpha mitogen-activated protein kinase via Sprouty2 downregulation. Mol Cell Biol. 2009;29:3332–43.
Gao J, Zhao Y, Lv Y, Chen Y, Wei B, et al. Mirk/Dyrk1B mediates G0/G1 to S phase cell cycle progression and cell survival involving MAPK/ERK signaling in human cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2013;13:2.
Ko JC, Wang YT, Yang JL. Dual and opposing roles of ERK in regulating G(1) and S-G(2)/M delays in A549 cells caused by hyperoxia. Exp Cell Res. 2004;297:472–83.
Meric-Bernstam F, Gonzalez-Angulo AM. Targeting the mTOR signaling network for cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:2278–87.
Ji D, Zhang Z, Cheng L, Chang J, Wang S, et al. The combination of RAD001 and MK-2206 exerts synergistic cytotoxic effects against PTEN mutant gastric cancer cells: involvement of MAPK-dependent autophagic, but not apoptotic cell death pathway. PLoS One. 2014;9, e85116.
Zito CR, Jilaveanu LB, Anagnostou V, Rimm D, Bepler G, et al. Multi-level targeting of the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase pathway in non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS One. 2012;7, e31331.
Engelman JA, Chen L, Tan X, Crosby K, Guimaraes AR, et al. Effective use of PI3K and MEK inhibitors to treat mutant Kras G12D and PIK3CA H1047R murine lung cancers. Nat Med. 2008;14:1351–6.
Qu Y, Wu X, Yin Y, Yang Y, Ma D, et al. Antitumor activity of selective MEK1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 in combination with PI3K/mTOR inhibitor BEZ235 in gefitinib-resistant NSCLC xenograft models. J Exp Clin Cancer Res CR. 2014;33:52.
Hata AN, Yeo A, Faber AC, Lifshits E, Chen Z, et al. Failure to induce apoptosis via BCL-2 family proteins underlies lack of efficacy of combined MEK and PI3K inhibitors for KRAS-mutant lung cancers. Cancer Res. 2014;74:3146–56.
Ballif BA, Blenis J. Molecular mechanisms mediating mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) kinase (MEK)-MAPK cell survival signals. Cell Growth Differ Mol Biol J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2001;12:397–408.
Allan LA, Morrice N, Brady S, Magee G, Pathak S, et al. Inhibition of caspase-9 through phosphorylation at Thr 125 by ERK MAPK. Nat Cell Biol. 2003;5:647–54.
Sahu RP, Batra S, Kandala PK, Brown TL, Srivastava SK. The role of K-ras gene mutation in TRAIL-induced apoptosis in pancreatic and lung cancer cell lines. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2011;67:481–7.
Mirza AM, Gysin S, Malek N, Nakayama K, Roberts JM, et al. Cooperative regulation of the cell division cycle by the protein kinases RAF and AKT. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:10868–81.
Gysin S, Lee SH, Dean NM, Mcmahon M. Pharmacologic inhibition of RAF→MEK→ERK signaling elicits pancreatic cancer cell cycle arrest through induced expression of p27Kip1. Cancer Res. 2005;65:4870–80.
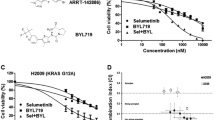
Ku BM, Jho EH, Bae YH, Sun JM, Ahn JS, et al. BYL719, a selective inhibitor of phosphoinositide 3-kinase alpha, enhances the effect of selumetinib (AZD6244, ARRY-142886) in KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Investig New Drugs. 2014.
Chen Y, Nowak I, Huang J, Keng PC, Sun H, et al. Erk/MAP kinase signaling pathway and neuroendocrine differentiation of non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol Off Publ Int Assoc Study Lung Cancer. 2014;9:50–8.
Haagensen EJ, Kyle S, Beale GS, Maxwell RJ, Newell DR. The synergistic interaction of MEK and PI3K inhibitors is modulated by mTOR inhibition. Br J Cancer. 2012;106:1386–94.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dogan Turacli, I., Ozkan, A.C. & Ekmekci, A. The comparison between dual inhibition of mTOR with MAPK and PI3K signaling pathways in KRAS mutant NSCLC cell lines. Tumor Biol. 36, 9339–9345 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3671-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3671-0