Abstract
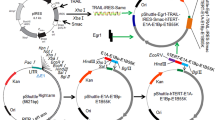
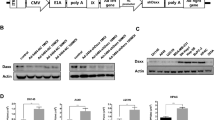
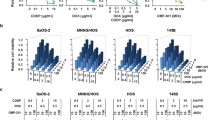
The amplification of MYCN is a typical characteristic of aggressive neuroblastomas, whereas acquired mutations of p53 lead to refractory and relapsed cases. We had previously examined the applicability of the replication-competent oncolytic adenovirus, ZD55-shMYCN, to deliver a short hairpin RNA targeting MYCN gene for p53-null and MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma cell line LA1-55N. Our data have shown that ZD55-shMYCN has an additive tumor growth inhibitory response through shRNA-mediated MYCN knockdown and ZD55-mediated cancer cell lysis. In this regard, ZD55-shMYCN can downregulate MYCN and perform anticancer effects, thereby acquiring significance in the administration of MYCN-amplified and p53-null neuroblastomas. Hence, we further investigated the anticancer properties of ZD55-shMYCN in neuroblastomas. Our data showed that ZD55-shMYCN induced G2/M arrest via decreasing the levels of cyclin D1 and cyclin B1 irrespective of p53 status. ZD55-shMYCN effectively induced apoptosis in neuroblastomas through activation of caspase-3 and enhancing PARP cleavage. Furthermore, ZD55-shMYCN could downregulate phosphoinositide 3-kinase and pAkt and upregulate RKIP levels. Similarly, pro-apoptosis was revealed by the histopathologic examination of paraffin-embedded section of resected tumors of mice xenograft. In vitro and in vivo studies, we elucidate the apoptosis properties and mechanisms of action of ZD55-shMYCN, which provide a promising approach for further clinical development.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Matthay KK. Neuroblastoma: a clinical challenge and biologic puzzle. CA: Cancer J Clin. 1995;45(3):179–92.
Castleberry RP. Predicting outcome in neuroblastoma. N Engl J Med. 1999;340(25):1992–3. doi:10.1056/NEJM199906243402510.
Cornero A, Acquaviva M, Fardin P, Versteeg R, Schramm A, Eva A, et al. Design of a multi-signature ensemble classifier predicting neuroblastoma patients’ outcome. BMC Bioinf. 2012;13(4):S13. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-13-S4-S13.
Oh YK, Park TG. siRNA delivery systems for cancer treatment. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2009;61(10):850–62. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2009.04.018.
Kang JH, Rychahou PG, Ishola TA, Qiao J, Evers BM, Chung DH. MYCN silencing induces differentiation and apoptosis in human neuroblastoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;351(1):192–7. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.10.020.
Novina CD, Sharp PA. The RNAi revolution. Nature. 2004;430(6996):161–4. doi:10.1038/430161a.
Sorensen DR, Leirdal M, Sioud M. Gene silencing by systemic delivery of synthetic siRNAs in adult mice. J Mol Biol. 2003;327(4):761–6.
Carette JE, Overmeer RM, Schagen FH, Alemany R, Barski OA, Gerritsen WR, et al. Conditionally replicating adenoviruses expressing short hairpin RNAs silence the expression of a target gene in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2004;64(8):2663–7.
Wang QZ, Lv YH, Diao Y, Xu R. The design of vectors for RNAi delivery system. Curr Pharm Des. 2008;14(13):1327–40.
Martuza RL, Malick A, Markert JM, Ruffner KL, Coen DM. Experimental therapy of human glioma by means of a genetically engineered virus mutant. Science. 1991;252(5007):854–6.
Toth K, Doronin K, Tollefson AE, Wold WS. A multitasking oncolytic adenovirus vector. Mol Ther: J Am Soc Gene Ther. 2003;7(4):435–7.
Lin E, Nemunaitis J. Oncolytic viral therapies. Cancer Gene Ther. 2004;11(10):643–64. doi:10.1038/sj.cgt.7700733.
Aghi M, Martuza RL. Oncolytic viral therapies—the clinical experience. Oncogene. 2005;24(52):7802–16. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209037.
Zhang ZL, Zou WG, Luo CX, Li BH, Wang JH, Sun LY, et al. An armed oncolytic adenovirus system, ZD55-gene, demonstrating potent antitumoral efficacy. Cell Res. 2003;13(6):481–9. doi:10.1038/sj.cr.7290191.
Liu XY. Targeting gene-virotherapy of cancer and its prosperity. Cell Res. 2006;16(11):879–86. doi:10.1038/sj.cr.7310108.
Li Y, Zhang B, Zhang H, Zhu X, Feng D, Zhang D, et al. Oncolytic adenovirus armed with shRNA targeting MYCN gene inhibits neuroblastoma cell proliferation and in vivo xenograft tumor growth. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2013;139(6):933–41. doi:10.1007/s00432-013-1406-4.
van Noesel MM, Versteeg R. Pediatric neuroblastomas: genetic and epigenetic ‘danse macabre’. Gene. 2004;325:1–15.
Waters AM, Beierle EA. The interaction between FAK, MYCN, p53 and Mdm2 in neuroblastoma. Anti Cancer Agents Med Chem. 2014;14(1):46–51.
Singhal J, Yadav S, Nagaprashantha LD, Vatsyayan R, Singhal SS, Awasthi S. Targeting p53-null neuroblastomas through RLIP76. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2011;4(6):879–89. doi:10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-11-0025.
Singhal SS, Wickramarachchi D, Yadav S, Singhal J, Leake K, Vatsyayan R, et al. Glutathione-conjugate transport by RLIP76 is required for clathrin-dependent endocytosis and chemical carcinogenesis. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011;10(1):16–28. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0699.
Chesler L, Schlieve C, Goldenberg DD, Kenney A, Kim G, McMillan A, et al. Inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase destabilizes Mycn protein and blocks malignant progression in neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 2006;66(16):8139–46. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2769.
Chatterjee D, Bai Y, Wang Z, Beach S, Mott S, Roy R, et al. RKIP sensitizes prostate and breast cancer cells to drug-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(17):17515–23. doi:10.1074/jbc.M313816200.
Dangi-Garimella S, Yun J, Eves EM, Newman M, Erkeland SJ, Hammond SM, et al. Raf kinase inhibitory protein suppresses a metastasis signalling cascade involving LIN28 and let-7. EMBO J. 2009;28(4):347–58. doi:10.1038/emboj.2008.294.
Yeung K, Seitz T, Li S, Janosch P, McFerran B, Kaiser C, et al. Suppression of Raf-1 kinase activity and MAP kinase signalling by RKIP. Nature. 1999;401(6749):173–7. doi:10.1038/43686.
Hellmann J, Rommelspacher H, Muhlbauer E, Wernicke C. Raf kinase inhibitor protein enhances neuronal differentiation in human SH-SY5Y cells. Dev Neurosci. 2010;32(1):33–46. doi:10.1159/000236595.
Moreno L, Marshall LV, Pearson AD. At the frontier of progress for paediatric oncology: the neuroblastoma paradigm. Br Med Bull. 2013;108:173–88. doi:10.1093/bmb/ldt033.
Levy D, Aerts I, Michon J, Lumbroso-Le Rouic L, Cellier C, Orbach D. Childhood cancer: progress but prognosis still very unequal. Example of retinoblastoma and high-risk neuroblastoma. Bull Cancer. 2014;101(3):250–7. doi:10.1684/bdc.2014.1904.
Charron M. Contemporary approach to diagnosis and treatment of neuroblastoma. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2013;57(1):40–52.
Stacey DW. Cyclin D1 serves as a cell cycle regulatory switch in actively proliferating cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2003;15(2):158–63.
Guo Y, Stacey DW, Hitomi M. Post-transcriptional regulation of cyclin D1 expression during G2 phase. Oncogene. 2002;21(49):7545–56. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205907.
Gabrielli BG, Sarcevic B, Sinnamon J, Walker G, Castellano M, Wang XQ, et al. A cyclin D-Cdk4 activity required for G2 phase cell cycle progression is inhibited in ultraviolet radiation-induced G2 phase delay. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(20):13961–9.
Chen Q, Zhang X, Jiang Q, Clarke PR, Zhang C. Cyclin B1 is localized to unattached kinetochores and contributes to efficient microtubule attachment and proper chromosome alignment during mitosis. Cell Res. 2008;18(2):268–80. doi:10.1038/cr.2008.11.
Innocente SA, Abrahamson JL, Cogswell JP, Lee JM. p53 regulates a G2 checkpoint through cyclin B1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96(5):2147–52.
Park M, Chae HD, Yun J, Jung M, Kim YS, Kim SH, et al. Constitutive activation of cyclin B1-associated cdc2 kinase overrides p53-mediated G2-M arrest. Cancer Res. 2000;60(3):542–5.
Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M, Luo X, Wang X. Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during apoptosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1999;15:269–90. doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.15.1.269.
Sairanen T, Szepesi R, Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML, Saksi J, Paetau A, Lindsberg PJ. Neuronal caspase-3 and PARP-1 correlate differentially with apoptosis and necrosis in ischemic human stroke. Acta Neuropathol. 2009;118(4):541–52. doi:10.1007/s00401-009-0559-3.
Yeung K, Janosch P, McFerran B, Rose DW, Mischak H, Sedivy JM, et al. Mechanism of suppression of the Raf/MEK/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway by the raf kinase inhibitor protein. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20(9):3079–85.
Trakul N, Rosner MR. Modulation of the MAP kinase signaling cascade by Raf kinase inhibitory protein. Cell Res. 2005;15(1):19–23. doi:10.1038/sj.cr.7290258.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Zhang, H., Zhu, X. et al. Oncolytic adenovirus-mediated short hairpin RNA targeting MYCN gene induces apoptosis by upregulating RKIP in neuroblastoma. Tumor Biol. 36, 6037–6043 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3280-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3280-y