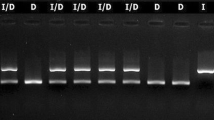
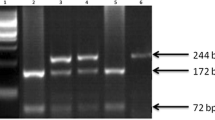
Abstract
MDM2 protein is an important regulator of the p53 pathway and has a large effect on the anti-tumorigenic activity of the p53. Presently, we aimed to analyze the possible association of p53 and mdm2 in the development and progression of non-small cell lung cancer. In addition, impact of an important gene promoter polymorphism of MDM2 (T309G, rs 2279744) on its gene expression and ultimately of the TP53 was investigated in non-small cell lung cancer patients. A case–control study using peripheral blood samples of 100 non-small cell lung cancer patients and 100 cancer free healthy controls was conducted. Expression profile of MDM2 and TP53 gene were evaluated by using quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction assay, and MDM2 promoter polymorphism were analyzed by amplification refractory mutation system polymerase chain reaction. Non-small cell lung cancer patients expressed more than 6-fold increased mdm2 and about 7-folds decreased in p53 expression levels compared to healthy controls. Higher fold change increase of mdm2 and/or decrease of p53 were associated with advanced status and poor clinical outcome of the patients. A significant increase in mdm2 of about 14-folds and decrease in p53 of about 16.5-fold were observed among patients with MDM2 (309GG) genotype vs just 2.2-fold increase in mdm2 and 1.9-fold decrease in p53 among patients with MDM2 (309TT) genotype. In conclusion, present study demonstrated that MDM2 (309 T > G) polymorphism may be one of the important factors for the increased expression mdm2, which was associated with down-regulation of p53 at messenger RNA (mRNA) level and ultimately may contribute in the poor clinical outcome of the non-small cell lung cancer patients, thus may prove as a promising target for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer at molecular level.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MDM2:
-
Mouse double minute 2 homologue
- ARMS:
-
Amplification refractory mutation system
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- SCC:
-
Squamous cell carcinoma
- ADC:
-
Adenocarcinoma
References
Estimated cancer incidence, mortality and prevalence Worldwide in 2012.GLOBOCAN 2012. http://globocan.iarc.fr/Default.aspx.
Prabhat SM, Mehar CS, Bidhu KM, Shukla NK, Deo SVS, Anant M, et al. Clinico-pathological profile of lung cancer at AIIMS: a changing paradigm in India. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(1):489–94.
Rayburn E, Zhang R, He J, Wang H. MDM2 and human malignancies: expression, clinical pathology, prognostic markers, and implications for chemotherapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2005;5:27–41.
Hirata H, Hinoda Y, Kikuno N, Kawamoto K, Suehiro Y, Tanaka Y, et al. MDM2 SNP309 polymorphism as risk factor for susceptibility and poor prognosis in renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:4123–9.
Terry K, McGrath M, Lee IM, Buring J, De Vivo I. MDM2 SNP309 is associated with endometrial cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2008;17:983–6.
Olsson H, Hultman P, Rosell J, Soderkvist P, Jahnson S. MDM2 SNP309 promoter polymorphism and p53 mutations in urinary bladder carcinoma stage T1. BMC Urol. 2013;13:5.
Zhang GX, Li YQ, Pan XL. Polymorphism of MDM2 promoter, regulated by helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide, is associated with both an increased susceptibility to gastric carcinoma and poor prognosis in Chinese patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;26:280.
Mohan A, Guleria R, Pathak AK, Bhutani M, Pal H, Charu M, et al. Quality of life measures in lung cancer. Ind J Cancer. 2005;42:125–32.
Zhang X, Miao X, Guo Y, Tan W, Zhou Y, Sun T, et al. Genetic polymorphisms in cell cycle regulatory genes MDM2 and TP53 are associated with susceptibility to lung cancer. Hum Mutat. 2006;27:110–7.
Weglarz L, Molin I, Orchel A, Parfiniewicz B, Dzierzewicz Z. Quantitative analysis of the level of p53 and p21WAF1 mRNA in human colon cancer HT-29 cells treated with inositol hexaphosphate. Acta Biochim Pol. 2006;53:349–56.
Xiao M, Zhang L, Zhu X, Huang J, Jiang H, Hu S, et al. Genetic polymorphisms of MDM2 and TP53 genes are associated with risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in a Chinese population. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:147.
Shi D, Gu W. Dual roles of MDM2 in the regulation of p53: ubiquitination dependent and ubiquitination independent mechanisms of MDM2 repression of p53 activity. Genes Cancer. 2012;3(3–4):240–8.
Bond GL, Hu W, Bond EE, Robins H, Lutzker SG, Arva NC, et al. A single nucleotide polymorphism in the MDM2 promoter attenuates the p53 tumor suppressor pathway and accelerates tumor formation in humans. Cell. 2004;119:591–602.
Thut CJ, Goodrich JA, Tjian R. Repression of p53-mediated transcription by MDM2: a dual mechanism. Genes Dev. 1997;11:1974–86.
Wadgaonkar R, Collins T. Murine double minute (MDM2) blocks p53-coactivator interaction, a new mechanism for inhibition of p53-dependent gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:13760–7.
Zhang, Wang H. MDM2 oncogene as a novel target for human cancer therapy. Curr Pharm Des. 2000;6:393–416.
Gorgoulis VG, Zacharatos P, Kotsinas A, Liloglou T, Kyroudi A, Veslemes M, et al. Alterations of the p16-pRb pathway and the chromosome locus 9p21-22 in non-small-cell lung carcinomas: relationship with p53 and MDM2 protein expression. Am J Pathol. 1998;153(6):1749–65.
Gorgoulis VG, Zoumpourlis V, Rassidakis GZ, Karameris A, Rassidakis AN, Spandidos DA, et al. A molecular and immunohistochemical study of the MDM2 protein isoforms and p53 gene product in bronchogenic carcinoma. J Pathol. 1996;180:129–37.
Aikawa H, Sato M, Fujimura S, Takahashi H, Endo C, Sakurada A, et al. MDM2 expression is associated with progress of disease and WAF1 expression in resected lung cancer. Int J Mol Med. 2000;5:631–3.
Dworakowska D, Jassem E, Jassem J, Peters B, Dziadziuszko R, Zylicz M, et al. MDM2 gene amplification: a new independent factor of adverse prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Lung Cancer. 2004;43(3):285–95.
Lee JS, Yoon A, Kalapurakal SK, Ro JY, Lee JJ, Tu N, et al. Expression of p53 oncoprotein in non-small-cell lung cancer: a favorable prognostic factor. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13:1893–903.
Nathanson SD, Linden MD, Tender P, Zarbo RJ, Jacobsen G. Nelson LT relationship among p53, stage, and prognosis of large bowel cancer. Dis Colon Rectum. 1994;37(6):527–34.
Ahnen DJ, Feigl P, Quan G, Fenoglio-Preiser C, Lovato LC, Bunn Jr PA, et al. Ki-ras mutation and p53 overexpression predict the clinical behavior of colorectal cancer: a Southwest Oncology Group study. Cancer Res. 1998;58(6):1149–58.
Acknowledgments
The authors specially thank all of the patients who participated in this study.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Javid, J., Mir, R., Julka, P.K. et al. Association of p53 and mdm2 in the development and progression of non-small cell lung cancer. Tumor Biol. 36, 5425–5432 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3208-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3208-6