Abstract
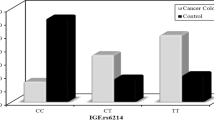
Given the role of insulin resistance in colorectal cancer (CRC), we explored whether genetic variants in insulin (INS), insulin receptor (INSR), insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1), insulin receptor substrate 2 (IRS2), insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1), and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 (IGFBP3) genes were associated with CRC risk. A total of 600 subjects, including 261 cases with CRC and 339 controls, were enrolled in this case-control study. Six polymorphisms in INS (rs689), INSR (rs1799817), IRS1 (rs1801278), IRS2 (rs1805097), IGF1 (rs5742612), and IGFBP3 (rs2854744) genes were genotyped using PCR-RFLP method. No significant difference was observed for INS, INSR, IRS1, IRS2, IGF1, and IGFBP3 genes between the cases and controls. However, the INSR rs1799817 “TT + CT” genotype and “CT” genotype compared with “CC” genotype occurred more frequently in the women with CRC than women controls (P = 0.007; OR = 1.93, 95 %CI = 1.20–3.11 and P = 0.002, OR = 2.15, 95 %CI = 1.31–3.53, respectively), and the difference remained significant after adjustment for confounding factors including age, BMI, smoking status, NSAID use, and family history of CRC (P = 0.018; OR = 1.86, 95 %CI = 1.11-3.10 and P = 0.004, OR = 2.18, 95 %CI = 1.28–3.71, respectively). In conclusion, to our knowledge, this study indicated for the first time that the INSR rs1799817 TT + CT genotype and CT genotype compared with the CC genotype had 1.86-fold and 2.18-fold increased risks for CRC among women, respectively. Furthermore, this finding is in line with previous studies which found significant associations between other variants of the INSR gene and CRC risk. Nevertheless, further studies are required to confirm our findings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893–917.
Caan BJ, Coates AO, Slattery ML, Potter JD, Quesenberry Jr CP, Edwards SM. Body size and the risk of colon cancer in a large case–control study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1998;22:178–84.
Giovannucci E. Insulin, insulin-like growth factors and colon cancer: a review of the evidence. J Nutr. 2001;131:3109S–20.
Limburg PJ, Stolzenberg-Solomon RZ, Vierkant RA, Roberts K, Sellers TA, Taylor PR, et al. Insulin, glucose, insulin resistance, and incident colorectal cancer in male smokers. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4:1514–21.
Giovannucci E. Insulin and colon cancer. Cancer Causes Control. 1995;6:164–79.
Larsson SC, Orsini N, Wolk A. Diabetes mellitus and risk of colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97:1679–87.
Wang L, Cai S, Teng Z, Zhao X, Chen X, Bai X. Insulin therapy contributes to the increased risk of colorectal cancer in diabetes patients: a meta-analysis. Diagn Pathol. 2013;8:180.
Baxter RC, Turtle JR. Regulation of hepatic growth hormone receptors by insulin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978;84:350–7.
Kiunga GA, Raju J, Sabljic N, Bajaj G, Good CK, Bird RP. Elevated insulin receptor protein expression in experimentally induced colonic tumors. Cancer Lett. 2004;211:145–53.
Withers DJ. Insulin receptor substrate proteins and neuroendocrine function. Biochem Soc Trans. 2001;29:525–9.
Schubert M, Brazil DP, Burks DJ, Kushner JA, Ye J, Flint CL, et al. Insulin receptor substrate-2 deficiency impairs brain growth and promotes tau phosphorylation. J Neurosci. 2003;23:7084–92.
Dearth RK, Cui X, Kim HJ, Hadsell DL, Lee AV. Oncogenic transformation by the signaling adaptor proteins insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-1 and IRS-2. Cell Cycle. 2007;6:705–13.
Reuveni H, Flashner-Abramson E, Steiner L, Makedonski K, Song R, Shir A, et al. Therapeutic destruction of insulin receptor substrates for cancer treatment. Cancer Res. 2013;73:4383–94.
White MF. Insulin signaling in health and disease. Science. 2003;302:1710–1.
Björndahl M, Cao R, Nissen LJ, Clasper S, Johnson LA, Xue Y, et al. Insulin-like growth factors 1 and 2 induce lymphangiogenesis in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:15593–8.
Kirman I, Poltoratskaia N, Sylla P, Whelan RL. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 3 inhibits growth of experimental colocarcinoma. Surgery. 2004;136:205–9.
Davies M, Gupta S, Goldspink G, Winslet M. The insulin-like growth factor system and colorectal cancer: clinical and experimental evidence. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2006;21:201–8.
Lusis AJ, Attie AD, Reue K. Metabolic syndrome: from epidemiology to systems biology. Nat Rev Genet. 2008;9:819–30.
Pechlivanis S, Pardini B, Bermejo JL, Wagner K, Naccarati A, Vodickova L, et al. Insulin pathway related genes and risk of colorectal cancer: INSR promoter polymorphism shows a protective effect. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2007;14:733–40.
Gunter MJ, Hayes RB, Chatterjee N, Yeager M, Welch R, Schoen RE, et al. Insulin resistance-related genes and advanced left-sided colorectal adenoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2007;16:703–8.
Landi D, Gemignani F, Naccarati A, Pardini B, Vodicka P, Vodickova L, et al. Polymorphisms within micro-RNA-binding sites and risk of sporadic colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2008;29:579–84.
Landi D, Moreno V, Guino E, Vodicka P, Pardini B, Naccarati A, et al. Polymorphisms affecting micro-RNA regulation and associated with the risk of dietary-related cancers: a review from the literature and new evidence for a functional role of rs17281995 (CD86) and rs1051690 (INSR), previously associated with colorectal cancer. Mutat Res. 2011;717:109–15.
Karimi K, Mahmoudi T, Karimi N, Dolatmoradi H, Arkani M, Farahani H, et al. Is there an association between variants in candidate insulin pathway genes IGF-I, IGFBP-3, INSR, and IRS2 and risk of colorectal cancer in the Iranian population? Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14:5011–6.
Tucci S, Futterweit W, Concepcion ES, Greenberg DA, Villanueva RB, Davies TF, et al. Evidence for association of polycystic ovary syndrome in Caucasian women with a marker at the insulin receptor gene locus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:446–9.
Malodobra M, Pilecka A, Gworys B, Adamiec R. Single nucleotide polymorphisms within functional regions of genes implicated in insulin action and association with the insulin resistant phenotype. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011;349:187–93.
Morgan R, Bishop A, Owens DR, Luzio SD, Peters JR, Rees A. Allelic variants at insulin-receptor and insulin gene loci and susceptibility to NIDDM in Welsh population. Diabetes. 1990;39:1479–84.
Kovacs P, Hanson RL, Lee Y-H, Yang X, Kobes S, Permana PA, et al. The role of insulin receptor substrate-1 gene (IRS1) in type 2 diabetes in Pima Indians. Diabetes. 2003;52:3005–9.
Lautier C, El Mkadem SA, Renard E, Brun JF, Gris JC, Bringer J, et al. Complex haplotypes of IRS2 gene are associated with severe obesity and reveal heterogeneity in the effect of Gly1057Asp mutation. Hum Genet. 2003;113:34–43.
Slattery ML, Samowitz W, Curtin K, Ma KN, Hoffman M, Caan B, et al. Associations among IRS1, IRS2, IGF1, and IGFBP3 genetic polymorphisms and colorectal cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2004;13:1206–14.
Wagner K, Hemminki K, Grzybowska E, Klaes R, Butkiewicz D, Pamula J, et al. The insulin-like growth factor-I pathway mediator genes: SHC1Met300Val shows a protective effect in breast cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2004;25:2473–8.
Hu Y, Zhou M, Zhang K, Kong X, Hu X, Li K, et al. Lack of association between insulin receptor substrate2 rs1805097 polymorphism and the risk of colorectal and breast cancer: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2014;9:e86911.
Yukseloglu EH, Celik SK, Kucuk MU, Yalin E, Ozkal SS, Ates C, et al. IRS-2 G1057D polymorphism in Turkish patients with colorectal cancer. Prz Gastroenterol. 2014;9:88–92.
Probst-Hensch NM, Yuan JM, Stanczyk FZ, Gao YT, Ross RK, Yu MC. IGF-1, IGF-2 and IGFBP-3 in prediagnostic serum: association with colorectal cancer in a cohort of Chinese men in Shanghai. Br J Cancer. 2001;85:1695–9.
Al-Zahrani A, Sandhu MS, Luben RN, Thompson D, Baynes C, Pooley KA, et al. IGF1 and IGFBP3 tagging polymorphisms are associated with circulating levels of IGF1, IGFBP3 and risk of breast cancer. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15:1–10.
Pechlivanis S, Wagner K, Chang-Claude J, Hoffmeister M, Brenner H, Försti A. Polymorphisms in the insulin like growth factor 1 and IGF binding protein 3 genes and risk of colorectal cancer. Cancer Detect Prev. 2007;31:408–16.
Quan H, Tang H, Fang L, Bi J, Liu Y, Li H. IGF1(CA)19 and IGFBP-3-202A/C gene polymorphism and cancer risk: a meta-analysis. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014;69:169–78.
Wong HL, Koh WP, Probst-Hensch NM, Van den Berg D, Yu MC, Ingles SA. Insulin-like growth factor1 promoter polymorphisms and colorectal cancer: a functional genomics approach. Gut. 2008;57:1090–6.
Le Marchand L, Kolonel LN, Henderson BE, Wilkens LR. Association of an exon 1 polymorphism in the IGFBP3 gene with circulating IGFBP-3 levels and colorectal cancer risk: the multiethnic cohort study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2005;14:1319–21.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to all the subjects for participating. This work was supported by a grant from Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases Research Center, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahmoudi, T., Majidzadeh-A, K., Karimi, K. et al. An exon variant in insulin receptor gene is associated with susceptibility to colorectal cancer in women. Tumor Biol. 36, 3709–3715 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-3010-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-3010-x