Abstract
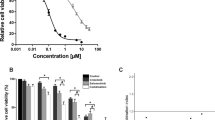
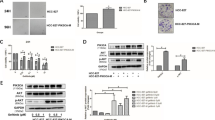
Targeted therapy based on ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors (ALK-TKIs) has made significant achievements in individuals with EML4-ALK (echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like 4 gene and the anaplastic lymphoma kinase gene) fusion positive nonsmall-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, a high fraction of patients receive inferior clinical response to such treatment in the initial therapy, and the exact mechanisms underlying this process need to be further investigated. In this study, we revealed a persistently activated PI3K/AKT signaling that mediates the drug ineffectiveness. We found that genetic or pharmacological inhibition of ALK markedly abrogated phosphorylated STAT3 and ERK, but it failed to suppress AKT activity or induce apoptosis, in EML4-ALK-positive H2228 cells. Furthermore, targeted RNA interference of PI3K pathway components restored sensitivity to TAE684 treatment at least partially due to increased apoptosis. Combined TAE684 with PI3K inhibitor synergistically inhibited the proliferation of EML4-ALK-positive cells in vitro and significantly suppressed the growth of H2228 xenografts in vivo, suggesting the potential clinical application of such combinatorial therapy regimens in patients with EML4-ALK positive lung cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iwahara T, Fujimoto J, Wen D, Cupples R, Bucay N, Arakawa T, et al. Molecular characterization of ALK, a receptor tyrosine kinase expressed specifically in the nervous system. Oncogene. 1997;14:439–49.
Morris SW, Kirstein MN, Valentine MB, Dittmer K, Shapiro DN, Look AT, et al. Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Science. 1995;267:316–7.
Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S, Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 2007;448:561–6.
Horn L, Pao W. EML4-ALK: honing in on a new target in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:4232–5.
Schulte JH, Bachmann HS, Brockmeyer B, Depreter K, Oberthur A, Ackermann S, et al. High ALK receptor tyrosine kinase expression supersedes ALK mutation as a determining factor of an unfavorable phenotype in primary neuroblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:5082–92.
Ogawa S, Takita J, Sanada M, Hayashi Y. Oncogenic mutations of ALK in neuroblastoma. Cancer Sci. 2011;102:302–8.
Murugan AK, Xing M. Anaplastic thyroid cancers harbor novel oncogenic mutations of the ALK gene. Cancer Res. 2011;71:4403–11.
Christensen JG, Zou HY, Arango ME, Li Q, Lee JH, McDonnell SR, et al. Cytoreductive antitumor activity of PF-2341066, a novel inhibitor of anaplastic lymphoma kinase and c-Met, in experimental models of anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 2007;6:3314–22.
Galkin AV, Melnick JS, Kim S, Hood TL, Li N, Li L, et al. Identification of NVP-TAE684, a potent, selective, and efficacious inhibitor of NPM-ALK. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104:270–5.
Doebele RC, Pilling AB, Aisner DL, Kutateladze TG, Le AT, Weickhardt AJ, et al. Mechanisms of resistance to crizotinib in patients with ALK gene rearranged non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:1472–82.
Popat S, Vieira de Araujo A, Min T, Swansbury J, Dainton M, Wotherspoon A, et al. Lung adenocarcinoma with concurrent exon 19 EGFR mutation and ALK rearrangement responding to erlotinib. J Thorac Oncol. 2011;6:1962–3.
Dai Z, Kelly JC, Meloni-Ehrig A, Slovak ML, Boles D, Christacos NC, et al. Incidence and patterns of ALK FISH abnormalities seen in a large unselected series of lung carcinomas. Mol Cytogenet. 2012;5:44.
Katayama R, Shaw AT, Khan TM, Mino-Kenudson M, Solomon BJ, Halmos B, et al. Mechanisms of acquired crizotinib resistance in ALK-rearranged lung Cancers. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4:120ra17.
Chou TC, Talalay P. Quantitative analysis of dose-effect relationships: the combined effects of multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzym Regul. 1984;22:27–55.
Chou TC. Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer Res. 2010;70:440–6.
Kanaji N, Bandoh S, Ishii T, Tadokoro A, Watanabe N, Takahama T, et al. Detection of EML4-ALK fusion genes in a few cancer cells from transbronchial cytological specimens utilizing immediate cytology during bronchoscopy. Lung Cancer. 2012;77:293–8.
Li Y, Ye X, Liu J, Zha J, Pei L. Evaluation of EML4-ALK fusion proteins in non-small cell lung cancer using small molecule inhibitors. Neoplasia. 2011;13:1–11.
Amin HM, Lai R. Pathobiology of ALK+ anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2007;110:2259–67.
Tanizaki J, Okamoto I, Takezawa K, Sakai K, Azuma K, Kuwata K, et al. Combined effect of ALK and MEK inhibitors in EML4-ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 2012;106:763–7.
Kwak EL, Bang YJ, Camidge DR, Shaw AT, Solomon B, Maki RG, et al. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(18):1693–703.
Camidge DR, Bang YJ, Kwak EL, Iafrate AJ, Varella-Garcia M, Fox SB, et al. Activity and safety of crizotinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: updated results from a phase 1 study. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13(10):1011–9.
McDermott U, Iafrate AJ, Gray NS, Shioda T, Classon M, Maheswaran S, et al. Genomic alterations of anaplastic lymphoma kinase may sensitize tumors to anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2008;68(9):3389–95.
Koivunen JP, Mermel C, Zejnullahu K, Murphy C, Lifshits E, Holmes AJ, et al. EML4-ALK fusion gene and efficacy of an ALK kinase inhibitor in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:4275–83.
Rikova K, Guo A, Zeng Q, Possemato A, Yu J, Haack H, et al. Global survey of phosphotyrosine signaling identifies oncogenic kinases in lung cancer. Cell. 2007;131:1190–203.
Chiarle R, Voena C, Ambrogio C, Piva R, Inghirami G. The anaplastic lymphoma kinase in the pathogenesis of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:11–23.
Voena C, Di Giacomo F, Panizza E, D'Amico L, Boccalatte FE, Pellegrino E, et al. The EGFR family members sustain the neoplastic phenotype of ALK+ lung adenocarcinoma via EGR1. Oncogenesis. 2013;2:e43.
Rodon J, Dienstmann R, Serra V, Tabernero J. Development of PI3K inhibitors: lessons learned from early clinical trials. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013;10:143–53.
Hynes NE, Dey JH. PI3K inhibition overcomes trastuzumab resistance: blockade of ErbB2/ErbB3 is not always enough. Cancer Cell. 2009;15:353–5.
Ding J, Romani J, Zaborski M, MacLeod RA, Nagel S, Drexler HG, et al. Inhibition of PI3K/mTOR overcomes nilotinib resistance in BCR-ABL1 positive leukemia cells through translational down-regulation of MDM2. PLoS One. 2013;8:e83510.
Donev IS, Wang W, Yamada T, Li Q, Takeuchi S, Matsumoto K, et al. Transient PI3K inhibition induces apoptosis and overcomes HGF-mediated resistance to EGFR-TKIs in EGFR mutant lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:2260–9.
Conflict of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Lin Yang and Guangchao Li contributed equally to this work and are joint first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, L., Li, G., Zhao, L. et al. Blocking the PI3K pathway enhances the efficacy of ALK-targeted therapy in EML4-ALK-positive nonsmall-cell lung cancer. Tumor Biol. 35, 9759–9767 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2252-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2252-y