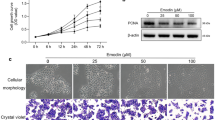
Abstract
Backgrounds
Chlorin e6-mediated photodynamic therapy (Ce6-PDT) showed anti-microbial and anti-inflammatory effects on acne vulgaris model previously. Excess sebum production in sebocytes is a crucial cause of acne. However, information on the effect of Ce6-PDT associated with lipogenesis in sebocytes has not been reported so far.
Methods
The oil red O staining, triglyceride assay and cholesterol assay were used to investigate lipid synthesis in human sebocytes. The expressions of various molecular signals associated with lipogenesis were examined by western blot analysis.
Results
Ce6-PDT reduced the lipid content of cultured sebocytes. The inactivation of Akt, mTOR, Raptor, PPARγ and C/EBPα, as well as the activation of AMPK, were revealed to be the molecular signals associated with sebostatic modulation by Ce6-PDT.
Conclusion
Ce6-PDT using halogen light exerts antilipogenesis in sebocytes and may be utilized for the treatment of acne vulgaris.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Melnik, B. Dietary intervention in acne: Attenuation of increased mTORC1 signaling promoted by western diet. Dermatoendocrinol 4, 20–32 (2012).
Suh, D. H. & Kwon, H. H. What’s new in the physiopathology of acne? Br J Dermatol 172, 13–19 (2015).
Zouboulis, C. C. et al. What is the pathogenesis of acne? Exp Dermatol 14, 143–152 (2005).
Williams, H. C., Dellavalle, R. P. & Garner, S. Acne vulgaris. Lancet 379, 361–372 (2012).
Yoon, J. Y., Kwon, H. H., Min, S. U., Thiboutot, D. M. & Suh, D. H. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate improves acne in humans by modulating intracellular molecular targets and inhibiting P. acnes. J Invest Dermatol 133, 429–440 (2013).
Mourelatos, K., Eady, E. A., Cunliffe, W. J., Clark, S. M. & Cove, J. H. Temporal changes in sebum excretion and propionibacterial colonization in preadolescent children with and without acne. Br J Dermatol 156, 22–31 (2007).
Ottaviani, M., Camera, E. & Picardo, M. Lipid mediators in acne. Mediators Inflamm 2010, 858176, doi: 10. 1155/2010/858176 (2010).
Zouboulis, C. C., Jourdan, E. & Picardo, M. Acne is an inflammatory disease and alterations of sebum composition initiate acne lesions. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 28, 527–532 (2014).
Choi, J. J. et al. TNF-a increases lipogenesis via JNK and PI3K/Akt pathways in SZ95 human sebocytes. J Dermatol Sci 65, 179–188 (2012).
McNairn, A. J. et al. TGFβ signaling regulates lipogenesis in human sebaceous glands cells. BMC Dermatol 13, 2, doi: 10.1186/1471-5945-13-2 (2013).
Melnik, B. C. Linking diet to acne metabolomics, inflammation, and comedogenesis: an update. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 8, 371–388, doi: 10.2147/CCID.S69135 (2015).
Mirdamadi, Y. et al. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 can modulate the phosphoinositide-3-kinase/Akt/FoxO1 pathway in SZ95 sebocytes in vitro. Mol Cell Endocrinol 415, 32–44 (2015).
Zouboulis, C. C., Angres, S. & Seltmann, H. Regulation of stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase and fatty acid delta-6 desaturase-2 expression by linoleic acid and arachidonic acid in human sebocytes leads to enhancement of proinflammatory activity but does not affect lipogenesis. Br J Dermatol 165, 269–276 (2011).
Jiang, S., Wang, W., Miner, J. & Fromm, M. Cross regulation of sirtuin 1, AMPK, and PPAR? in conjugated linoleic acid treated adipocytes. PLoS One 7, e48874, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048874 (2012).
Jang, J. et al. Berberine activates AMPK to suppress proteolytic processing, nuclear translocation and target DNA binding of SREBP-1c in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol Med Rep 15, 4139–4147 (2017).
Kim, S. Y., Hyun, M. Y., Go, K. C., Zouboulis, C. C. & Kim, B. J. Resveratrol exerts growth inhibitory effects on human SZ95 sebocytes through the inactivation of the PI3-K/Akt pathway. Int J Mol Med 35, 1042–1050 (2015).
Savage, L. J. & Layton, A. M. Treating acne vulgaris: systemic, local and combination therapy. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol 3, 563–580 (2010).
Lucky, S. S., Soo, K. C. & Zhang, Y. Nanoparticles in photodynamic therapy. Chem Rev 115, 1990–2042 (2015).
Jeon, Y. M. et al. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy using chlorin e6 with halogen light for acne bacteria-induced inflammation. Life Sci 124, 56–63 (2015).
Wang, Y. Y., Ryu, A. R., Jin, S., Jeon, Y. M. & Lee, M. Y. Chlorin e6-mediated photodynamic therapy suppresses P. acnes-induced inflammatory response via NF?B and MAPKs signaling pathway. PLoS One 12, e0170599, doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0170599 (2017).
Ryu, A. R. & Lee, M. Y. Chlorin e6-mediated photodynamic therapy promotes collagen production and suppresses MMPs expression via modulating AP-1 signaling in P. acnes-stimulated HaCaT cells. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 20, 71–77 (2017).
Lee, S. E. et al. Effect of crotonaldehyde on the induction of COX-2 expression in human endothelial cells. Mol Cell Toxicol 13, 345–350 (2017).
Kim, J. H., Ryu, A. R., Kang, M. J. & Lee, M. Y. Berberine-induced changes in protein expression and antioxidant enzymes in melanoma cells. Mol Cell Toxicol 12, 53–61 (2016).
Smith, K. R. & Thiboutot, D. M. Thematic review series: skin lipids. Sebaceous gland lipids: friend or foe? J Lipid Res 49, 271–281 (2008).
Zouboulis, C. C., Schagen, S. & Alestas, T. The sebocyte culture: a model to study the pathophysiology of the sebaceous gland in sebostasis, seborrhoea and acne. Arch Dermatol Res 300, 397–413 (2008).
Masure, J., Bonnel, D., Stauber, J., Hunt, D. & Hofland, H. E. 528 DRM01, a novel, topical sebum inhibitor for the treatment of acne. J Invest Dermatol 136, S93, doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2016.02.566 (2016).
Hunt, D. W. et al. Inhibition of sebum production with the acetyl coenzyme a carboxylase inhibitor Olumacostat Glasaretil. J Invest Dermatol 137, 1415–1423 (2017).
Gupta, M., Mahajan, V. K., Mehta, K. S., Chauhan, P. S. & Rawat, R. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) and PPAR agonists: the ‘future’ in dermatology therapeutics? Arch Dermatol Res 307, 767–780 (2015).
Park, J. Y., Kim, Y., Im, J. A., You, S. & Lee, H. Inhibition of adipogenesis by oligonol through Akt-mTOR inhibition in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2014, 895272, doi: 10.1155/2014/895272 (2014).
Tuo, J. et al. ALA-PDT suppressing the cell growth and reducing the lipogenesis in human SZ95 sebocytes by mTOR signaling pathway in vitro. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 18, 295–301 (2017).
Laplante, M. & Sabatini, D. M. An emerging role of mTOR in lipid biosynthesis. Curr Biol 19, R1046–R1052 (2009).
Park, J. & Jang, H. J. Anti-diabetic effects of natural products an overview of therapeutic strategies. Mol Cell Toxicol 13, 1–20 (2017).
Cho, H. J., Park, J., Lee, H. W., Lee, Y. S. & Kim, J. B. Regulation of adipocyte differentiation and insulin action with rapamycin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 321, 942–948 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryu, AR., Kim, YW. & Lee, MY. Chlorin e6 and halogen light as a sebostatic photomedicine modulates linoleic acid-induced lipogenesis. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 15, 49–56 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-019-0006-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-019-0006-z