Abstract
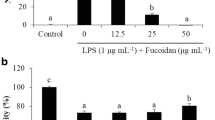
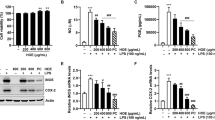
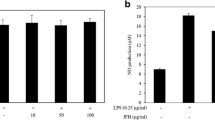
Fucoidan, a sulfated polysaccharide, is an active component found in various species of seaweed. Although this compound has a strong anti-inflammatory activity, the underlying mechanisms exerted by fucoidan have not been fully elucidated. In the present study, the anti-inflammatory effects of fucoidan on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated macrophages and zebrafish larvae were examined. The present data indicated that fucoidan significantly suppressed the secretion of pro-inflammatory mediators including nitric oxide (NO ) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), and cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-1β in RAW 264.7 macrophages without any significant cytotoxicity, the protective effects of which were accompanied by a marked reduction in their regulatory gene expression at the transcription levels. Fucoidan also inhibited translocation of the nuclear factor-kappa B from the cytoplasm to the nucleus and attenuated LPS-induced production of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Moreover, fucoidan reduced NO and PGE2 production and ROS accumulation in LPS-stimulated zebrafish larvae, which was associated with a diminished recruitment of neutrophils and macrophages. Based on the results of this study, we suggest that fucoidan has excellent potential as a therapeutic agent for inflammatory disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Conti, B., Tabarean, I., Andrei, C. & Bartfai, T. Cytokines and fever. Front Biosci 9:1433–1449 (2004).
Freire, M. O. & Van Dyke, T. E. Natural resolution of inflammation. Periodontol 2000 63:149–164 (2013).
Amin, A. R., Attur, M. & Abramson, S. B. Nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenases: distribution, regulation, and intervention in arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 11: 202–209 (1999).
Cunha, T. M. et al. Crucial role of neutrophils in the development of mechanical inflammatory hypernociception. J Leukoc Biol 83:824–832 (2008).
Williams, M. R., Azcutia, V., Newton, G., Alcaide, P. & Luscinskas, F. W. Emerging mechanisms of neutrophil recruitment across endothelium. Trends Immunol 32:461–469 (2011).
Zhang, L. & Wang, C. C. Inflammatory response of macrophages in infection. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 13:138–152 (2014).
Muralidharan, S. & Mandrekar, P. Cellular stress response and innate immune signaling: integrating pathways in host defense and inflammation. J Leukoc Biol 94:1167–1184 (2013).
Czura, C. J., Friedman, S. G. & Tracey, K. J. Neural inhibition of inflammation: the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. J Endotoxin Res 9:409–413 (2003).
McDaniel, M. L., Kwon, G., Hill, J. R., Marshall, C. A. & Corbett, J. A. Cytokines and nitric oxide in islet inflammation and diabetes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 211:24–32 (1996).
Brüne, B. et al. Redox control of inflammation in macrophages. Antioxid Redox Signal 19:595–637 (2013).
Mills, E. L. & O’Neill, L. A. Reprogramming mitochondrial metabolism in macrophages as an anti-in flammatory signal. Eur J Immunol 46:13–21 (2016).
Varga, A. et al. Ragweed pollen extract intensifies lipopolysaccharide-induced priming of NLRP3 inflammasome in human macrophages. Immunology 138:392–401 (2013)
Haddad, J. J. & Land, S. C. Redox signaling-mediated regulation of lipopolysaccharide-induced proinflammatory cytokine biosynthesis in alveolar epithelial cells. Antioxid Redox Signal 4:179–193 (2002).
Abuajah, C. I., Ogbonna, A. C. & Osuji, C. M. Functional components and medicinal properties of food: a review. J Food Sci Technol 52:2522–2529 (2015).
Bocanegra, A., Bastida, S., Benedí, J., Ródenas, S. & Sánchez-Muniz, F. J. Characteristics and nutritional and cardiovascular-health properties of seaweeds. J Med Food 12:236–258 (2009).
Cardoso, M. J., Costa, R. R. & Mano, J. F. Marine origin polysaccharides in drug delivery dystems. Mar Drugs 14:pii: E34 (2016).
de Jesus Raposo, M. F., de Morais, A. M. & de Morais, R. M. Marine polysaccharides from algae with potential biomedical applications. Mar Drugs 13:2967–3028 (2015).
Park, H. Y. et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of fucoidan through inhibition of NF-kB, MAPK and Akt activation in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV2 microglia cells. Food Chem Toxicol 49:1745–1752 (2011).
Park, H. S. et al. Induction of apoptosis by fucoidan in human leukemia U937 cells through activation of p38 MAPK and modulation of Bcl-2 family. Mar Drugs 11:2347–2364 (2013).
Park, H. Y. et al. Fucoidan inhibits the proliferation of human urinary bladder cancer T24 cells by blocking cell cycle progression and inducing apoptosis. Molecules 19:5981–5998 (2014).
Senthilkumar, K. & Kim, S. K. Anticancer effects of fucoidan. Adv Food Nutr Res 72:195–213 (2014).
Wang, P. et al. 2014. Anti-metastasis effect of fucoidan from Undaria pinnatifida sporophylls in mouse hepatocarcinoma Hca-F cells. PLoS One 9:e106071 (2014).
Fitton, J. H., Stringer, D. N. & Karpiniec, S. S. Therapies from fucoidan: An update. Mar Drugs 13:5920–5946 (2015).
Huang, T. H. et al. Prophylactic administration of fucoidan represses cancer metastasis by inhibiting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in Lewis tumor-bearing mice. Mar Drugs 13:1882–1900 (2015).
Kim, B. S., Kang, H. J., Park, J. Y. & Lee, J. Fucoidan promotes osteoblast differentiation via JNK-and ERK-dependent BMP2-Smad 1/5/8 signaling in human mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Mol Med 47:e128 (2015).
Seok, J. et al. Efficacy of Cistanche tubulosa and Laminaria japonica extracts (MK-R7) supplement in preventing patterned hair loss and promoting scalp health. Clin Nutr Res 4:124–131 (2015).
Chen, Y. M. et al. Fucoidan supplementation improves exercise performance and exhibits anti-fatigue action in mice. Nutrients 7:239–252 (2014).
Lee, S. H. et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of fucoidan extracted from Ecklonia cava in zebrafish model. Carbohydr Polym 92:84–89 (2013).
Kim, E. A. et al. Protective effect of fucoidan against AAPH-induced oxidative stress in zebrafish model. Carbohydr Polym 102:185–191 (2014).
Li, Q. & Verma, I. M. NF-kappaB regulation in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2:725–734 (2002).
Lu, Y. C. et al. Chondroprotective role of sesamol by inhibiting MMPs expression via retaining NF-kB signaling in activated SW1353 cells. J Agric Food Chem 59:4969–4978 (2011).
Rigoglou, S. & Papavassiliou, A. G. The NF-kB signalling pathway in osteoarthritis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 45:2580–2584 (2013).
Mitroulis, I. et al. Leukocyte integrins: role in leukocyte recruitment and as therapeutic targets in inflammatory disease. Pharmacol Ther 147:123–135 (2015).
Aderem, A. & Ulevitch, R. J. Toll-like receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature 406:782–787 (2000).
Nikaido, H. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability revisited. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 67:593–656 (2003).
Ginsburg, I. & Koren E. Are cationic antimicrobial peptides also “double-edged swords”?, Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 6:453–462 (2008).
Yu, H. et al. Scavenger receptor A (SR-A) is required for LPS-induced TLR4 mediated NF-kB activation in macrophages. Biochim Biophys Acta 1823:1192–1198 (2012).
Kauppinen, A., Suuronen, T., Ojala, J., Kaarniranta, K. & Salminen, A. Antagonistic crosstalk between NF-kB and SIRT1 in the regulation of inflammation and metabolic disorders. Cell Signal 25:1939–1948 (2013).
Tan, H. Y. et al. The reactive oxygen species in macrophage polarization: Reflecting its dual role in progression and treatment of human diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016:2795090 (2016).
Dibbert, B. et al. Cytokine-mediated Bax deficiency and consequent delayed neutrophil apoptosis: a general mechanism to accumulate effector cells in inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:13330–13335 (1999).
Sikora, J. P. Immunotherapy in the management of sepsis. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 50:317–324 (2002).
Matthay, M. A. & Zimmerman, G. A. Acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome: four decades of inquiry into pathogenesis and rational management. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 33:319–327 (2005).
Schiavuzzo, J. G. et al. Muscle hyperalgesia induced by peripheral P2X3 receptors is modulated by inflammatory mediators. Neuroscience 285:24–33 (2015).
Carvalho, A. C. et al. Protective effects of fucoidan, a P-and L-selectin inhibitor, in murine acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 43:82–87 (2014).
Oh, K., Moon, H. G., Lee, D. S. & Yoo, Y. B. Tissue transglutaminase-interleukin-6 axis facilitates perito neal tumor spreading and metastasis of human ovarian cancer cells. Lab Anim Res 31:188–197 (2015).
Lee, H. et al. Improved Therapeutic profiles of PLA2-free bee venom prepared by ultrafiltration method. Toxicol Res 31:33–40 (2015).
Wang, L. et al. Sonchus asper extract inhibits LPS-induced oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory cytokine production in RAW264.7 macrophages. Nutr Res Pract 9:579–585 (2015).
Eom, S. A. et al. Protective effects of PEP-1-Catalase on stress-induced cellular toxicity and MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease. BMB Rep 48:395–400 (2015).
Wijesinghe, W. A. et al. Aßsessment of anti-inflammatory effect of 5β-hydroxypalisadin B isolated from red seaweed Laurencia snackeyi in zebrafish embryo in vivo model. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 37:110–117 (2014).
Yang, L., Bu, L., Sun, W., Hu, L. & Zhang, S. Functional characterization of mannose-binding lectin in zebrafish: implication for a lectin-dependent complement system in early embryos. Dev Comp Immunol 46:314–322 (2014).
Le Guyader, D. et al. Origins and unconventional behavior of neutrophils in developing zebrafish. Blood 111:132–141 (2008).
Herbomel, P., Thisse, B. & Thisse, C. Zebrafish early macrophages colonize cephalic mesenchyme and developing brain, retina, and epidermis through a M-CSF receptor-dependent invasive process. Dev Biol 238:274–288 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, JW., Hwang, S.J., Han, M.H. et al. Fucoidan inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in RAW 264.7 macrophages and zebrafish larvae. Mol. Cell. Toxicol. 13, 405–417 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-017-0045-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13273-017-0045-2