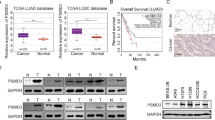
Abstract
Background
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) contributes to the vast majority of cancer-related deaths. Proteasome 26S subunit, non-ATPase 12 (PSMD12), a subunit of 26S proteasome complex, is known to play the tumor-promoting role in several types of cancer but its function in NSCLC remains elusive.
Objective
To explore the role and underlying mechanisms of PSMD12 in NSCLC.
Methods
The PSMD12 expression in human normal lung epithelial cell line (BEAS-2B) and four NSCLC cell lines (A549, NCI-H1299, NCI-H1975, Calu-1) were determined by qRT-PCR and western blot. Malignant phenotypes of NSCLC cells were detected by CCK-8, EdU staining, immunofluorescence staining for E-cadherin, flow cytometry, and Transwell assays to assess cell viability, proliferation, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), apoptosis, migration and invasion. Dual luciferase assay was used to verify the regulatory role of transcription factor on the promoter.
Results
We identified the upregulation of PSMD12 in NSCLC tissues based on the GEO datasets, which further verified in NSCLC and BEAS-2B cell lines. PSMD12 knockdown significantly suppressed malignant behaviors of NSCLC cells, including cell growth, invasion, and migration, while PSMD12 overexpression presented the opposite effects. Interestingly, we found that PSMD12 upregulated the tumor-promoting factor TrxR1 mRNA expression. For its potential mechanisms, we demonstrated that PSMD12 elevated transcription factor Nrf2 protein level and promoted Nrf2 nuclear translocation. And Nrf2 further increased TrxR1 promoter activity and enhanced TrxR1 transcription. Meanwhile, we proved that TrxR1 overexpression erased the inhibitory effect of PSMD12 knockdown.
Conclusion
PSMD12 promotes NSCLC progression by activating the Nrf2/TrxR1 pathway, providing a novel prognostic and therapeutic target for NSCLC treatment.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Baek SY, Kim MR (2020) Neuroprotective effect of Carotenoid-Rich Enteromorpha prolifera Extract via TrkB/Akt pathway against oxidative stress in hippocampal neuronal cells. Mar Drugs 18(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/md18070372
Busker S, Qian W, Haraldsson M, Espinosa B, Johansson L, Attarha S, Kolosenko I, Liu J, Dagnell M, Grander D et al (2020) Irreversible TrxR1 inhibitors block STAT3 activity and induce cancer cell death. Sci Adv 6(12):eaax7945. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aax7945
Chen G, Chen Q, Zeng F, Zeng L, Yang H, Xiong Y, Zhou C, Liu L, Jiang W, Yang N et al (2017) The serum activity of thioredoxin reductases 1 (TrxR1) is correlated with the poor prognosis in EGFR wild-type and ALK negative non-small cell Lung cancer. Oncotarget 8(70):115270–115279. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.23252
Choi JH, Lee YB, Jung J, Hwang SG, Oh IH, Kim GJ (2016) Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α regulates the Migration of Bone Marrow mesenchymal stem cells via integrin α 4. Stem Cells Int 2016:7932185. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7932185
Delgobo M, Goncalves RM, Delazeri MA, Falchetti M, Zandona A, Nascimento das Neves R, Almeida K, Fagundes AC, Gelain DP, Fracasso JI et al (2021) Thioredoxin reductase-1 levels are associated with NRF2 pathway activation and Tumor recurrence in non-small cell Lung cancer. Free Radic Biol Med 177:58–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.10.020
Ding Q, Wang H, Wang Y, Lu Y (2022) A thioredoxin reductase 1 inhibitor pyrano [3,2-a] phenazine inhibits A549 cells proliferation and migration through the induction of reactive oxygen species production. Mol Biol Rep 49(9):8835–8845. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07733-2
Dong R, Wang D, Wang X, Zhang K, Chen P, Yang CS, Zhang J (2016) Epigallocatechin-3-gallate enhances key enzymatic activities of hepatic thioredoxin and glutathione systems in selenium-optimal mice but activates hepatic Nrf2 responses in selenium-deficient mice. Redox Biol 10:221–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2016.10.009
Du X, Shen X, Dai L, Bi F, Zhang H, Lu C (2020) PSMD12 promotes Breast cancer growth via inhibiting the expression of pro-apoptotic genes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 526(2):368–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.03.095
Gencheva R, Arnér ESJ (2022) Thioredoxin reductase inhibition for Cancer Therapy. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 62:177–196. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-052220-102509
Hammad A, Zheng ZH, Gao Y, Namani A, Shi HF, Tang X (2019) Identification of novel Nrf2 target genes as prognostic biomarkers in colitis-associated Colorectal cancer in Nrf2-deficient mice. Life Sci 238:116968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116968
He W, Xia Y, Cao P, Hong L, Zhang T, Shen X, Zheng P, Shen H, Liang G, Zou P (2019) Curcuminoid WZ35 synergize with cisplatin by inducing ROS production and inhibiting TrxR1 activity in gastric cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38(1):207. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1215-y
Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C (2018) The biology and management of non-small cell Lung cancer. Nature 553(7689):446–454. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25183
Hui X, Cao L, Xu T, Zhao L, Huang K, Zou Z, Ren P, Mao H, Yang Y, Gao S et al (2022) PSMD12-Mediated M1 ubiquitination of Influenza A Virus at K102 regulates viral replication. J Virol 96(15):e0078622. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.00786-22
Jiang J, Huang D, Jiang Y, Hou J, Tian M, Li J, Sun L, Zhang Y, Zhang T, Li Z et al (2021) Lactate modulates Cellular Metabolism through histone lactylation-Medi ated Gene expression in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Front Oncol 11:647559. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.647559
Jin M, Wang J, Ji X, Cao H, Zhu J, Chen Y, Yang J, Zhao Z, Ren T, Xing J (2019) MCUR1 facilitates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and Metastasis via the mitochondrial calcium dependent ROS/Nrf2/Notch pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38(1):136. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1135-x
Kandolf S, Grishkovskaya I, Belacic K, Bolhuis DL, Amann S, Foster B, Imre R, Mechtler K, Schleiffer A, Tagare HD et al (2022) Cryo-EM structure of the plant 26S proteasome. Plant Commun 3(3):100310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xplc.2022.100310
Kim KC, Lee IK, Kang KA, Piao MJ, Ryu MJ, Kim JM, Lee NH, Hyun JW (2014) Triphlorethol-A from Ecklonia cava up-regulates the oxidant sensitive 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1. Mar Drugs 12(11):5357–5371. https://doi.org/10.3390/md12115357
Li Y, Sun C, Tan Y, Zhang H, Li Y, Zou H (2021) ITGB1 enhances the Radioresistance of human non-small cell Lung Cancer cells by modulating the DNA damage response and YAP1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int J Biol Sci 17(2):635–650. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.52319
Lignitto L, LeBoeuf SE, Homer H, Jiang S, Askenazi M, Karakousi TR, Pass HI, Bhutkar AJ, Tsirigos A, Ueberheide B et al (2019) Nrf2 activation promotes Lung Cancer Metastasis by inhibiting the degradation of Bach1. Cell 178(2):316–329e18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.06.003
Meador CB, Sequist LV, Piotrowska Z (2021) Targeting EGFR exon 20 insertions in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: recent advances and clinical updates. Cancer Discov 11(9):2145–2157. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-21-0226
Narayanan S, Cai CY, Assaraf YG, Guo HQ, Cui Q, Wei L, Huang JJ, Ashby CR Jr., Chen ZS (2020) Targeting the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway to overcome anti-cancer drug resistance. Drug Resist Updat 48:100663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drup.2019.100663
Onoki T, Izumi Y, Takahashi M, Murakami S, Matsumaru D, Ohta N, Wati SM, Hatanaka N, Katsuoka F, Okutsu M et al (2021) Skeletal muscle-specific Keap1 disruption modulates fatty acid utilization and enhances exercise capacity in female mice. Redox Biol 43:101966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2021.101966
Osmani L, Askin F, Gabrielson E, Li QK (2018) Current WHO guidelines and the critical role of immunohistochemical markers in the subclassification of non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC): moving from targeted therapy to immunotherapy. Semin Cancer Biol 52(Pt 1):103–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.11.019
Pan Z, Feng Y, Wang Z, Lei Z, Han Q, Zhang J (2022) MERS-CoV nsp1 impairs the cellular metabolic processes by selectively downregulating mRNAs in a novel granules. Virulence 13(1):355–369. https://doi.org/10.1080/21505594.2022.2032928
Piantadosi CA, Carraway MS, Babiker A, Suliman HB (2008) Heme oxygenase-1 regulates cardiac mitochondrial biogenesis via Nrf2-mediated transcriptional control of nuclear respiratory factor-1. Circ Res 103(11):1232–1240. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.0000338597.71702.ad
Qi J, Tang X, Li W, Chen W, Yao G, Sun L (2020) Mesenchymal stem cells inhibited the differentiation of MDSCs via COX2/PGE2 in experimental sialadenitis. Stem Cell Res Ther 11(1):325. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-020-01837-x
Rajavel T, Banu Priya G, Suryanarayanan V, Singh SK, Pandima Devi K (2019) Daucosterol disturbs redox homeostasis and elicits oxidative-stress mediated apoptosis in A549 cells via targeting thioredoxin reductase by a p53 dependent mechanism. Eur J Pharmacol 855:112–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.04.051
Remark R, Becker C, Gomez JE, Damotte D, Dieu-Nosjean MC, Sautès-Fridman C, Fridman WH, Powell CA, Altorki NK, Merad M et al (2015) The non-small cell Lung cancer immune contexture. A major determinant of Tumor characteristics and patient outcome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 191(4):377–390. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201409-1671PP
Sahebkar A, Cicero AFG, Di Giosia P, Pomilio I, Stamerra CA, Giorgini P, Ferri C, von Haehling S, Banach M, Jamialahmadi T (2020) Pathophysiological mechanisms of statin-associated myopathies: possible role of the ubiquitin-proteasome system. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 11(5):1177–1186. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12579
Skribek M, Rounis K, Tsakonas G, Ekman S (2022) Complications following novel therapies for non-small cell Lung cancer. J Intern Med 291(6):732–754. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.13445
Suzuki T, Motohashi H, Yamamoto M (2013) Toward clinical application of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway. Trends Pharmacol Sci 34(6):340–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2013.04.005
Tsakonas G, Martin-Bernabe A, Rounis K, Moreno-Ruiz P, Botling J, De Petris L, Ylipaa A, Mezheyeuski A, Micke P, Ostman A et al (2021) High density of NRF2 expression in malignant cells is Associated with increased risk of CNS Metastasis in early-stage NSCLC. Cancers (Basel) 13(13):3151. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133151
Wang Z, Li Z, Xu H, Liao Y, Sun C, Chen Y, Sheng M, Lan Q, Wang Z (2021) PSMD12 promotes glioma progression by upregulating the expression of Nrf2. Ann Transl Med 9(8):700. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm-21-1481
Wang H, Yang G, Tian Y, Li J, Meng L, Jiang X, Xin Y (2022) Sulforaphane inhibits angiotensin II-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis by acetylation modification of Nrf2. Aging 14(16):6740–6755. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.204247
Zhan Y, Xu D, Tian Y, Qu X, Sheng M, Lin Y, Ke M, Jiang L, Xia Q, Kaldas FM et al (2022) Novel role of macrophage TXNIP-mediated CYLD-NRF2-OASL1 axis in stress-induced liver inflammation and cell death. JHEP Rep 4(9):100532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhepr.2022.100532
Zhang DD, Chapman E (2020) The role of natural products in revealing NRF2 function. Nat Prod Rep 37(6):797–826. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9np00061e
Zhang HS, Zhang ZG, Du GY, Sun HL, Liu HY, Zhou Z, Gou XM, Wu XH, Yu XY, Huang YH (2019) Nrf2 promotes Breast cancer cell migration via up-regulation of G6PD/HIF-1alpha/Notch1 axis. J Cell Mol Med 23(5):3451–3463. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14241
Zhang H, Li C, Liao S, Tu Y, Sun S, Yao F, Li Z, Wang Z (2022) PSMD12 promotes the activation of the MEK-ERK pathway by upregulating KIF15 to promote the malignant progression of Liver cancer. Cancer Biol Ther 23(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2022.2125260
Zhu H, Jia Z, Trush MA, Li YR (2016) Nrf2 Deficiency promotes Melanoma Growth and Lung Metastasis. React Oxyg Species (Apex) 2(4):308–314. https://doi.org/10.20455/ros.2016.853
Funding
This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Ningxia Province (under Grant 2022AAC03352).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Author contributions
Conceptualization: all authors. Methodology: J.L. and S.M. Formal analysis and investigation: X.W. and J.D. Writing - original draft preparation: J.L. and F.M. Writing - review and editing: S.M.
Competing interest
The authors disclose no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material Table S1: Primer sequences of specific genes
Supplementary Material Table S2: Information of antibodies used for western blot analysis
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, J., Ma, S., Wang, X. et al. PSMD12 promotes non-small cell lung cancer progression through activating the Nrf2/TrxR1 pathway. Genes Genom 46, 263–277 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-023-01484-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-023-01484-5