Abstract
Background
Coptisine is a natural alkaloid compound and is known to have multiple beneficial effects including antioxidant activity. However, whether it can protect lung fibroblasts from oxidative damage has not been studied yet.
Objectives
To investigate the potential inhibitory effect of coptisine against oxidative stress in V79-4 lung fibroblast cells.
Methods
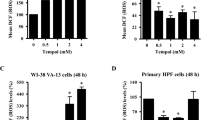
V79-4 cells were treated with H2O2 (1 mM) in the presence or absence of coptisine (50 µg/ml), N-acetyl cysteine (NAC, 10 mM) or zinc protoporphyrin IX (ZnPP, 10 µM) for the indicated times. The alleviating effects of coptisine on cytotoxicity, cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, DNA damage, mitochondrial dynamics, and inhibition of ATP production against H2O2 were investigated. Western blot analysis was used to analyze the expression levels of specific proteins.
Results
Coptisine inhibited H2O2-induced cytotoxicity and DNA damage by blocking abnormal ROS generation. H2O2 treatment caused cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase accompanied by increased expression of cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) inhibitor p21WAF1/CIP1 and decreased expression of cyclin B1 and cyclin A. However, these effects were attenuated in the presence of coptisine or NAC. Coptisine also prevented apoptosis by decreasing the rate of Bax/Bcl-2 expression in H2O2-stimulated cells and suppressing the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential and the cytosolic release of cytochrome c. In addition, the activation of nuclear factor-erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) was markedly promoted by coptisine in the presence of H2O2. However, zinc protoporphyrin IX, a potent inhibitor of HO-1, attenuated the ROS scavenging and anti-apoptotic effects of coptisine.
Conclusions
Based on current data, we suggest that coptisine can be used as a potential treatment for oxidative stress-related lung disease.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aristizabal-Pachon AF, Castillo WO (2019) Genotoxic evaluation of occupational exposure to antineoplastic drugs. Toxicol Res 36:29–36
Ballester B, Milara J, Cortijo J (2019) Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and lung cancer: Mechanisms and molecular targets. Int J Mol Sci 20:E593
Bock FJ, Tait SWG (2020) Mitochondria as multifaceted regulators of cell death. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 21:85–100
Bonelli M, Savitskaya A, Steiner CW, Rath E, Bilban M, Wagner O, Bach FH, Smolen JS, Scheinecker C (2012) Heme oxygenase-1 end-products carbon monoxide and biliverdin ameliorate murine collagen induced arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 30:73–78
Cameli P, Carleo A, Bergantini L, Landi C, Prasse A, Bargagli E (2020) Oxidant/antioxidant disequilibrium in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis pathogenesis. Inflammation 43:1–7
Chanda D, Otoupalova E, Smith SR, Volckaert T, De Langhe SP, Thannickal VJ (2019) Developmental pathways in the pathogenesis of lung fibrosis. Mol Aspects Med 65:56–69
Chen HB, Luo CD, Liang JL, Zhang ZB, Lin GS, Wu JZ, Li CL, Tan LH, Yang XB, Su ZR, Xie JH, Zeng HF (2017) Anti-inflammatory activity of coptisine free base in mice through inhibition of NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Eur J Pharmacol 811:222–231
Choi YH (2019) Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway contributes to the protective effects of coptisine against oxidative stress-induced DNA damage and apoptosis in HaCaT keratinocytes. Gen Physiol Biophys 38:281–294
Choi YH (2020) Trans-cinnamaldehyde protects C2C12 myoblasts from DNA damage, mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis caused by oxidative stress through inhibiting ROS production. Genes Genomics 2020 Aug 27. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-020-00987-9
Ding Y, Zhang Z, Yue Z, Ding L, Zhou Y, Huang Z, Huang H (2019) Rosmarinic acid ameliorates H2O2-induced oxidative stress in L02 cells through MAPK and Nrf2 pathways. Rejuvenation Res 22:289–298
Dutto I, Tillhon M, Cazzalini O, Stivala LA, Prosperi E (2015) Biology of the cell cycle inhibitor p21(CDKN1A): molecular mechanisms and relevance in chemical toxicology. Arch Toxicol 89:155–178
Fetoni AR, Paciello F, Rolesi R, Paludetti G, Troiani D (2019) Targeting dysregulation of redox homeostasis in noise-induced hearing loss: Oxidative stress and ROS signaling. Free Radic Biol Med 135:46–59
He K, Kou S, Zou Z, Hu Y, Feng M, Han B, Li X, Ye X (2016) Hypolipidemic effects of alkaloids from Rhizoma Coptidis in diet-induced hyperlipidemic hamsters. Planta Med 82:690–697
Hu Y, Wang L, Xiang L, Wu J, Huang W, Xu C, Meng X, Wang P (2019) Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling for coptisine challenge of inflammation in LPS-stimulated rats. Sci Rep 9:1450
Hu YR, Ma H, Zou ZY, He K, Xiao YB, Wang Y, Feng M, Ye XL, Li XG (2017) Activation of Akt and JNK/Nrf2/NQO1 pathway contributes to the protective effect of coptisine against AAPH-induced oxidative stress. Biomed Pharmacother 85:313–322
Huang T, Xiao Y, Yi L, Li L, Wang M, Tian C, Ma H, He K, Wang Y, Han B, Ye X, Li X (2017) Coptisine from Rhizoma Coptidis suppresses HCT-116 cells-related tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Sci Rep 7:38524
Hwangbo H, Kim SY, Lee H, Park SH, Hong SH, Park C, Kim GY, Leem SH, Hyun JW, Cheong J, Choi YH (2020) Auranofin enhances sulforaphane-mediated apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cells through inactivation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Biomol Ther (Seoul) 28:443–455
Kang KA, Lee KH, Chae S, Zhang R, Jung MS, Kim SY, Kim HS, Kim DH, Hyun JW (2005) Cytoprotective effect of tectorigenin, a metabolite formed by transformation of tectoridin by intestinal microflora, on oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide. Eur J Pharmacol 519:16–23
Karimian A, Ahmadi Y, Yousefi B (2016) Multiple functions of p21 in cell cycle, apoptosis and transcriptional regulation after DNA damage. DNA Repair 42:63–71
Kim DY, Kim JH, Lee JC, Won MH, Yang SR, Kim HC, Wie MB (2019b) Zinc oxide nanoparticles exhibit both cyclooxygenase- and lipoxygenase-mediated apoptosis in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Toxicol Res 35:83–91
Kim JS, Cho IA, Kang KR, Lim H, Kim TH, Yu SK, Kim HJ, Lee SA, Moon SM, Chun HS, Kim CS, Kim DK (2019) Reversine induces caspase-dependent apoptosis of human osteosarcoma cells through extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathways. Genes Genom 41:657–665
Kim JS, Cho IA, Kang KR, Lim H, Kim TH, Yu SK, Kim HJ, Lee SA, Moon SM, Chun HS, Kim CS, Kim DK (2019) Reversine induces caspase-dependent apoptosis of human osteosarcoma cells through extrinsic and intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathways. Genes Genom 41:657–665
Kim SY, Jo HY, Kim MH, Cha YY, Choi SW, Shim JH, Kim TJ, Lee KY (2008) H2O2-dependent hyperoxidation of peroxiredoxin 6 (Prdx6) plays a role in cellular toxicity via up-regulation of iPLA2 activity. J Biol Chem 283:33563–33568
Kiraz Y, Adan A, KartalYandim M, Baran Y (2016) Major apoptotic mechanisms and genes involved in apoptosis. Tumour Biol 37:8471–8486
Kwon OJ, Kim MY, Shin SH, Lee AR, Lee JY, Seo BI, Shin MR, Choi HG, Kim JA, Min BS, Kim GN, Noh JS, Rhee MH, Roh SS (2016) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of Rhei Rhizoma and Coptidis Rhizoma mixture on reflux esophagitis in rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2016:2052180
Larson-Casey JL, He C, Carter AB (2020) Mitochondrial quality control in pulmonary fibrosis. Redox Biol 8:101426
Lee MH, Cha HJ, Choi EO, Han MH, Kim SO, Kim GY, Hong SH, Park C, Moon SK, Jeong SJ, Jeong MJ, Kim WJ, Choi YH (2017) Antioxidant and cytoprotective effects of morin against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress are associated with the induction of Nrf-2mediated HO-1 expression in V79-4 Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts. Int J Mol Med 39:672–680
Lin Y, Guo HC, Kuang Y, Shang ZP, Li B, Chen K, Xu LL, Qiao X, Liang H, Ye M (2020) AChE inhibitory alkaloids from Coptis chinensis. Fitoterapia 141:104464
Liu H, Liu W, Zhou X, Long C, Kuang X, Hu J, Tang Y, Liu L, He J, Huang Z, Fan Y, Jin G, Zhang Q, Shen H (2017) Protective effect of lutein on ARPE-19 cells upon H2O2-induced G2/M arrest. Mol Med Rep 16:2069–2074
Luo C, Chen H, Wang Y, Lin G, Li C, Tan L, Su Z, Lai X, Xie J, Zeng H (2018) Protective effect of coptisine free base on indomethacin-induced gastric ulcers in rats: Characterization of potential molecular mechanisms. Life Sci 193:47–56
Lv M, Liu Y, Ma S, Yu Z (2019) Current advances in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: the pathogenesis, therapeutic strategies and candidate molecules. Fut Med Chem 11:2595–2620
Meng FC, Wu ZF, Yin ZQ, Lin LG, Wang R, Zhang QW (2018) Coptidis rhizoma and its main bioactive components: recent advances in chemical investigation, quality evaluation and pharmacological activity. Chin Med 13:13
Park C, Lee H, Noh JS, Jin CY, Kim GY, Hyun JW, Leem SH, Choi YH (2020) Hemistepsin A protects human keratinocytes against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress through activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys 691:108512
Pei XH, Xiong Y (2005) Biochemical and cellular mechanisms of mammalian CDK inhibitors: a few unresolved issues. Oncogene 24:2787–2795
Popgeorgiev N, Jabbour L, Gillet G (2018) Subcellular localization and dynamics of the Bcl-2 family of proteins. Front Cell Dev Biol 6:13
Rao PC, Begum S, Sahai M, Sriram DS (2017) Coptisine-induced cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase and reactive oxygen species-dependent mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in non-small-cell lung cancer A549 cells. Tumour Biol 39:1010428317694565
Seomun Y, Kim JT, Kim HS, Park JY, Joo CK (2005) Induction of p21Cip1-mediated G2/M arrest in H2O2-treated lens epithelial cells. Mol Vis 11:764–774
Shaw P, Chattopadhyay A (2020) Nrf2-ARE signaling in cellular protection: Mechanism of action and the regulatory mechanisms. J Cell Physiol 235:3119–3130
Swanton C (2004) Cell-cycle targeted therapies. Lancet Oncol 5:27–36
Villota C, Varas-Godoy M, Jeldes E, Campos A, Villegas J, Borgna V, Burzio LO. Burzio VA (2018) HPV-18 E2 protein downregulates antisense noncoding mitochondrial RNA-2, delaying replicative senescence of human keratinocytes. Aging 11:33–47
Wang J, Ran Q, Zeng HR, Wang L, Hu CJ, Huang QW (2018) Cellular stress response mechanisms of Rhizoma coptidis: a systematic review. Chin Med 13:27
Wang J, Wang L, Lou GH, Zeng HR, Hu J, Huang QW, Peng W, Yang XB (2019) Coptidis Rhizoma: a comprehensive review of its traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology. Pharm Biol 57:193–225
Wang Y (2008) Bulky DNA lesions induced by reactive oxygen species. Chem Res Toxicol 21:276–281
Wang Y, Wang Q, Zhang L, Ke Z, Zhao Y, Wang D, Chen H, Jiang X, Gu M, Fan S, Huang C (2017) Coptisine protects cardiomyocyte against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced damage via inhibition of autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 490:231–238
Wu J, Luo Y, Deng D, Su S, Li S, Xiang L, Hu Y, Wang P, Meng X (2019) Coptisine from Coptis chinensis exerts diverse beneficial properties: a concise review. J Cell Mol Med 23:7946–7960
Xiong S, Mu T, Wang G, Jiang X (2014) Mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in mammals. Protein Cell 5:737–749
Xu Z, Feng W, Shen Q, Yu N, Yu K, Wang S, Chen Z, Shioda S, Guo Y (2017) Rhizomacoptidis and berberine as a natural drug to combat aging and aging-related diseases via anti-oxidation and AMPK activation. Aging Dis 8:760–777
Yang DX, Qiu J, Zhou HH, Yu Y, Zhou DL, Xu Y, Zhu MZ, Ge XP, Li JM, Lv CJ, Zhang HQ, Yuan WD (2018) Dihydroartemisinin alleviates oxidative stress in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Life Sci 205:176–183
Yu Y, Cui Y, Niedernhofer LJ, Wang Y (2016) Occurrence, biological consequences, and human health relevance of oxidative stress-induced DNA damage. Chem Res Toxicol 29:2008–2039
Yu ZY, Ma D, He ZC, Liu P, Huang J, Fang Q, Zhao JY, Wang JS (2018) Heme oxygenase-1 protects bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from iron overload through decreasing reactive oxygen species and promoting IL-10 generation. Exp Cell Res 362:28–42
Zhai J, Li Z, Zhang H, Ma L, Ma Z, Zhang Y, Zou J, Li M, Ma L, Li X (2020) Coptisine ameliorates renal injury in diabetic rats through the activation of Nrf2 signaling pathway. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 393:57–65
Zhang L, Zhang J, Ye Z, Manevich Y, Ball LE, Bethard JR, Jiang YL, Broome AM, Dalton AC, Wang GY, Townsend DM, Tew KD (2019) Isoflavone ME-344 disrupts redox homeostasis and mitochondrial function by targeting heme oxygenase 1. Cancer Res 79:4072–4085
Zhang YL, Zhang X, Miao XZ, Yuan YY, Gao J, Li X, Liu YG, Tan P (2019a) Coptisine suppresses proliferation and inhibits metastasis in human pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells. J Asian Nat Prod Res 23:1–12
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (2019R1F1A105809412).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H-GJ, YHC and SHH designed the research; H-GJ, CP, HL, G-YK, SHC, JWH. KTK and Y-SK conducted the experiments, interpreted the results. YHC and SHH wrote and finalized the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jo, HG., Park, C., Lee, H. et al. Inhibition of oxidative stress induced-cytotoxicity by coptisine in V79-4 Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts through the induction of Nrf-2 mediated HO-1 expression. Genes Genom 43, 17–31 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-020-01018-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-020-01018-3