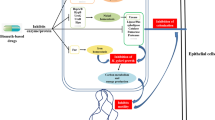
Abstract
Background
Helicobacter pylori is the most highlighted pathogen across the globe especially in developing countries. Severe gastric problems like ulcers, cancers are associated with H. pylori and its prevalence is widespread. Evolution in the genome and cross-resistance with different antibiotics are the major reason of its survival and pandemic resistance against current regimens.
Objectives
To prioritize potential drug target against H. pylori by comparing metabolic pathways of its available strains.
Methods
We used various computational tools to extract metabolic sets of all available (61) strains of H. pylori and performed pan genomics and subtractive genomics analysis to prioritize potential drug target. Additionally, the protein interaction and detailed structure-based studies were performed for further characterization of protein.
Results
We found 41 strains showing similar set of metabolic pathways. However, 19 strains were found with unique set of metabolic pathways. The metabolic set of these 19 strains revealed 83 unique proteins and BLAST against human proteome further funneled them to 38 non-homologous proteins. The druggability and essentiality testing further converged our findings to a single unique protein as a potential drug target against H. pylori.
Conclusion
We prioritized one protein-based drug target which upon subject to applied protocol was found as close homolog of the Saccharopine dehydrogenase. Our study has opened further avenues of research regarding the discovery of new drug targets against H. pylori.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arruda P, Neshich IP (2012) Nutritional-rich and stress-tolerant crops by saccharopine pathway manipulation. Food Energy Secur 1(2):141–147
Bastos J, Peleteiro B, Barros R, Alves L, Severo M, de Fátima Pina M, Pinto H, Carvalho S, Marinho A, Guimarães JT (2013) Sociodemographic determinants of prevalence and incidence of Helicobacter pylori infection in Portuguese adults. Helicobacter 18(6):413–422
Bruce MG, Maaroos HI (2008) Epidemiology of Helicobacter pylori infection. Helicobacter 13:1–6
Cakouros D, Mills K, Denton D, Paterson A, Daish T, Kumar S (2008) dLKR/SDH regulates hormone-mediated histone arginine methylation and transcription of cell death genes. J Cell Biol 182(3):481–495
Camacho C, Coulouris G, Avagyan V, Ma N, Papadopoulos J, Bealer K, Madden TL (2009) BLAST+ : architecture and applications. BMC Bioinformatics 10(1):421. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-10-421
Dooley CP, Cohen H, Fitzgibbons PL, Bauer M, Appleman MD, Perez-Perez GI, Blaser MJ (1989) Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection and histologic gastritis in asymptomatic persons. N Engl J Med 321(23):1562–1566. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm198912073212302
Eisenberg D, Lüthy R, Bowie JU (1997) VERIFY3D: assessment of protein models with three-dimensional profiles. Methods Enzymol 277:396–404
Fan X, Gunasena H, Cheng Z, Espejo R, Crowe SE, Ernst PB, Reyes VE (2000) Helicobacter pylori urease binds to class II MHC on gastric epithelial cells and induces their apoptosis. J Immunol 165(4):1918–1924
Garg VK, Avashthi H, Tiwari A, Jain PA, Ramkete PW, Kayastha AM, Singh VK (2016) MFPPI–Multi FASTA ProtParam Interface. Bioinformation 12(2):74
Gerhard MHS, Wadstrom T et al (2001) Helicobacter pylori, an adherent pain in the stomach. Helicobacter pylori: molecular and cellular biology. Horizon Scientific Press, Wymondham
Hartmann M, Zeier J (2018) l-lysine metabolism to N-hydroxypipecolic acid: an integral immune-activating pathway in plants. Plant J 96(1):5–21
Hodos RA, Kidd BA, Shameer K, Readhead BP, Dudley JT (2016) In silico methods for drug repurposing and pharmacology. WIREs Syst Biol Med 8(3):186–210
Jones P, Binns D, Chang H-Y, Fraser M, Li W, McAnulla C, McWilliam H, Maslen J, Mitchell A, Nuka G (2014) InterProScan 5: genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 30(9):1236–1240
Josenhans C, Suerbaum S (2002) The role of motility as a virulence factor in bacteria. Int J Med Microbiol 291(8):605–614. https://doi.org/10.1078/1438-4221-00173
Kanehisa M, Furumichi M, Tanabe M, Sato Y, Morishima K (2016) KEGG: new perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res 45(D1):D353–D361. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1092
Karttunen RA, Karttunen TJ, Yousfi MM, El-Zimaity HMT, Graham DY, El-Zaatari FAK (1997) Expression of mRNA for Interferon-Gamma, Interleukin-10, and Interleukin-12 (p40) in normal gastric mucosa and in mucosa infected with Helicobacter pylori. Scand J Gastroenterol 32(1):22–27. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365529709025058
Konc J, Janežič D (2010) ProBiS algorithm for detection of structurally similar protein binding sites by local structural alignment. Bioinformatics 26(9):1160–1168
Kusters JG, van Vliet AHM, Kuipers EJ (2006) Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori infection. Clin Microbiol Rev 19(3):449–490. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00054-05
Li YH, Xu JY, Tao L, Li XF, Li S, Zeng X, Chen SY, Zhang P, Qin C, Zhang C, Chen Z, Zhu F, Chen YZ (2016) SVM-Prot 2016: a web-server for machine learning prediction of protein functional families from sequence irrespective of similarity. PLoS One 11(8):e0155290. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0155290
Luo H, Lin Y, Gao F, Zhang C-T, Zhang R (2014) DEG 10, an update of the database of essential genes that includes both protein-coding genes and noncoding genomic elements. Nucleic Acids Res 42(Database issue):D574–D580. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1131
Malfertheiner P, Megraud F, O’morain C, Gisbert J, Kuipers E, Axon A, Bazzoli F, Gasbarrini A, Atherton J, Graham DY (2017) Management of Helicobacter pylori infection—the Maastricht V/Florence consensus report. Gut 66(1):6–30
McGuffin LJ, Bryson K, Jones DT (2000) The PSIPRED protein structure prediction server. Bioinformatics 16(4):404–405
Neshich IA, Kiyota E, Arruda P (2013) Genome-wide analysis of lysine catabolism in bacteria reveals new connections with osmotic stress resistance. ISME J 7(12):2400
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE (2004) UCSF Chimera—a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25(13):1605–1612
Šali A, Webb B, Madhusudhan M, Shen M-Y, Dong G, Martı-Renom MA, Eswar N, Alber F, Topf M, Oliva B (2014) Azat Badretdinov, Francisco Melo, John P. Overington, and Eric Feyfant email: modeller-care AT salilab.org http://salilab.org/modeller
Saracino I, Zaccaro C, Re G, Vaira D, Holton J (2013) The effects of two novel copper-based formulations on Helicobacter pylori. Antibiotics 2(2):265–273
Satoshi S, Akihiro T, Shigeyoshi I, Hideyuki K, Shoji M, Yoichiro I, Yoshio Y, Hiroyoshi O, Toshiro Y, Jiro I, Masakazu K (2008) IL-17 is involved in Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric inflammatory responses in a mouse model. Helicobacter 13(6):518–524. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-5378.2008.00629.x
Savoldi A, Carrara E, Graham DY, Conti M, Tacconelli E (2018) Prevalence of antibiotic resistance in Helicobacter pylori: a systematic review and meta-analysis in World Health Organization regions. Gastroenterology 155(5):1372–1382, e1317
Si X, Lan Y, Qiao L (2017) A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of bismuth-containing quadruple therapy combined with probiotic supplement for eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 56(10):752–759
Sievers F, Higgins DG (2014) Clustal Omega, accurate alignment of very large numbers of sequences. Multiple sequence alignment methods. Springer, Berlin, pp 105–116
Solnick JV, Schauer DB (2001) Emergence of diverse helicobacterspecies in the pathogenesis of gastric and enterohepatic diseases. Clin Microbiol Rev 14(1):59–97
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Lyon D, Junge A, Wyder S, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Bork P, Jensen LJ, Mering CV (2019) STRING v11: protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res 47(D1):D607–D613. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1131
Thung I, Aramin H, Vavinskaya V, Gupta S, Park JY, Crowe SE, Valasek MA (2016) Review article: the global emergence of Helicobacter pylori antibiotic resistance. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 43(4):514–533. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.13497
Tickle IJ, Laskowski RA, Moss DS (1998) Error estimates of protein structure coordinates and deviations from standard geometry by full-matrix refinement of γB-and βB2-crystallin. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 54(2):243–252
Tursi A, Di Mario F, Franceschi M, De Bastiani R, Elisei W, Baldassarre G, Ferronato A, Grillo S, Landi S, Zamparella M (2017) New bismuth-containing quadruple therapy in patients infected with Helicobacter pylori: a first Italian experience in clinical practice. Helicobacter 22(3):e12371
Uddin R, Rafi S (2017) Structural and functional characterization of a unique hypothetical protein (WP_003901628. 1) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: a computational approach. Med Chem Res 26(5):1029–1041
Uddin R, Saeed K (2014) Identification and characterization of potential drug targets by subtractive genome analyses of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Comput Biol Chem 48:55–63
Uddin R, Sufian M (2016) Core proteomic analysis of unique metabolic pathways of Salmonella enterica for the identification of potential drug targets. PLoS One 11(1):e0146796
Uddin R, Saeed K, Khan W, Azam SS, Wadood A (2015) Metabolic pathway analysis approach: identification of novel therapeutic target against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Gene 556(2):213–226
Uddin R, Siddiqui QN, Sufian M, Azam SS, Wadood A (2019) Proteome-wide subtractive approach to prioritize a hypothetical protein of XDR-Mycobacterium tuberculosis as potential drug target. Genes Genom 2019:1–12
Volkamer A, Kuhn D, Rippmann F, Rarey M (2012) DoGSiteScorer: a web server for automatic binding site prediction, analysis and druggability assessment. Bioinformatics 28(15):2074–2075
Wadood A, Jamal A, Riaz M, Khan A, Uddin R, Jelani M, Azam SS (2018) Subtractive genome analysis for in silico identification and characterization of novel drug targets in Streptococcus pneumonia strain JJA. Microb Pathog 115:194–198
Wang L, Lin Z, Chen S, Li J, Chen C, Huang Z, Ye B, Ding J, Li W, Wu L (2017) Ten-day bismuth-containing quadruple therapy is effective as first-line therapy for Helicobacter pylori–related chronic gastritis: a prospective randomized study in China. Clin Microbiol Infect 23(6):391–395
Waterhouse AM, Procter JB, Martin DM, Clamp M, Barton GJ (2009) Jalview Version 2—a multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 25(9):1189–1191
Yu NY, Wagner JR, Laird MR, Melli G, Rey S, Lo R, Dao P, Sahinalp SC, Ester M, Foster LJ, Brinkman FSL (2010) PSORTb 3.0: improved protein subcellular localization prediction with refined localization subcategories and predictive capabilities for all prokaryotes. Bioinformatics 26(13):1608–1615. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btq249
Zakharova N, Paster BJ, Wesley I, Dewhirst FE, Berg DE, Severinov KV (1999) Fused and overlapping rpoB and rpoC genes in Helicobacters, Campylobacters, and related bacteria. J Bacteriol 181(12):3857–3859
Zamani M, Ebrahimtabar F, Zamani V, Miller WH, Alizadeh-Navaei R, Shokri-Shirvani J, Derakhshan MH (2018) Systematic review with meta-analysis: the worldwide prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 47(7):868–876. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.14561
Zhang M, Luo H, Xi Z, Rogaeva E (2015) Drug repositioning for diabetes based on’omics’ data mining. PLoS One 10(5):e0126082
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the funds provided by the Pakistan Science Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uddin, R., Khalil, W. A comparative proteomic approach using metabolic pathways for the identification of potential drug targets against Helicobacter pylori. Genes Genom 42, 519–541 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-020-00921-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-020-00921-z