Abstract
Background
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is known as an inflammatory disease. NRF2 (Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2 Like2) encodes a transcription factor that binds to antioxidant response elements (AREs) and regulates the expression of genes involved in many antioxidant responses.
Objective
This study aimed to gain insight into individual anti-inflammatory activity to prevent T2D development in humans.
Methods
We performed a genome-wide association study (GWAS) to identify genetic variants influencing NRF2 expression in LCLs (lymphoblastoid cell lines) generated from 74 different individuals. Association analyses between T2D or its related traits and genetic risk score (GRS) calculated by combining genetic variants detected from GWAS for cellular NRF2 expression were performed using data from 8715 subjects. The T2D prediction model using GRS was evaluated by measuring the area under the curve (AUC) of the receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve.
Results
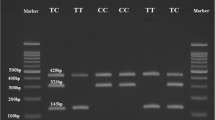
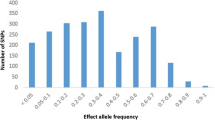
Our GWAS identified six genetic variants (SNP) showing suggestive evidence of associations with cellular NRF2 expression (P < 10− 6). Logistic regression analysis demonstrated that GRS was associated with an increased risk of T2D (P value = 0.003, OR = 1.13). In addition, linear regression analyses showed positive associations between GRS and fasting glucose (P value = 0.028, β = 0.62), 2-h glucose (P value = 0.0004, β = 1.13) and HbA1C (P value = 0.033, β = 0.03). In the T2D prediction model using GRS, the AUC of the ROC curve was 0.69.
Conclusion
This study highlights genetic variants associated with cellular NRF2 expression and suggests that the GRS of NRF2 expression-associated variants is likely to be a useful indicator of T2D development in the human population.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alberti KG, Zimmet PZ (1998) Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med 15:539–553
Alfieri C, Birkenbach M, Kieff E (1991) Early events in Epstein-Barr virus infection of human B lymphocytes. Virology 181:595–608
Asif M (2014) The prevention and control the type-2 diabetes by changing lifestyle and dietary pattern. J Educ Health Promot 3:1
Barry JC, Shakibakho S, Durrer C, Simtchouk S, Jawanda KK, Cheung ST, Mui AL, Little JP (2016) Hyporesponsiveness to the anti-inflammatory action of interleukin-10 in type 2 diabetes. Sci Rep 6:21244
Chen L, Magliano DJ, Zimmet PZ (2011) The worldwide epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus–present and future perspectives. Nat Rev Endocrinol 8:228–236
Cho YS, Go MJ, Kim YJ, Heo JY, Oh JH, Ban HJ, Yoon D, Lee MH, Kim DJ, Park M et al (2009) A large-scale genome-wide association study of Asian populations uncovers genetic factors influencing eight quantitative traits. Nat Genet 41:527–534
Deshmukh P, Unni S, Krishnappa G, Padmanabhan B (2017) The Keap1-Nrf2 pathway: promising therapeutic target to counteract ROS-mediated damage in cancers and neurodegenerative diseases. Biophys Rev 9:41–56
Donath MY, Shoelson SE (2011) Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Immunol 11:98–107
Dorus S, Gilbert SL, Forster ML, Barndt RJ, Lahn BT (2003) The CDY-related gene family: coordinated evolution in copy number, expression profile and protein sequence. Hum Mol Genet 12:1643–1650
Evans JL, Goldfine ID, Maddux BA, Grodsky GM (2003) Are oxidative stress-activated signaling pathways mediators of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction? Diabetes 52:1–8
Gambrill AC, Storey GP, Barria A (2011) Dynamic regulation of NMDA receptor transmission. J Neurophysiol 105:162–171
Grassi MA, Rao VR, Chen S, Cao D, Gao X, Cleary PA, Huang RS, Paterson AD, Natarajan R, Rehman J et al (2016) Lymphoblastoid cell lines as a tool to study inter-individual differences in the response to glucose. PLoS One 11:e0160504
Guariguata L, Whiting DR, Hambleton I, Beagley J, Linnenkamp U, Shaw JE (2014) Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2013 and projections for 2035. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 103:137–149
Hussain T, Mulherkar R (2012) Lymphoblastoid cell lines: a continuous in vitro source of cells to study carcinogen sensitivity and DNA repair. Int J Mol Cell Med 1:75–87
Kalra M, Gerdemann U, Luu JD, Ngo MC, Leen AM, Louis CU, Rooney CM, Gottschalk S (2018) Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)-derived BARF1 encodes CD4- and CD8-restricted epitopes as targets for T-cellimmunotherapy. Cytotherapy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcyt.2018.08.001
Kim YJ, Go MJ, Hu C, Hong CB, Kim YK, Lee JY, Hwang JY, Oh JH, Kim DJ, Kim NH et al (2011) Large-scale genome-wide association studies in East Asians identify new genetic loci influencing metabolic traits. Nat Genet 43:990–995
Krajka-Kuzniak V, Paluszczak J, Baer-Dubowska W (2017) The Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway: an update on its regulation and possible role in cancer prevention and treatment. Pharmacol Rep 69:393–402
Lahn BT, Tang ZL, Zhou J, Barndt RJ, Parvinen M, Allis CD, Page DC (2002) Previously uncharacterized histone acetyltransferases implicated in mammalian spermatogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:8707–8712
Martindale JL, Holbrook NJ (2002) Cellular response to oxidative stress: signaling for suicide and survival. J Cell Physiol 192:1–15
Mazella J, Beraud-Dufour S, Devader C, Massa F, Coppola T (2012) Neurotensin and its receptors in the control of glucose homeostasis. Front Endocrinol 3:143 (Lausanne)
Mittal M, Siddiqui MR, Tran K, Reddy SP, Malik AB (2014) Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue injury. Antioxid Redox Signal 20:1126–1167
Prasad RB, Groop L (2015) Genetics of type 2 diabetes-pitfalls and possibilities. Genes 6:87–123 (Basel)
Ramachandran A, Snehalatha C, Shetty AS, Nanditha A (2012) Trends in prevalence of diabetes in Asian countries. World J Diabetes 3:110–117
St-Gelais F, Jomphe C, Trudeau LE (2006) The role of neurotensin in central nervous system pathophysiology: what is the evidence? J Psychiatry Neurosci 31:229–245
Taguchi K, Motohashi H, Yamamoto M (2011) Molecular mechanisms of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway in stress response and cancer evolution. Genes Cells 16:123–140
Wieser R, Wrana JL, Massague J (1995) GS domain mutations that constitutively activate T beta R-I, the downstream signaling component in the TGF-beta receptor complex. EMBO J 14:2199–2208
Wong J, Tabet E (2015) The introduction of insulin in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Aust Fam Physician 44:278–283
Yun JH, Park YG, Lee KM, Kim J, Nho CW (2015) Curcumin induces apoptotic cell death via Oct4 inhibition and GSK-3beta activation in NCCIT cells. Mol Nutr Food Res 59:1053–1062
Zhang T, Zhou Y, Qi ST, Wang ZB, Qian WP, Ouyang YC, Shen W, Schatten H, Sun QY (2015) Nuf2 is required for chromosome segregation during mouse oocyte meiotic maturation. Cell Cycle 14:2701–2710
Zou X, Shen J, Chen F, Ting K, Zheng Z, Pang S, Zara JN, Adams JS, Soo C, Zhang X (2011) NELL-1 binds to APR3 affecting human osteoblast proliferation and differentiation. FEBS Lett 585:2410–2418
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (NRF-2017R1A2B4006508) and Hallym University Research Fund 2017 (HRF-201712-005). The authors appreciate the bioresources that were provided for this study from the National Bank of Korea, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Republic of Korea (4845-301, 4851-302 and 307).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study design: YSC, CWN. Data analysis and interpretation: JHS, K-ML, JS, KDK, CWN, YSC. Manuscript writing and revision: JHS, YSC. Figure production: JHS. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Jae Hun Shin, Kyung-Mi Lee, Chu Won Nho, Yoon Shin Cho declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Hallym University Institutional Review Board (HIRB-2017-030).
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, J.H., Lee, KM., Shin, J. et al. Genetic risk score combining six genetic variants associated with the cellular NRF2 expression levels correlates with Type 2 diabetes in the human population. Genes Genom 41, 537–545 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-019-00791-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-019-00791-0