Abstract
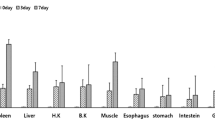
Although Streptococcus parauberis is the major bacterial pathogen affecting olive flounder, the translocation and dissemination of this pathogen in infected fish are not well understood. Therefore, we conducted real-time PCR and histopathologic examination to monitor the intensity of infection in multiple organs of the olive flounder after challenge with S. parauberis through subcutaneous injection. The bacterial burden in the fish kidney, when sampled at 0, 3, and 7 dpc, was 0, 6.2 ± 4.5 × 105, and 6.7 ± 5.5 × 106 CFU/100 mg of tissue, respectively, indicating that the infection progressed rapidly over time. Of the ten different tissues sampled, the heart and the brain were the major target organs of S. parauberis based on highest copy number as detected by our modified real-time PCR method. Histopathologic examination also showed that S. parauberis caused severe inflammation accompanied by leucocyte infiltration, connective tissue expansion, and a loss of cardiomyocytes in the brain and heart of fish sampled at dpc 7. However, the number of S. parauberis-positive fish at 3 dpc was much higher in the spleen (6/8 fish) than in the remaining organs, suggesting that the spleen is targeted in the early stages of infection relative to the heart (2/8 fish) or brain (3/8 fish). This study provides essential information for studies to find treatments for the effective elimination of S. parauberis in target organs (i.e., the brain and heart) of olive flounder.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baeck GW, Kim JH, Gomez DK, Park SC (2006) Isolation and characterization of Streptococcus sp. from diseased flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus) in Jeju Island. J Vet Sci 7:53–58
Bowater RO, Forbes-Faulkner J, Anderson IG, Condon K, Robinson B, Kong F, Gilbert GL, Reynolds A, Hyland S, McPherson G et al (2012) Natural outbreak of Streptococcus agalactiae (GBS) infection in wild giant Queensland grouper, Epinephelus lanceolatus (Bloch), and other wild fish in northern Queensland, Australia. J Fish Dis 35:173–186
Chen DF, Wang KY, Geng Y, Wang J, Huang XL, He M (2011) Pathological changes in cultured channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus spontaneously infected with Streptococcus iniae. Dis Aquat Organ 95:203–208
Choi HJ, Cho MY, Lee JI, Kwon MG, Choi DL, Kim JW, M.C. H, Lee DC (2009) The pathogenicity of Streptococcus parauberis isolated from cultured olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. J Fish Pathol 22:263–273
Domeénech A, Fernandez-Garayzabal JF, Pascual C, Garcia JA, Cutuli MT, Moreno MA, Collins MD, Dominguez L (1996) Streptococcosis in cultured turbot Scophthalmus maxiums (L.), associated with Streptococcus parauberis. J Fish Dis 19:33–38
Han HJ, Jung SJ, Oh MJ, Kim DH (2011) Rapid and sensitive detection of Streptococcus iniae by loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP). J Fish Dis 34:395–398
Hwang SD, Woo SH, Kim SH, Ha SJ, Jung YE, Park SI (2008) Immunomodulatory characteristics of Streptococcus parauberis isolated from infected olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. J Fish Pathol 21:157–166
Kanai K, Yamada M, Meng F, Takahashi I, Nagano T, Kawakami H, Yamashita A, Matsuoka S, Fukuda Y, Miyoshi Y et al (2009) Serological differentiation of Streptococcus parauberis strains isolated from cultured Japanese flounder in Japan. Fish Pathol 44:33–39
Kim JH, Kim E (2003) Diversity of the streptococcal strains isolated from diseased olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). J Korean Fish Soc 36:654–660
Kim JH, Gomez DK, Baeck GW, Shin GW, Heo GJ, Jung TS, Park SC (2006) Pathogenicity of Streptococcus parauberis to olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish Pathol 41:171–173
Mata AI, Gibello A, Casamayor A, Blanco MM, Domínguez L, Fernández-Garayzábal JF (2004) Multiplex PCR assay for detection of bacterial pathogens associated with warm-water streptococcosis in fish. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:3183–3187
Mori K, Fukuda Y, Togo A, Miyoshi Y, Endo M (2010) Practical inoculation site for experimental infection of Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus with Streptococcus parauberis. Fish Pathol 45:37–42
Nguyen TL, Lim YJ, Kim DH, Austin B (2016) Development of real-time PCR for detection and quantitation of Streptococcus parauberis. J Fish Dis 39:31–39
Park SB, Kwon K, Cha IS, Jang HB, Nho SW, Fagutao FF, Kim YK, Yu JE, Jung TS (2014) Development of a multiplex PCR assay to detect Edwardsiella tarda, Streptococcus parauberis, and Streptococcus iniae in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). J Vet Sci 15:163–166
Shutou K, Kanai K, Yoshikoshi K (2007) Role of capsule in immunogenicity of Streptococcus iniae to Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish Pathol 42:101–106
Won KM, Cho MY, Park MA, Kim KH, Park SI, Lee DC, M.G. K, Kim JW (2010) Pathological characteristics of olive flounder Paralichthys olivaceus experimentally infected with Streptococcus parauberis. Fish Sci 76:991–998
Woo SH, Kim HJ, Lee JS, Kim JW, Park SI (2006) Pathogenicity and classification of streptococci isolated from cultured marine fishes. J Fish Pathol 19:17–33
Zamri-Saad M, Amal MN, Siti-Zahrah A (2010) Pathological changes in red tilapias (Oreochromis spp.) naturally infected by Streptococcus agalactiae. J Comp Pathol 143:227–229
Zhang T, Fang HH (2006) Applications of real-time polymerase chain reaction for quantification of microorganisms in environmental samples. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 70:281–289
Acknowledgements
This research was a part of the project titled ‘Omics based on fishery disease control technology development and industrialization (20150242)’, funded by the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Hyunsu Kim declares that he has no conflict of interest. Ahran Kim declares that he has no conflict of interest. Sun Mi Kim declares that he has no conflict of interest. Thanh Luan Nguyen declares that he has no conflict of interest. Yunjin Lim declares that he has no conflict of interest. Heyong Jin Roh declares that he has no conflict of interest. Nameun Kim declares that he has no conflict of interest. Do-Hyung Kim declares that he has no conflict of interest. Yung Hyun Choi declares that he has no conflict of interest. Suhkmann Kim declares that he has no conflict of interest. Heui-Soo Kim declares that he has no conflict of interest. Mee Sun Ock declares that he has no conflict of interest. Hee-Jae Cha declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All experiments were carried out in accordance with the guidelines and regulation approved by Ethical Committee of Pukyong National University.
Additional information
Hyunsu Kim and Ahran Kim have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, H., Kim, A., Kim, S.M. et al. Genome based quantification of Streptococcus parauberis in multiple organs of infected olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Genes Genom 39, 897–902 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-017-0553-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13258-017-0553-4