Abstract
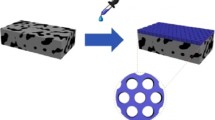
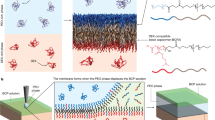
A general approach is developed for controlling the pore size and pore chemistry of integral isoporous membranes derived from the assembly of polystyrene-b-poly-4-vinyl pyridine (PS-b-P4VP) diblock copolymer. In this approach, initially, the sub-50 nm pore surface, decorated with poly-4-vinyl pyridine (P4VP) polymer brush, is coated with polyacrylic acid (PAA). PAA offers a majority of anionic and a minority of neutral acid functionalities. The neutral acid groups adhere to the P4VP segments of the pore wall through hydrogen bonding interactions and the anionic sites remain free. The availability of the anionic sites sets the stage for a layer-by-layer deposition of cationic and anionic polymers, in a sequential manner, on the pore-wall surface through a continuous flow of a dilute polyelectrolyte solution through the nanoporous membrane. In this way, multiple layers, stabilized through electrostatic interactions, can be deposited leading to a continuous decrease in the pore size and a known surface charge. Due to the known facile nature of the large area isoporous asymmetric membrane formation and modular nature of the polyelectrolyte assembly, the present approach is anticipated to yield new block copolymer membranes with tailored separation, sensing, and catalytic properties.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. N. Savariar, K. Krishnamoorthy, and S. Thayumanavan, Nat. Nanotechnol., 3, 112 (2008).
J. A. G. Gnecchi, Self 4.7.0, 11–2 (2011).
Adham, Samer, C. Kuang-ping, and L. Geno, Optimization of Membrane Treatment for Direct and Clarified Water Filtration., Vol. 91111, American Water Works Association, 2006.
A. Schafer, Natural Organics Removal Using Membranes: Principles, Performance, and Cost, CRC Press, 2001.
B. S. Lalia, V. Kochkodan, R. Hashaikeh, and N. Hilal, Desalination, 326, 77 (2013).
Acknowledgements
This work was by National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (NRF-2015R-1D1A1A01057796 and 2015R1A2A2A01006008) and Global Frontier R&D Program (No. 2013M3A6B1078869).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baettig, J., Oh, J., Bang, J. et al. Sequential coating of nanopores with charged polymers: A general approach for controlling pore properties of self-assembled block copolymer membranes. Macromol. Res. 25, 1091–1099 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-017-5142-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-017-5142-5