Abstract
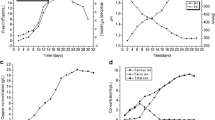
Physicochemical factors such pH value would affect the microbial metabolism during chalcopyrite bioleaching. To this end, the effects of pH on the expression of critical functional genes during bioleaching were evaluated. A mixed culture of moderate thermophiles was used for chalcopyrite bioleaching at initial pH values of 1.0, 2.0, and 3.0, and bioleaching processes were monitored via measuring the physicochemical parameters. Quantitative real-time PCR assay was used to monitor the dynamics of microbial community structures and the expression of critical iron/sulfur oxidation genes (4Fe-4S ferredoxin and sulfate adenylyltransferase genes, respectively). Redundancy analysis and calculation of correlation coefficients were used to reveal linkages between gene expression and various physicochemical factors. The leaching processes at initial pH of 1.0 and 3.0 were prolonged compared with that at initial pH of 2.0. It was shown that Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans and Acidithiobacillus caldus were the dominant species during the early stage in free and attached cells, respectively, while Ferroplasma thermophilum became predominant in the later phase. The gene expression in Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans and Ferroplasma thermophilum was greatly affected by pH values. On the other hand, the relationship between pH and gene expression in Acidithiobacillus caldus was not significant. The study unraveled the importance of pH value on chalcopyrite bioleaching, and pH selectively influenced the expression of key functional genes of some specific species.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bick JA, Dennis JJ, Zylstra GJ, Nowack J, Leustek T (2000) Identification of a new class of 5′-adenylylsulfate (APS) reductases from sulfate-assimilating bacteria. J Bacteriol 182:135–142. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.182.1.135-142.2000
Christel S, Fridlund J, Buetti-Dinh A, Buck M, Watkin EL, Dopson M (2016) RNA transcript sequencing reveals inorganic sulfur compound oxidation pathways in the acidophile Acidithiobacillus ferrivorans. FEMS Microbiol Lett 363. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnw057
Coram NJ, Rawlings DE (2002) Molecular relationship between two groups of the genus Leptospirillum and the finding that Leptospirillum ferriphilum sp. nov. dominates South African commercial biooxidation tanks that operate at 40 °C. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:838–845
Feng S, Yang H, Wang W (2015) Insights into the enhancement mechanism coupled with adapted adsorption behavior from mineralogical aspects in bioleaching of copper-bearing sulfide ore by Acidithiobacillus sp. RSC Adv 5:98057–98066. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra15934b
Guo X et al (2014) Comparative genome analysis reveals metabolic versatility and environmental adaptations of Sulfobacillus thermosulfidooxidans strain ST. PLoS One 9:e99417. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0099417
Halinen A-K, Rahunen N, Kaksonen AH, Puhakka JA (2009a) Heap bioleaching of a complex sulfide ore: part I: effect of pH on metal extraction and microbial composition in pH controlled columns. Hydrometallurgy 98:92–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2009.04.005
Halinen A-K, Rahunen N, Kaksonen AH, Puhakka JA (2009b) Heap bioleaching of a complex sulfide ore: part II. Effect of temperature on base metal extraction and bacterial compositions. Hydrometallurgy 98:101–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2009.04.004
Hille RPV, Zyl AWV, Spurr NRL, Harrison STL (2010) Investigating heap bioleaching: effect of feed iron concentration on bioleaching performance. Miner Eng 23:518–525
Liljeqvist M, Rzhepishevska OI, Dopson M (2013) Gene identification and substrate regulation provide insights into sulfur accumulation during bioleaching with the psychrotolerant acidophile Acidithiobacillus ferrivorans. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:951–957. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02989-12
Lin Q, Zheng CL, Liu JS (2013) Characterization of iron-sulfur cluster assembly protein isca from Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Biochem Mosc 78:244–251. https://doi.org/10.1134/S000629791303005X
Liu XY, Wu B, Chen BW, Wen JK, Ruan RM, Yao GC, Wang DZ (2010) Bioleaching of chalcocite started at different pH: response of the microbial community to environmental stress and leaching kinetics. Hydrometallurgy 103:1–6
Marín S, Acosta M, Galleguillos P, Chibwana C, Strauss H, Demergasso C (2017) Is the growth of microorganisms limited by carbon availability during chalcopyrite bioleaching? Hydrometallurgy 168:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2016.10.003
Ojumu TV, Petersen J (2011) The kinetics of ferrous ion oxidation by Leptospirillum ferriphilum in continuous culture: the effect of pH. Hydrometallurgy 106:5–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2010.11.007
Plumb JJ, Muddle R, Franzmann PD (2008) Effect of pH on rates of iron and sulfur oxidation by bioleaching organisms. Miner Eng 21:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2007.08.018
Vera M, Schippers A, Sand W (2013) Progress in bioleaching: fundamentals and mechanisms of bacterial metal sulfide oxidation—part A. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:7529–7541. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4954-2
Wang YG et al (2012) Bioleaching of chalcopyrite by defined mixed moderately thermophilic consortium including a marine acidophilic halotolerant bacterium. Bioresour Technol 121:348–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.06.114
Wang J, Gan X, Zhao H, Hu M, Li K, Qin W, Qiu G (2016) Dissolution and passivation mechanisms of chalcopyrite during bioleaching: DFT calculation, XPS and electrochemistry analysis. Miner Eng 98:264–278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2016.09.008
Wang J, Liao R, Tao L, Zhao H, Zhai R, Qin W, Qiu G (2017) A comprehensive utilization of silver-bearing solid wastes in chalcopyrite bioleaching. Hydrometallurgy 169:152–157
Watling HR, Collinson DM, Shiers DW, Bryan CG, Watkin ELJ (2013) Effects of pH, temperature and solids loading on microbial community structure during batch culture on a polymetallic ore. Miner Eng 48:68–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2012.10.014
Yu RL et al (2014) The shift of microbial community under the adjustment of initial and processing pH during bioleaching of chalcopyrite concentrate by moderate thermophiles. Bioresour Technol 162:300–307
Zeng J, Huang X, Liu YD, Liu JS, Qiu GZ (2007) Expression, purification, and characterization of a [Fe2S2] cluster containing ferredoxin from Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Curr Microbiol 55:518–523
Zeng WM et al (2010) Community structure and dynamics of the free and attached microorganisms during moderately thermophilic bioleaching of chalcopyrite concentrate. Bioresour Technol 101:7068–7075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.04.003
Zeng WM, Tan SN, Chen M, Qiu GZ (2011) Detection and analysis of attached microorganisms on the mineral surface during bioleaching of pure chalcopyrite with moderate thermophiles. Hydrometallurgy 106:46–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2010.11.014
Zhang R, Wei M, Ji H, Chen X, Qiu G, Zhou H (2009) Application of real-time PCR to monitor population dynamics of defined mixed cultures of moderate thermophiles involved in bioleaching of chalcopyrite. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 81:1161–1168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1792-8
Zhou H, Zhang R, Hu P, Zeng W, Xie Y, Wu C, Qiu G (2008) Isolation and characterization of Ferroplasma thermophilum sp. nov., a novel extremely acidophilic, moderately thermophilic archaeon and its role in bioleaching of chalcopyrite. J Appl Microbiol 105:591–601
Zhou HB, Zeng WM, Yang ZF, Xie YJ, Qiu GZ (2009) Bioleaching of chalcopyrite concentrate by a moderately thermophilic culture in a stirred tank reactor. Bioresour Technol 100:515–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.06.033
Zhou D et al (2015) Expression of critical sulfur- and iron-oxidation genes and the community dynamics during bioleaching of chalcopyrite concentrate by moderate thermophiles. Curr Microbiol 71:62–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-015-0817-7
Zhu JY et al (2012) Investigation of energy gene expressions and community structures of free and attached acidophilic bacteria in chalcopyrite bioleaching. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 39:1833–1840. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-012-1190-1
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 31470230, 51320105006, and 51604308), the Youth Talent Foundation of Hunan Province of China (No. 2017RS3003), the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province of China (No. 2018JJ2486), and the postdoctoral research funding plan in Hunan Province (No. 207159) and Central South University (No. 140050014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Informed consent
Informed consent is not required in this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, T., Zhou, D., Liu, Y. et al. Effects of pH value on the expression of key iron/sulfur oxidation genes during bioleaching of chalcopyrite on thermophilic condition. Ann Microbiol 69, 627–635 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-019-01453-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-019-01453-y