Abstract
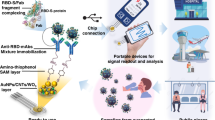
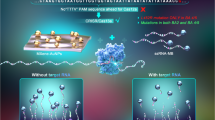
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to a substantial increase in the advancement of point-of-care (POC) diagnostic tools due to their potential utility in detecting and managing the spread of the disease. Currently, many diagnostic techniques necessitate advanced laboratory equipment and specialized expertise to deliver dependable, cost-effective, specific, and sensitive POC tests for COVID-19 diagnosis. Herein, we report a highly sensitive electrochemical sensor array that features S-RBD protein, covalently anchored on the surface-engineered Pt-black-coated microdisk gold electrodes to monitor severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Computer simulations were performed using different electrode gaps to optimize and fabricate the gold microdisk electrode array. The high sensitivity was ensured by decreasing the electrode gap as well as by depositing Pt-black nanoparticles on the microdisk gold electrodes, by means of chronopotentiometry. The electrical readout depends on monitoring changes in the cyclic voltammograms at the electrode/electrolyte interface as a result of the competitive interaction between monoclonal COVID-19 antibodies and varying antigen concentrations. Overall, the developed electrochemical sensor array exhibits promising electroanalytical capabilities by displaying an excellent linear response ranging from 100 to 1 µg/ml with a detection limit of ~ (0.23 ng/ml). In addition, as a proof-of-concept application, the developed electrochemical sensor array was employed as a sensing platform for the detection of heat-inactivated SARS-CoV-2. Such accomplishments highlight the advantages of low-cost localized electronic devices with high sensitivity and rapid multiple samples detection capabilities to play a crucial role in controlling the spread of infectious diseases like COVID-19.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
World Health Organization (WHO): Weekly Epidemiological Update on COVID-19—25 January 2022, https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on-covid-19---25-january-2022.
Rai, P., Kumar, B.K., Deekshit, V.K., Karunasagar, I., Karunasagar, I.: Detection technologies and recent developments in the diagnosis of COVID-19 infection. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 105, 441–455 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-11061-5
Kaltenboeck, B., Wang, C.: Advances in real-time PCR: application to clinical laboratory diagnostics. Adv. Clin. Chem. 40, 219–259 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2423(05)40006-2
Radonić, A., Thulke, S., Mackay, I.M., Landt, O., Siegert, W., Nitsche, A.: Guideline to reference gene selection for quantitative real-time PCR. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 313, 856–862 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.11.177
Smith, C.J., Osborn, A.M.: Advantages and limitations of quantitative PCR (Q-PCR)-based approaches in microbial ecology. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 67, 6–20 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2008.00629
Lee, J.S., Ahn, J.J., Kim, S.J., et al.: POCT detection of 14 respiratory viruses using multiplex RT-PCR. BioChip J. J. 15, 371–380 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-021-00037-w
Freeman, M., Walker, S.J., Vrana, K.E.: Quantitative RT-PCR: pitfalls and potential. Biotechniques (1999). https://doi.org/10.2144/99261rv01
Vashist, S.K.: In vitro diagnostic assays for COVID-19: recent advances and emerging trends. Diagnostics 10, 1–7 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10040202
Loeffelholz, M.J., Tang, Y.-W.: Laboratory diagnosis of emerging human coronavirus infections—the state of the art. Emerg. Microb. Infect. 9, 747–756 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/22221751.2020.1745095
Liu, X., Wang, J., Xu, X., Liao, G., Chen, Y., Hu, C.-H.: Patterns of IgG and IgM antibody response in COVID-19 patients. Emerg. Microb. Infect. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/22221751.2020.1773324
Ha, Y., Kim, I.: Recent developments in innovative magnetic nanoparticles-based immunoassays: from improvement of conventional immunoassays to diagnosis of COVID-19. BioChip J. J. 16, 351–365 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-022-00064-1
Kim, S.K., Sung, H., Hwang, S.H., et al.: A new quantum dot-based lateral flow immunoassay for the rapid detection of influenza viruses. BioChip J. J. 16, 175–182 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-022-00053-4
Grant, B.D., Anderson, C.E., Williford, J.R., Alonzo, L.F., Glukhova, V.A., Boyle, D.S., Weigl, B.H., Nichols, K.P.: SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus nucleocapsid antigen-detecting half-strip lateral flow assay toward the development of point of care tests using commercially available reagents. Anal. Chem. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c01975
Pan, R., Li, G., Liu, S., Zhang, X., Liu, J., Su, Z., Wu, Y.: Emerging nanolabels-based immunoassays: principle and applications in food safety, TrAC. Trends Anal. Chem. 145, 116462 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2021.116462
Itoh, K., Kawamitsu, T., Osaka, Y., Sato, K., Suzuki, Y., Kiriba, C., Saito, Y., Hirose, R., Ichihara, H., Saito, M., Mitsuke, Y., Kuzumi, K., Miyashita, H., Tsutani, H.: False positive results in severe acute respiratory coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) rapid antigen tests for inpatients. J. Infect. Chemother. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiac.2021.03.011
Yamaniha, K., Kinjo, T., Akamine, M., Setoguchi, M., Tateyama, M., Fujita, J.: False-positive for SARS-CoV-2 antigen test in a man with acute HIV infection. J. Infect. Chemother. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiac.2021.04.011
Jesadabundit, W., Jampasa, S., Patarakul, K., Siangproh, W., Chailapakul, O.: Enzyme-free impedimetric biosensor-based molecularly imprinted polymer for selective determination of L-hydroxyproline. Biosens. Bioelectron. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113387
Son, M.H., Park, S.W., Sagong, H.Y., et al.: Recent advances in electrochemical and optical biosensors for cancer biomarker detection. BioChip J. J. 17, 44–67 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-022-00089-6
Assaifan, A.K., Alqahtani, F.A., Alnamlah, S., et al.: Detection and real-time monitoring of LDL-cholesterol by redox-free impedimetric biosensors. BioChip J. J. 16, 197–206 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-022-00058-z
Eom, G., Hwang, A., Kim, H., et al.: Ultrasensitive detection of ovarian cancer biomarker using au nanoplate SERS immunoassay. BioChip J. J. 15, 348–355 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-021-00031-2
Quoc, T.V., Ngoc, V.N., Bui, T.T., et al.: High-frequency interdigitated array electrode-based capacitive biosensor for protein detection. BioChip J. J. 13, 403–415 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-019-3412-3
Fabiani, L., Saroglia, M., Galatà, G., De Santis, R., Fillo, S., Luca, V., Faggioni, G., D’Amore, N., Regalbuto, E., Salvatori, P.: Magnetic beads combined with carbon black-based screen-printed electrodes for COVID-19: a reliable and miniaturized electrochemical immunosensor for SARS-CoV-2 detection in saliva. Biosens. Bioelectron. 171, 1–9 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112686
Kwon, N., Lee, S., Jang, M., et al.: Synthesis of truncated DNA aptamer and its application to an electrochemical biosensor consisting of an aptamer and a MXene heterolayer for yellow fever virus. BioChip J. J. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-023-00133-z
Beduk, D., et al.: ‘All In One’ SARS-CoV-2 variant recognition platform: machine learning-enabled point of care diagnostics. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 10, 100105 (2022)
Salahandish, R., et al.: Bi-ECDAQ: An electrochemical dual-immuno-biosensor accompanied by a customized bi-potentiostat for clinical detection of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid proteins. Biosens. Bioelectron. 203, 114018 (2022)
Kim, S., Lee, J.H.: Current advances in paper-based biosensor technologies for rapid COVID-19 diagnosis. BioChip J. J. 16, 376–396 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-022-00078-9
Hosseini, M., et al.: Development of sandwich electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for COVID-19 diagnosis by SARS-CoV-2 spike protein detection based on Au@BSA-luminol nanocomposites. Bioelectrochemistry 147, 108161 (2022)
Bong, J.H., Kim, T.H., Jung, J., et al.: Competitive immunoassay of SARS-CoV-2 using pig sera-derived anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. BioChip J. J. 15, 100–108 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-021-00011-6
de Lima, L.F., Ferreira, A.L., Torres, M.D.T., de Araujo, W.R., de la Fuente-Nunez, C.: Minute-scale detection of SARS-CoV-2 using a low-cost biosensor composed of pencil graphite electrodes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2106724118
El-Said, W.A., Al-Bogami, A.S., Alshitari, W., et al.: Electrochemical microbiosensor for detecting COVID-19 in a patient sample based on gold microcuboids pattern. BioChip J. J. 15, 287–295 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-021-00030-3
Bin, X., Sargent, E.H., Kelley, S.O.: Nanostructuring of sensors determines the efficiency of biomolecular capture. Anal. Chem. 82, 5928–5931 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1021/ac101164n
Soleymani, L., Fang, Z., Sargent, E.H., Kelley, S.O.: Programming the detection limits of biosensors through controlled nanostructuring. Nat. Nanotechnol. 4, 844–848 (2009)
Asif, A., Park, S.H., Soomro, A.M., Khalid, M.A.U., Salih, A.R.C., Kang, B., Ahmed, F., Kim, K.H., Choi, K.H.: Microphysiological system with continuous analysis of albumin for hepatotoxicity modeling and drug screening. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2021.03.035
Sardesai, N.P., Ganesana, M., Karimi, A., Leiter, J.C., Andreescu, S.: Platinum-doped ceria based biosensor for in vitro and monitoring of lactate during hypoxia. Anal. Chem. 87(5), 2996–3003 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1021/ac5047455
Kamal Ahmed, R., Saad, E.M., Fahmy, H.M., El Nashar, R.M.: Design and application of molecularly imprinted polypyrrole/platinum nanoparticles modified platinum sensor for the electrochemical detection of Vardenafil. Microchem. J.. J. 171, 106771 (2021)
Park, J.A., Kwon, N., Park, E., Kim, Y., Jang, H., Min, J., Lee, T.: Electrochemical biosensor with aptamer/porous platinum nanoparticle on round-type micro-gap electrode for saxitoxin detection in fresh water. Biosens. Bioelectron. 210, 114300 (2022)
Aydın, E.B., Aydın, M., Sezgintürk, M.K.: Highly selective and sensitive sandwich immunosensor platform modified with MUA-capped GNPs for detection of spike Receptor Binding Domain protein: a precious marker of COVID 19 infection. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 345, 130355 (2021)
Chen, X., Guo, Z., Tang, Y., Shen, Y., Miao, P.: A highly sensitive gold nanoparticle-based electrochemical aptasensor for theophylline detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 25(999), 54–59 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.10.039. (Epub 2017 Nov 9)
Lu, Z., Xu, S., Wang, H., He, E., Liu, J., Dai, Y., Xie, J., Song, Y., Wang, Y., Wang, Y., et al.: PtNPt/MWCNT-PEDOT:PSS-modified microelectrode arrays for the synchronous dopamine and neural spike detection in rat models of sleep deprivation. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 4, 4872–4884 (2021)
Xiao, G., Song, Y., Zhang, Y., Xu, S., Xing, Y., Wang, M., Cai, X.: Platinum/graphene oxide coated microfabricated arrays for multinucleus neural activities detection in the rat models of Parkinson’s disease treated by apomorphine. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2, 4010–4019 (2019)
Walls, A.C., Park, Y.J., Tortorici, M.A., Wall, A., McGuire, A.T., Veesler, D.: Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. Cell 181(2), 281-292.e6 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.02
Huang, Y., Yang, C., Xu, X.-F., Xu, W., Liu, S.-W.: Structural and functional properties of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein: potential antivirus drug development for COVID-19. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 41, 1141–1149 (2020)
Nguyen, H.L., Lan, P.D., Thai, N.Q., Nissley, D.A., O’Brien, E.P., Li, M.S.: Does SARS-CoV-2 bind to human ACE2 more strongly than does SARS-CoV? J. Phys. Chem. B 124, 7336–7347 (2020)
Saitou, M.: Electrochemical characterization of platinum black electrodeposited from electrolyte including lead acetate trihydrate. Surf. Coat. Technol. 201(6), 3611–3614 (2006)
Castiello, F.R., et al.: Interfacial capacitance immunosensing using interdigitated electrodes: the effect of insulation/immobilization chemistry. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 21(28), 15787–15797 (2019)
Park, B.-W., Yoon, D.-Y., Kim, D.-S.: Formation and modification of a binary self-assembled monolayer on a nano-structured gold electrode and its structural characterization by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. J. Electroanal. Chem.Electroanal Chem. 661(2), 329–335 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2011.08.013
Gollas, B., Elliott, J.M., Bartlett, P.N.: Electrodeposition and properties of nanostructured platinum films studied by quartz crystal impedance measurements at 10 MHz. Electrochim. Acta. Acta 45(22–23), 3711–3724 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0013-4686(00)00464-3
Santos, A.: Fundamentals and applications of impedimetric and redox capacitive biosensors. J. Anal. Bioanal. Tech. (2014). https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-9872.S7-016
Bath, B.D., Michael, D.J., Trafton, B.J., Joseph, J.D., Runnels, P.L., Wightman, R.M.: Subsecond adsorption and desorption of dopamine at carbon-fiber microelectrodes. Anal. Chem. 72(24), 5994–6002 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1021/ac000849y
Taheri, R.A., Rezayan, A.H., Rahimi, F., Mohammadnejad, J., Kamali, M.: Comparison of antibody immobilization strategies in detection of Vibrio cholerae by surface plasmon resonance. Biointerphases 11(4), 041006 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1116/1.4971270
Zhao, Z., Huang, C., Huang, Z., Lin, F., He, Q., Tao, D., Jaffrezic-Renault, N., Guo, Z.: Advancements in electrochemical biosensing for respiratory virus detection: a review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2021.116253
Zhang, Z., Hu, W., Li, L., Ding, H., Li, H.: Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies and clinical laboratory tests: when, why, and what is expected? J. Clin. Lab. Anal.Clin. Lab. Anal. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.22307
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Gachon University research fund (GCU-202002710001, GCU-202303970001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zeeshan, Selvam, S.P., Park, J. et al. Electrochemical Detection of S-RBD Protein for Point-of-Care SARS-CoV-2 Monitoring Using Platinum-Black-Based Sensor Array. BioChip J (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-024-00153-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-024-00153-3