Abstract
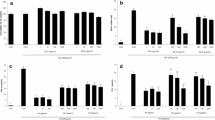
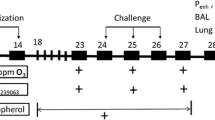
In the present study we focused on the anti-asthmatic and antioxidant effects of Zingiber officinalis roscoe L. (ZO) aqueous extract. This study includes 20 adult male rats, which were grouped into four; Group I: control group; Group II: asthmatic group (Ovalbumin sensitized/challenge model, Oval group); Group III: received ovalbumin sensitized/challenge associated a dose of 207 mg/kg body weight (BW) of ZO (Oval + D1 group); Group IV: received ovalbumin sensitized/challenge associated a dose of 414 mg/k BW of ZO (Oval + D2 group). After 21 days, blood and lung samples were collected for biochemical, hematological, and histopathological analyses. The ameliorative effect of ZO phytochemical compounds was also assessed by in silico approach on transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) receptors. The oxidative/antioxidative status was evaluated in the lung tissues. Our results show that ZO extract alleviated the ovalbumin-induced hematological and biochemical disruptions associated oxidative injury. In fact, white and red blood cells (WBC and RBC, respectively), aspartate aminotransaminase (ASAT), malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione (GSH), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) were significantly disrupted (p < 0.05) in Oval group and alleviated following ZO treatment. Besides, several histopathological features were outlined in lung tissues of Oval group. Interestingly, ZO was found to exert ameliorative effects on tissue level. In silico analyses, particularly the binding affinities, the number of H-bonds, the embedding distance and the molecular interactions of ZO phytochemical compounds with either STAT6 or TNF-α supported the in vivo results. These findings confirm the potential ethno-pharmacological effects of ZO against asthma and its associated complications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ade S, Adjibode O, Awanou B et al (2017) Résultats de la prise en charge de l’asthme persistant sévère dans des conditions de ressources limitées : expérience du Bénin. Rev FrAllerg 57(3):271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reval.2017.02.171
Aeschbach R, Löliger J, Scott BC et al (1994) Antioxidant actions of thymol, carvacrol, 6-Gingerol Zingerone and Hydroxytyrosol. Food Chem Toxicol 32(1):31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-6915(84)90033-4
Afzal M, Al-Hadidi D, Menon M et al (2001) Ginger: an ethnomedical, chemical and pharmacological review. Drug Metab Drug Interact 18(3–4):159–190. https://doi.org/10.1515/DMDI.2001.18.3-4.159
Akacha A, Badraoui R, Rebai T et al (2022) Effect of Opuntia ficus indica extract on methotrexate-induced testicular injury: a biochemical, docking and histological study. J Biomol Struct Dyn 40(10):4341–4351. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2020.1856187
Al-Afaleg NO, Al-Senaidy A, El-Ansary A (2011) Oxidative stress and antioxidant status in Saudi asthmatic patients. Clin Biochem 44(8–9):612–617. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2011.01.016
Al-Harbi NO, Nadeem A, Al-Harbi MM et al (2016) Airway oxidative stress causes vascular and hepatic inflammation via upregulation of IL-17A in a murine model of allergic asthma. Internat Immunopharmacol 34:173–182
Amri N, Rahmouni F, Chokri MA et al (2017) Histological and biochemical biomarkers analysis reveal strong toxicological impacts of pollution in hybrid sparrow (Passer domesticus × Passer hispaniolensis) in Southern Tunisia. Environ Sci Poll Res 24(21):17845–17852. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9352-3
Badraoui R, Sahnoun Z, Abdelmoula NB et al (2007) May antioxidants status depletion by tetradifon induce secondary genotoxicity in female wistar rats via oxidative stress? Pestic Biochem Physiol 88(2):149–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2006.10.007
Badraoui R, Rebai T, Elkahoui S et al (2020) Allium Subhirsutum L. as a potential source of antioxidant and anticancer bioactive molecules: HR-LCMS phytochemical profiling, in vitro and in vivo pharmacological study. Antioxidants 9(10):1003. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9101003
Badraoui R, Adnan M, Bardakci F et al (2021a) Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine interact differently with ACE2 domains reported to bind with the coronavirus spike protein: mediation by ACE2 polymorphism. Molecules 26(3):673. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26030673
Badraoui R, Alrashedi MM, El-May MV et al (2021b) Acute respiratory distress syndrome: a life threatening associated complication of SARS-CoV-2 infection inducing COVID-19. J Biomol Struct Dyn 39(17):6842–6851. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2020.1803139
Bano T, Kumar N, Dudhe R (2012) Free radical scavenging properties of pyrimidine derivatives. Org Med Chem Lett 2:34. https://doi.org/10.1186/2191-2858-2-34
Bayrami G, Boskabady MH (2012) The potential effect of the extract of Crocus sativus and Safranal on the total and differential white blood cells of ovalbumin-sensitized guinea pigs. Res Pharm Sci 7(4):249–255
Borrelli F, Capasso R, Aviello G et al (2005) Effectiveness and safety of ginger in the treatment of pregnancy-induced nausea and vomiting. Obstet Gynecol 105(4):849–856. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.AOG.0000154890.47642.23
Cho YS, Lee J, Lee TH et al (2004) Alpha-lipoic acid inhibits airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness in a mouse model of asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 114(2):429–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2004.04.004
Dadkhah A, Fatemi F, Farsani ME et al (2014) Hepatoprotective effects of iranian hypericum scabrum essential oils against oxidative stress induced by acetaminophen in rats. Braz Arch Biol Technol 57:340–348. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-89132014005000012
Dasari S, Ganjayi MS, Yellanurkonda P et al (2018) Role of glutathione s-transferases in detoxification of a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, methylcholanthrene. Chem Biol Interact 294:81–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2018.08.023
Delmas MC, Fuhrman C, pour le groupe épidémiologie et recherche clinique de la SPLF. (2010) Asthma in France: a review of descriptive epidemiological data. Rev Mal Respir 27(2):151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmr.2009.09.001
Draper HH, Hadley M (1990) Malondialdehyde determination as index of lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 186:421–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(90)86135-i
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82(1):70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(59)90090-6
Flohé L, Günzler WA (1984) Assays of glutathione peroxidase. Methods Enzymol 105:114–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0076-6879(84)05015-1
Gupta S, Sharma A (2014) Medicinal properties of Zingiber officinale roscoe—a review. IOSR J Pharm Biol Sci 9(5):124–129. https://doi.org/10.9790/3008-0955124129
Hakim A, Kallel H, Sahnoun Z, et al (2008) Lack of nephrotoxicity following 15-day therapy with high doses of colistin in rats. Med Sci Monit 14(4):BR74–BR77. https://www.medscimonit.com/abstract/index/idArt/850282
Haksar A, Sharma A, Chawla R et al (2006) Zingiber officinale exhibits behavioral radioprotection against radiation-induced CTA in a gender-specific manner. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 84(2):179–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2006.04.008
Hchicha K, Korb M, Badraoui R et al (2021) A novel sulfate-bridged binuclear copper (II) complex: structure, optical, ADMET and in vivo approach in a murine model of bone metastasis. New J Chem 45(31):13775–13784. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NJ02388H
Hussain T, Tan B, Yin Y et al (2016) Oxidative stress and inflammation: what polyphenols can do for us? Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016:7432797. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7432797
Jittiwat J, Wattanathorn J (2012) Ginger pharmacopuncture improves cognitive impairment and oxidative stress following cerebral ischemia. J Acupunct Meridian Stud 5(6):295–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jams.2012.09.003
Jollow DJ, Mitchell JR, Zampaglione N et al (1974) Bromobenzene-induced liver necrosis. Protective role of glutathione and evidence for 3,4-Bromobenzene oxide as the hepatotoxic metabolite. PHA 11(3):151–169. https://doi.org/10.1159/000136485
Joobeur S, Mhamed SC, Saad AB, et al (2015) L’asthme allergique au centre tunisien. Pan Afr Med J 20 (133). https://doi.org/10.11604/pamj.2015.20.133.5642
Kayali R, Cakatay U, Akçay T et al (2006) Effect of alpha-lipoic acid supplementation on markers of protein oxidation in post-mitotic tissues of ageing rat. Cell Biochem Funct 24(1):79–85. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbf.1190
Khan AM, Shahzad M, Raza Asim MB et al (2015) Zingiber officinale ameliorates allergic asthma via suppression of Th2-mediated immune response. Pharm Biol 53(3):359–367. https://doi.org/10.3109/13880209.2014.920396
Li E, Landers CT, Tung HY et al (2018) Fungi in mucoobstructive airway diseases. Annals ATS 15(Suppl 3):S198–S204. https://doi.org/10.1513/AnnalsATS.201803-154AW
Mhadhbi N, Issaoui N, Hamadou WS, Alam JM, Elhadi AS, Naïli H, Badraoui R (2022) Physico-chemical properties, pharmacokinetics, molecular docking and in-vitro pharmacological study of a cobalt (ii) complex based on 2-aminopyridine. ChemistrySelect 7(3):e202103592. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202103592
Mims JW (2015) Asthma: definitions and pathophysiology. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 5(Suppl 1):S2-6. https://doi.org/10.1002/alr.21609
Misso NLA, Brooks-Wildhaber J, Ray S et al (2005) Plasma concentrations of dietary and nondietary antioxidants are low in severe asthma. Eur Respir J 26(2):257–264. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.05.00006705
Mukherjee AA, Kandhare AD, Rojatkar SR et al (2017) Ameliorative effects of artemisia pallens in a murine model of ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma via modulation of biochemical perturbations. Biomed Pharmacother 94:880–889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.08.017
Mzid M, Badraoui R, Khedir SB et al (2017) Protective effect of ethanolic extract of Urtica Urens L. against the toxicity of imidacloprid on bone remodeling in rats and antioxidant activities. Biomed Pharmacother 91:1022–1041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.05.023
Podlogar JA, Verspohl EJ (2012) Antiinflammatory effects of ginger and some of its components in human bronchial epithelial (BEAS-2B) cells. Phytother Res 26(3):333–336. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.3558
Rouhi H, Ganji F, Nasri H (2006) Effects of ginger on the improvement of asthma [the evaluation of its treatmental effects]. Pak J Nutr 5(4):373–376
Saoudi M, Badraoui R, Chira A et al (2021) The role of Allium Subhirsutum L. in the attenuation of dermal wounds by modulating oxidative stress and inflammation in wistar albino rats. Molecules 26(16):4875. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26164875
Tokac M, Bacanli M, Dumlu EG et al (2017) The ameliorative effects of Pycnogenol® on liver ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Turk J Pharmaceutic Sci 14(3):257. https://doi.org/10.4274/tjps.49369
Yocum GT, Hwang JJ, Mikami M et al (2020) Ginger and its bioactive component 6-shogaol mitigate lung inflammation in a murine asthma model. Am J Physiol-Lung Cell Mol Physiol 318(2):L296–L303. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00249.2019
Zammel N, Amri N, Chaabane R et al (2018) Proficiencies of Zingiber officinale against spine curve and vertebral damage induced by corticosteroid therapy associated with gonadal hormone deficiency in a rat model of osteoporosis. Biomed Pharmacother 103:1429–1435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.04.159
Zammel N, Oudadesse H, Allagui I et al (2021a) Evaluation of lumbar vertebrae mineral composition in rat model of severe osteopenia: a Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) analysis. Vibrat Spectrosc 115:103279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vibspec.2021.103279
Zammel N, Saeed M, Bouali N et al (2021b) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of Zingiber officinale roscoe and Allium Subhirsutum: in silico biochemical and histological study. Foods 10(6):1383. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10061383
Zammel N, Jedli O, Rebai T, et al (2022) Kidney injury and oxidative damage alleviation by Zingiber officinale: pharmacokinetics and protective approach in a combined murine model of osteoporosis. 3 Biotech 12(5),1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03170-x
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to express their gratitude to Dr. Rim Chaabane for her biochemical support. This research received grants from the deanship of scientific research, University of Ha’il. Project number: RG-21 100.
Funding
None molecular data accession numbers for16S rRNA gene, other rRNA genes, ITS, WGS, SRA etc., or culture collection numbers for new taxa have been used in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, O.J., T.R., and R.B.; methodology, O.J., H.B.N., and R.B.; Experimental analysis: O.J., N.Z., T.R., and R.B; validation, W.S.H., S.E., A.J., and R.B.; formal analysis, N.Z., A.E.S, and O.J.; investigation, M.S., H.N., and R.B.; resources, T.R., and R.B.; data curation, N.Z., A.J.S., H.N., and R.B.; software, O.J., H.B.N., and R.B.; writing—original draft preparation, O.J., H.B.N., and R.B.; writing—review and editing, O.J. and R.B.; visualization, M.M.A., A.J.S., A.E.S., and R.B.; supervision, H.B.N., and R.B.; project administration, R.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in the publication.
Informed consent
Not applicable for this study.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jedli, O., Ben-Nasr, H., Zammel, N. et al. Attenuation of ovalbumin-induced inflammation and lung oxidative injury in asthmatic rats by Zingiber officinale extract: combined in silico and in vivo study on antioxidant potential, STAT6 and TNF-α pathways. 3 Biotech 12, 191 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03249-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03249-5