Abstract
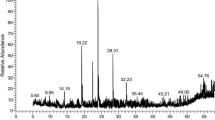
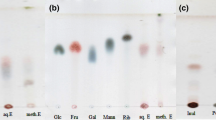
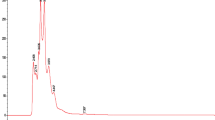
Spondias mombin is used in the folk medicine for the treatment of diarrhea and dysentery, indicating that extracts obtained from this species may present pharmacological activities against pathogenic microorganisms. The purpose of this work was to investigate the chemical composition and evaluate the antimicrobial activity of extracts obtained from the leaves (aqueous) and bark (hydroethanolic) of S. mombin both as single treatments and in combination with conventional drugs. Following a qualitative chemical prospection, the extracts were analyzed by HPLC–DAD. The antimicrobial activities were evaluated by microdilution. The combined activity of drugs and extracts was verified by adding a subinhibitory concentration of the extract in the presence of variable drug concentrations. The Minimum Fungicidal Concentration (MFC) was determined by a subculture of the microdilution test, while the effect of the in vitro treatments on morphological transition was analyzed by subculture in moist chambers. While the qualitative analysis detected the presence of phenols and flavonoids, the HPLC analysis identified quercetin, caffeic acid, and catechin as major components in the leaf extract, whereas kaempferol and quercetin were found as major compounds in the bark extract. The extracts showed effective antibacterial activities only against the Gram-negative strains. With regard to the combined activity, the leaf extract potentiated the action of gentamicin and imipenem (against Staphylococcus aureus), while the bark extract potentiated the effect of norfloxacin (against S. aureus), imipenem (against Escherichia coli), and norfloxacin (against Pseudomonas aeruginosa). A more significant antifungal (fungistatic) effect was achieved with the bark extract (even though at high concentrations), which further enhanced the activity of fluconazole. The extracts also inhibited the emission of filaments by Candida albicans and Candida tropicalis. Together, these findings suggest that that the extract constituents may act by favoring the permeability of microbial cells to conventional drugs, as well as by affecting virulence mechanisms in Candida strains.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IPDs:
-
Infectious and parasitic diseases
- URCA:
-
Universidade Regional do Cariri
- HPLC-DAD:
-
High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Diode Array Detector
- ATCC:
-
American type culture collection
- HIA:
-
Heart infusion agar
- BHI:
-
Brain heart infusion
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- MIC:
-
Minimum inhibitory concentration
- INCQS:
-
Instituto Nacional de Controle de Qualidade em Saúde—National Institute of Quality Control in Health
- FIOCRUZ:
-
Fundação Instituto Osvaldo Cruz
- SDA:
-
Sabouraud dextrose agar
- SDB:
-
Sabouraud dextrose broth
- MFC:
-
Minimum fungicidal concentration
- IC50 :
-
Concentration that inhibits 50% of the microbial growth
- PDA:
-
Potato dextrose agar
- HCA:
-
Higher concentration assessed
- one-way ANOVA:
-
One-way analysis of variance
- CDRI:
-
Central Drug Research Institute
- AELSM:
-
Aqueous extract of the leaves of Spondias mombin
- HEBSM:
-
Hydroethanolic extract of the bark of Spondias mombin
- MDR:
-
Multidrug-resistant
- BAM complex:
-
β‐Barrel assembly machine complex
- SD:
-
Standard deviations
- FCZ:
-
Fluconazole
References
Abadi ATB, Rizvanov AA, Haertlé T, Blatt NL (2019) World Health Organization report: current crisis of antibiotic resistance. BioNanoScience 9:778–788
Agbaje EO, Ismail AI, Oguntokun OJ (2020) Antimicrobial and antipyretic activities of aqueous leaf extract of Spondias mombin Linn. (Anarcadiaceae). J Med Herbs Ethnomed 6:21–29
Akinmoladun AC, Khan MF, Sarkar J, Farombi EO, Maurya R (2015) Distinct radical scavenging and antiproliferative properties of Spondias mombin and antioxidant activity-guided isolation of quercetin-3-O-D-glucopyranoside and undec-1-ene. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol 9:506–513. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJPP2015.4279
Albergaria ETD, Silva MVD, Silva AGD (2019) Levantamento etnobotânico de plantas medicinais em comunidades rurais localizadas na Unidade de Conservação Tatu-Bola, município de Lagoa Grande, PE-Brasil. Rev Fitos 13:137–154
Albuquerque UP, Hanazaki N (2006) As pesquisas etnodirigidas na descoberta de novos fármacos de interesse médico e farmacêutico: fragilidades e pespectivas. Rev Bras Farmacogn 16:678–689. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-695X2006000500015
Alhadrami HA, Hamed AA, Hassan HM, Belbahri L, Rateb ME, Sayed AM (2020) Flavonoids as potential anti-MRSA agents through modulation of PBP2a: a computational and experimental study. Antibiotics 9:562–577. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9090562
Almeida RS, Freitas PR, Araújo ACJ, Menezes IRA, Santos EL, Tintino SR, Amaral W (2020) GC-MS profile and enhancement of antibiotic activity by the essential oil of Ocotea odorífera and Safrole: inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus efflux pumps. Antibiotics 9:247–262. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9050247
Anand J, Rai N (2017) Anticandidal synergistic activity of green tea catechins, antimycotics and copper sulphate as a mean of combinational drug therapy against candidiasis. J Mycol Med 27:33–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mycmed.2016.08.004
Asgeirsson H, Thalme A, Weiland O (2018) Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia and endocarditis–epidemiology and outcome: a review. Infect Dis 50:175–192. https://doi.org/10.1080/23744235.2017.1392039
Aslam B, Wang W, Arshad MI, Khurshid M, Muzammil S, Rasool MH, Salamat MKF (2018) Antibiotic resistance: a rundown of a global crisis. Infect Drug Resist 11:1645–1658. https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S173867
Barbosa DA, Lucena RF, Cruz DD (2019) Traditional knowledge as basis for phytochemical prospecting of Sideroxylon obtusifolium (Roem. & Schult.) TD Penn. aiming at conservation in the Brazilian semi-arid zone. Ethnobot Res App 18:1–10. https://doi.org/10.32859/era.18.3.1-10
Bezerra JWA, Costa AR, Silva MAP, Rocha MI, Boligon AA, Rocha JBT, Barros LM, Kamdem JP (2017) Chemical composition and toxicological evaluation of Hyptis suaveolens (L.) Poiteau (LAMIACEAE) in Drosophila melanogaster and Artemia salina. S Afr J Bot 113:437–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajb.2017.10.003
Bezerra JWA, Costa AR, Freitas MA et al (2019) Chemical composition, antimicrobial, modulator and antioxidant activity of essential oil of Dysphania ambrosioides (L.) Mosyakin & Clemants. Comp Immunol, Microbiol Infect Dis 65:58–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cimid.2019.04.010
Bezerra JWA, Rodrigues FC, Cruz RP, Silva LED, Amaral W, Andrade Rebelo R, Coutinho HDM, Morais-Braga MFB (2020) Antibiotic potential and chemical composition of the essential oil of Piper caldense C. DC. (Piperaceae). Appl Sci 10:631–641. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10020631
Calixto-Junior JT, Morais SM, Martins CG, Vieira LG, Morais-Braga MFB, Carneiro JN, Coutinho HDM (2015) Phytochemical analysis and modulation of antibiotic activity by Luehea paniculata Mart. & Zucc. (Malvaceae) in multiresistant clinical isolates of Candida spp. BioMed Res Int 2015:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/807670
Candiracci M, Citterio B, Piatti E (2012) Antifungal activity of the honey flavonoid extract against Candida albicans. Food Chem 131:493–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.09.012
Canonico B, Candiracci M, Citterio B, Curci R, Squarzoni S, Mazzoni A, Piatti E (2014) Honey flavonoids inhibit Candida albicans morphogenesis by affecting DNA behavior and mitochondrial function. Future Microbiol 9:445–456. https://doi.org/10.2217/fmb.14.17
Carvalho GG, Peres GC, Mendonça RMC, Santos Filho EX (2020) Phytochemical prospection and antibacterial activity of native plants from the cerrado of goiás, Brazil. Res Rev J Pharmacogn Phytochem 9:29–37
Cassini A, Högberg LD, Plachouras D, Quattrocchi A, Hoxha A, Simonsen GS, Ouakrim DA (2019) Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: a population-level modelling analysis. Lancet Infect Dis 19:56–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30605-4
Castillo CL (2015) Plantas medicinales utilizadas en el tratamiento de enfermedades ginecológicas en Leticia y Puerto Nariño (Amazonas, Colombia). Etnobiología 13:53–72
Chaves TP, Clementino ELC, Felismino DC, Silva H, Santos JS (2018) Phytochemical composition and antimicrobial and toxicological activity of Spondias mombin L. (jobo). Rev Cuba de Plantas Med 23:1–7
Cordeiro BMPC, Santos NDL, Ferreira MRA, Araújo LCC, Junior ARC, Santos ADC, Almeida JRGS (2018) Hexane extract from Spondias tuberosa (Anacardiaceae) leaves has antioxidant activity and is an anti-Candida agent by causing mitochondrial and lysosomal damages. BMC Complement Altern Med 18:1–10
Costa AR, Almeida-Bezerra JW, Cruz RP, Freitas MA, Silva VB, Neto JC, Kamdem JP (2020) In vitro antibiotic and modulatory activity of Mesosphaerum suaveolens (L.) Kuntze against Candida strains. Antibiotics 9:46–57. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9020046
Coutinho HDM, Costa JGM, Lima EO, Falcão-Silva VS, Siqueira-Júnior JP (2008) Enhancement of the antibiotic activity against a multiresistant Escherichia coli by Mentha arvensis L. and Chlorpromazine. Chemotherapy 54:328–330. https://doi.org/10.1159/000151267
Cristofoli NL, Lima CAR, Vieira MMC, Andrade KS, Ferreira SR (2019) Antioxidant and antimicrobial potential of cajazeira leaves (Spondias mombin) extracts. Sep Sci Technol 54:580–590. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2018.1508233
Cruz RP, Freitas TS, Costa MS et al (2020) Effect of α-bisabolol and its β-cyclodextrin complex as tetk and nora efflux pump inhibitors in Staphylococcus aureus strains. Antibiotics 9:28–39. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9010028
De Freitas RFD, Canelli AP, de Aro AA, Sartoratto A, Franzini CM, de Góes VFF (2020) Avaliação “in vitro” da eficácia do extrato hidroalcoólico do cajá (Spondias mombin L.) e da graviola (Annona muricata L.) sobre microorganismos orais. Braz J Dev 6:66772–66793. https://doi.org/10.34117/bjdv6n9-204
Delmondes A, Lima CNF, Pimentel G et al (2016) Natural resource use in traditional community for the treatment of diarrheal diseases in children from the Northeast of Brazil. J Medicinal Plants 4:30–34
Eix EF, Nett JE (2020) How biofilm growth affects Candida-host interactions. Front Microbiol 11:1–8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.01437
Ernst EJ, Klepser ME, Ernst ME, Messer SA, Pfaller MA (1999) In vitro pharmacodynamic properties of MK-0991 determined by time-kill methods. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 33:75–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0732-8893(98)00130-8
Freitas MA, Santos AT, Machado AJ et al (2017) Fern extracts potentiate fluconazole activity and inhibit morphological changes in Candida species. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 7:1025–1030. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtb.2017.09.018
Gu Y, Li H, Dong H, Zeng Y, Zhang Z, Paterson NG, Dong C (2016) Structural basis of outer membrane protein insertion by the BAM complex. Nature 531:64–69
Hajdu Z, Hohmann J (2012) An ethnopharmacological survey of the traditional medicine utilized in the community of Porvenir, Bajo Paraguá Indian Reservation, Bolivia. J Ethnopharmacol 139:838–857. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2011.12.029
Henriques M, Williams D (2020) Pathogenesis and virulence of Candida albicans and Candida glabrata. Pathogens 9:752–754. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090752
Hoang S, Georget A, Asselineau J, Venier AG, Leroyer C, Rogues AM, Thiébaut R (2018) Risk factors for colonization and infection by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in patients hospitalized in intensive care units in France. PLoS ONE 13:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0193300
Horn J, Stelzner K, Rudel T, Fraunholz M (2018) Inside job: Staphylococcus aureus host-pathogen interactions. Int J Med Microbiol 308:607–624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmm.2017.11.009
Houghton PJ, Howes MJ, Lee CC, Steventon G (2007) Uses and abuses of in vitro tests in ethnopharmacology: visualizing an elephant. J Ethnopharmacol 110:391–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2007.01.032
Ivanov M et al (2021) Flavones, flavonols, and glycosylated derivatives—impact on Candida albicans growth and virulence, expression of CDR1 and ERG11. Cytotoxicity Pharmaceuticals 14:27. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph14010027
Javadpour MM, Juban MM, Lo WCJ, Bishop SM, Alberty JB, Cowell SM, McLaughlin ML (1996) De novo antimicrobial peptides with low mammalian cell toxicity. J Med Chem 39:3107–3113. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm9509410
Kannanoor M, Lakshmi BA, Kim S (2021) Synthesis of silver nanoparticles conjugated with kaempferol and hydrocortisone and an evaluation of their antibacterial effects. 3 Biotech 11:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02880-y
Khalil IA, Troeger C, Blacker BF et al (2018) Morbidity and mortality due to Shigella and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhoea: the Global Burden of Disease Study 1990–2016. Lancet Infect Dis 18:1229–1240. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30475-4
Kwun MS, Lee DG (2020) Quercetin-induced yeast apoptosis through mitochondrial dysfunction under the accumulation of magnesium in Candida albicans. Fungal Biol 124:83–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funbio.2019.11.009
Martins N, Barros L, Henriques M, Silva S, Ferreira IC (2015) Activity of phenolic compounds from plant origin against Candida species. Indust Crops Prod 74:648–670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.05.067
Matos FJA (2009) Introdução a Fitoquímica Experimental, 3rd edn. Edições UFC, Fortaleza
Morais-Braga MFB, Carneiro JN, Machado AJ et al (2016a) High-performance liquid chromatography-diodic array detector, fungistatic, and anti-morphogenical analysis of extracts from Psidium brownianum Mart. ex DC. against yeasts of the genus Candida. Int J Food Prop 19:1837–1851. https://doi.org/10.1080/10942912.2015.1079786
Morais-Braga MFB, Sales DL, Carneiro JNP et al (2016b) Psidium guajava L. and Psidium brownianum Mart ex DC.: chemical composition and anti–Candida effect in association with fluconazole. Microb Pathog 95:200–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2016.04.013
Nwidu LL, Elmorsy E, Oboma YI, Carter WG (2018) Hepatoprotective and antioxidant activities of Spondias mombin leaf and stem extracts against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity. J Taibah Univ Medical Sci 13:262–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtumed.2018.03.006
Okwuosa OM, Chukwura EI, Chukwuma GO, Okwuosa CN, Enweani IB, Agbakoba NR, Umedum CU (2012) Phytochemical and antifungal activities of Uvaria chamae leaves and roots, Spondias mombin leaves and bark and Combretum racemosum leaves. Afr J Med Med Sci 41:99–103
Oliveira FA, Rorato VC, Almeida-Apolonio AA, Rodrigues AB, Barros AL, Sangalli A, Oliveira KMD (2017) In vitro antifungal activity of Myracrodruon urundeuva Allemão against human vaginal Candida species. An Acad Bras Ciênc 89:2423–2432. https://doi.org/10.1590/0001-3765201720170254
Pessoa LZDS, Duarte JL, Ferreira RMDA, Oliveira AEMFM, Cruz RAS, Faustino SMM, Araújo RS (2018) Nanosuspension of quercetin: preparation, characterization and effects against Aedes aegypti larvae. Rev Bras Farmacogn 28:618–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjp.2018.07.003
Pristov KE, Ghannoum MA (2019) Resistance of Candida to azoles and echinocandins worldwide. Clin Microbiol Infect 25:792–798. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2019.03.028
Rey-Blanes C, Pérez-Portero Y, Morris-Quevedo HJ, Casas V, Abdala R, Quesada AR, Medina MÁ (2020) In vitro evaluation of the antitumoral and antiangiogenic effects of extracts from Spondias mombin L. leaves. Biomed Pharmacother 131:110716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110716
Rocha MFG, Sales JA, Rocha MG, Galdino LM, Aguiar L, Pereira-Neto WDA, Brilhante RSN (2019) Antifungal effects of the flavonoids kaempferol and quercetin: a possible alternative for the control of fungal biofilms. Biofouling 35:320–328. https://doi.org/10.1080/08927014.2019.1604948
Rodrigues FC, Santos ATL, Machado AJT et al (2019) Chemical composition and anti-Candida potencial of the extracts of Tarenaya spinosa (Jacq.) Raf. (Cleomaceae). Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis 64:14–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cimid.2019.02.005
Romo JA, Kumamoto CA (2020) On commensalism of Candida. J Fungi 6:16–29. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6010016
Roumy V, Macedo JCR, Bonneau N, Samaillie J, Azaroual N, Encinas LA, Pinçon C (2020) Plant therapy in the Peruvian Amazon (Loreto) in case of infectious diseases and its antimicrobial evaluation. J Ethnopharmacol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2019.112411
Salazar-Aranda R, Granados-Guzmán G, Pérez-Meseguer J, González GM, Torres NW (2015) Activity of polyphenolic compounds against Candida glabrata. Molecules 20:17903–17912. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules201017903
Samuggam S et al (2021) Green synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles using Spondias mombin extract and their antimicrobial activity against biofilm-producing bacteria. Molecules 26:2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26092681
Santos ATL, Carneiro JNP, Cruz RP et al (2019a) UPLC-MS-ESI-QTOF analysis and antifungal activity of the Spondias tuberosa Arruda leaf and root hydroalcoholic extracts. Antibiotics 8:240–253. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8040240
Santos FSM, Bezerra JWA, Kamdem JP, Boligon AA, Anraku MM, Silva ARP, Santos JEG (2019b) Polyphenolic composition, antibacterial, modulator and neuroprotective activity of Tarenaya spinosa (Jacq.) Raf. (Cleomaceae). Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 9:12–17. https://doi.org/10.4103/2221-1691.250264
Santos LT, Carneiro JNP, Santos ATL et al (2019c) Antifungal effect of cafeic acid isolated and combined against yeast of genus Candida spp. Cadernos Cult Ciênc 18:24–34
Sidrim JJC, Rocha MFG (2010) Micologia médica à luz de autores contemporâneos. Guanabara Koogan, Rio de Janeiro, p 388
Silva FDS, Landell MF, Paulino GVB, Coutinho HDM, Albuquerque UP (2020a) Antifungal activity of selected plant extracts based on an ethnodirected study. Acta Bot Bras 34:442–448. https://doi.org/10.1590/0102-33062020abb0003
Silva TS, Soares AA, Rocha TM, Pimenta AT, Miron D, Silva RJ, Leal LK (2020b) Spondias mombin: quality control and anti-inflammatory activity in human neutrophils. J Herb Med. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hermed.2020.100393
Temitope OO, Ogunmodede AF, Fasusi OA, Thonda AO, Odufunwa AE (2017) Synergistic antibacterial and antifungal activities of Spondias mombin extracts and conventional antibiotic and antifungal agents on selected clinical microorganisms. Scholars J Appl Med Sci 5:307–318. https://doi.org/10.21276/sjams.2017.5.2.3
Tyers M, Wright GD (2019) Drug combinations: a strategy to extend the life of antibiotics in the 21st century. Nat Rev Microbiol 17:141–155. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-018-0141-x
Vipin C, Saptami K, Fida F, Mujeeburahiman M, Rao SS, Arun AB, Rekha PD (2020) Potential synergistic activity of quercetin with antibiotics against multidrug-resistant clinical strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. PLoS ONE 15:11-e0241304. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0241304
Wu M, Brown AC (2021) Applications of catechins in the treatment of bacterial infections. Pathogens 10:546. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10050546
Acknowledgements
The autthors are grateful to the brazilian research agencies FUNCAP, CAPES, CNPq and FINEP by the support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Methodology—antimicrobial assays (MAF, RPC and ATLS); methodology—chemical analysis (AAB, JWAB and AJTM); methodology—statistical analysis (JFSS and TSF); supervision of work—(FABC and MFBMB); coordination of the project (HDMC, JGMC and MFBMB); resources (JER, CFB and MKNS); final draft of the manuscript (ACAMM and JRF).
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statements
This article is according with to the international, national and institutional rules considering biodiversity rights.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Freitas, M.A., da Cruz, R.P., dos Santos, A.T.L. et al. HPLC–DAD analysis and antimicrobial activities of Spondias mombin L. (Anacardiaceae). 3 Biotech 12, 61 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03126-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-022-03126-1