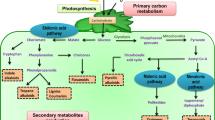
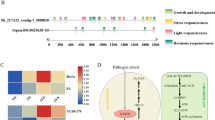
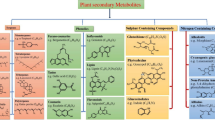
Abstract
Transcriptional factors act as mediators in regulating stress response in plants from signal perception to processing the directed gene expression. WRKY, MYB, AP2/ERF, etc. are some of the major families of transcription factors known to mediate stress mechanisms in plants by regulating the production of secondary metabolites. NAC domain-containing proteins are among these large transcription factors families in plants. These proteins play impulsive roles in plant growth, development, and various abiotic as well as biotic stresses. They are involved in regulating the different signaling pathways of plant hormones that direct a plant's immunity against pathogens, thereby affecting their immune responses. However, their role in stress regulation or defence mechanism in plants through the secondary metabolite biosynthesis pathway is studied for very few cases. Emerging concern over the requirement of medicinal plants for the production of biocompatible drugs and antibiotics, the study of these vast, affecting proteins should be focused to improve their qualitative and quantitative production further. In medicinal plants, phytochemicals and secondary metabolites are the major biochemicals that impose antimicrobial and other medicinal properties in these plants. This review compiles the NAC transcription factors reported in selected medicinal plants and their possible roles in different mechanisms. Further, the comprehensive understanding of the molecular mechanism, genetic engineering, and regulation responses of NAC TFs in medicinal plants, can lead to improvement in stress response, immunity, and production of usable secondary metabolites.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting this review are from previously reported studies and datasets, which have been cited.
References
Aeschbach R, Löliger J, Scott BC, Murcia A, Butler J, Halliwell B, Aruoma OI (1994) Antioxidant actions of thymol, carvacrol, 6-gingerol, zingerone and hydroxytyrosol. Food Chem Toxicol 32:31–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-6915(84)90033-4
Al-Lahham S, Sbieh R, Jaradat N, Almasri M, Mosa A, Hamayel A, Hammad F (2020) Antioxidant, antimicrobial and cytotoxic properties of four different extracts derived from the roots of Nicotiana tabacum L. Eur J Integr Med 33:101039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eujim.2019.101039
Amiripour M, Sadat Noori SA, Shariati V, Soltani Howyzeh M (2019) Transcriptome analysis of Ajowan (Trachyspermum ammi L.) inflorescence. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 28:496–508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13562-019-00504-4
Ariey F et al (2014) A molecular marker of artemisinin-resistant Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Nature 505:50–55. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12876
Azuma Y, Ozasa N, Ueda Y, Takagi N (1986) Pharmacological studies on the anti-inflammatory action of phenolic compounds. J Dent Res 65:53–56. https://doi.org/10.1177/00220345860650010901
Bairwa R, Sodha RS, Rajawat BS (2012) Trachyspermum Ammi. Pharmacogn Rev 6:56–60. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-7847.95871
Bhutani KK, Gohil VM (2010) Natural products drug discovery research in India: status and appraisal. Indian J Exp Biol 48:199–207
Bu Q et al (2008) Role of the Arabidopsis thaliana NAC transcription factors ANAC019 and ANAC055 in regulating jasmonic acid-signaled defense responses. Cell Res 18:756–767. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2008.53
Caretto S, Quarta A, Durante M, Nisi R, De Paolis A, Blando F, Mita G (2011) Methyl jasmonate and miconazole differently affect arteminisin production and gene expression in Artemisia annua suspension cultures. Plant Biol 13:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1438-8677.2009.00306.x
Cherukupalli N, Divate M, Mittapelli SR, Khareedu VR, Vudem DR (2016) De novo assembly of leaf transcriptome in the medicinal plant Andrographis paniculata. Front Plant Sci 7:1203. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01203
Dewey RE, Xie J (2013) Molecular genetics of alkaloid biosynthesis in Nicotiana tabacum. Phytochemistry 94:10–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2013.06.002
Dixon RA (2001) Natural products and plant disease resistance. Nature 411:843–847. https://doi.org/10.1038/35081178
Duan M et al (2017) A lipid-anchored NAC transcription factor is translocated into the nucleus and activates glyoxalase i expression during drought stress. Plant Cell 29:1748–1772. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00044
Efferth T (2006) Molecular pharmacology and pharmacogenomics of artemisinin and its derivatives in cancer cells. Curr Drug Targets 7:407–421. https://doi.org/10.2174/138945006776359412
Frerigmann H, Gigolashvili T (2014) MYB34, MYB51, and MYB122 distinctly regulate indolic glucosinolate biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Plant 7:814–828. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssu004
Fu Y, Guo H, Cheng Z, Wang R, Li G, Huo G, Liu W (2013) NtNAC-R1, a novel NAC transcription factor gene in tobacco roots, responds to mechanical damage of shoot meristem. Plant Physiol Biochem PPB 69:74–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.05.004
Fu J, Liu Q, Wang C, Liang J, Liu L, Wang Q (2018) ZmWRKY79 positively regulates maize phytoalexin biosynthetic gene expression and is involved in stress response. J Exp Bot 69:497–510. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erx436
Fujita M et al (2004) A dehydration-induced NAC protein, RD26, is involved in a novel ABA-dependent stress-signaling pathway. Plant J Cell Mol Biol 39:863–876. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02171.x
Gong ZZ, Yamagishi E, Yamazaki M, Saito K (1999) A constitutively expressed Myc-like gene involved in anthocyanin biosynthesis from Perilla frutescens: molecular characterization, heterologous expression in transgenic plants and transactivation in yeast cells. Plant Mol Biol 41:33–44. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1006237529040
Goossens A et al (2003) A functional genomics approach toward the understanding of secondary metabolism in plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:8595–8600. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1032967100
Grover A, Singh S, Pandey P, Patade VY, Gupta SM, Nasim M (2014) Overexpression of NAC gene from Lepidium latifolium L. enhances biomass, shortens life cycle and induces cold stress tolerance in tobacco: potential for engineering fourth generation biofuel crops. Mol Biol Rep 41:7479–7489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3638-z
Gujjar RS, Akhtar M, Singh M (2014) Transcription factors in abiotic stress tolerance. Indian J Plant Physiol 19:306–316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-014-0121-8
Han QQ, Qiao P, Song YZ, Zhang JY (2015) Structural analysis and tissue-specific expression patterns of a novel salt-inducible NAC transcription factor gene fromNicotiana tabacumcv. Xanthi J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 89:700–706. https://doi.org/10.1080/14620316.2014.11513140
Hao YJ et al (2011) Soybean NAC transcription factors promote abiotic stress tolerance and lateral root formation in transgenic plants. Plant J Cell Mol Biol 68:302–313. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2011.04687.x
Hong JC (2016) General aspects of plant transcription factor families. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 35–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-800854-6.00003-8
Hong E, Kim G-H (2008) Anticancer and antimicrobial activities of .BETA.-Phenylethyl Isothiocyanate in Brassica rapa L. Food Sci Technol Res 14:377–382. https://doi.org/10.3136/fstr.14.377
Hu R, Qi G, Kong Y, Kong D, Gao Q, Zhou G (2010) Comprehensive analysis of NAC domain transcription factor gene family in Populus trichocarpa. BMC Plant Biol 10:145. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-10-145
Hussein G, Miyashiro H, Nakamura N, Hattori M, Kakiuchi N, Shimotohno K (2000) Inhibitory effects of Sudanese medicinal plant extracts on hepatitis C virus (HCV) protease. Phytother Res 14:510–516. https://doi.org/10.1002/1099-1573(200011)14:7%3c510::aid-ptr646%3e3.0.co;2-b
Jensen MK, Kjaersgaard T, Petersen K, Skriver K (2010) NAC genes: time-specific regulators of hormonal signaling in Arabidopsis. Plant Signal Behav 5:907–910. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.5.7.12099
Jeong JS et al (2010) Root-specific expression of OsNAC10 improves drought tolerance and grain yield in rice under field drought conditions. Plant Physiol 153:185–197. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.154773
Jin X, Ren J, Nevo E, Yin X, Sun D, Peng J (2017) divergent evolutionary patterns of NAC transcription factors are associated with diversification and gene duplications in angiosperm. Front Plant Sci 8:1156. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01156
Kaneda T et al (2009) The transcription factor OsNAC4 is a key positive regulator of plant hypersensitive cell death. EMBO J 28:926–936. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2009.39
Kato K, Shoji T, Hashimoto T (2014) Tobacco nicotine uptake permease regulates the expression of a key transcription factor gene in the nicotine biosynthesis pathway. Plant Physiol 166:2195–2204. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.114.251645
Kennedy DO, Wightman EL (2011) Herbal extracts and phytochemicals: plant secondary metabolites and the enhancement of human brain function. Adv Nutr 2:32–50. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.110.000117
Khraiwesh B, Zhu JK, Zhu J (2012) Role of miRNAs and siRNAs in biotic and abiotic stress responses of plants. Biochem Biophys Acta 1819:137–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.05.001
Kleinow T, Himbert S, Krenz B, Jeske H, Koncz C (2009) NAC domain transcription factor ATAF1 interacts with SNF1-related kinases and silencing of its subfamily causes severe developmental defects in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci 177:360–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2009.06.011
Kolodziejczyk-Czepas J (2012) Trifolium species-derived substances and extracts–biological activity and prospects for medicinal applications. J Ethnopharmacol 143:14–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2012.06.048
Li B, Qin Y, Duan H, Yin W, Xia X (2011) Genome-wide characterization of new and drought stress responsive microRNAs in Populus euphratica. J Exp Bot 62:3765–3779. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/err051
Li S, Zhang P, Zhang M, Fu C, Yu L (2013) Functional analysis of a WRKY transcription factor involved in transcriptional activation of the DBAT gene in Taxus Chinensis. Plant Biol 15:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1438-8677.2012.00611.x
Li D et al (2014) Arabidopsis ABA receptor RCAR1/PYL9 interacts with an R2R3-type MYB transcription factor, AtMYB44. Int J Mol Sci 15:8473–8490. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15058473
Li S et al (2019) The AREB1 transcription factor influences histone acetylation to regulate drought responses and tolerance in Populus trichocarpa. Plant Cell 31:663–686. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00437
Liu C et al (2016) Characterization of a Citrus R2R3-MYB transcription factor that regulates the flavonol and hydroxycinnamic acid biosynthesis. Sci Rep 6:25352. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep25352
Lv Z et al (2016) Overexpression of a Novel NAC domain-containing transcription factor gene (AaNAC1) enhances the content of artemisinin and increases tolerance to drought and botrytis cinerea in Artemisia annua. Plant Cell Physiol 57:1961–1971. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcw118
Lv Z, Wang Y, Liu Y, Peng B, Zhang L, Tang K, Chen W (2019) The SPB-Box transcription factor AaSPL2 Positively regulates artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua L. Front Plant Sci 10:409. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00409
Mahmood K, Xu Z, El-Kereamy A, Casaretto JA, Rothstein SJ (2016) The arabidopsis transcription factor ANAC032 represses anthocyanin biosynthesis in response to high sucrose and oxidative and abiotic stresses. Front Plant Sci 7:1548. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01548
Mahmoud AL (1994) Antifungal action and antiaflatoxigenic properties of some essential oil constituents. Lett Appl Microbiol 19:110–113. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-765x.1994.tb00918.x
Manaharan T, Thirugnanasampandan R, Jayakumar R, Ramya G, Ramnath G, Kanthimathi MS (2014) Antimetastatic and anti-inflammatory potentials of essential oil from edible Ocimum sanctum leaves. Sci World J 2014:239508. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/239508
Mans DR, da Rocha AB, Schwartsmann G (2000) Anti-cancer drug discovery and development in Brazil: targeted plant collection as a rational strategy to acquire candidate anti-cancer compounds. Oncologist 5:185–198. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.5-3-185
Mitsuda N, Iwase A, Yamamoto H, Yoshida M, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Ohme-Takagi M (2007) NAC transcription factors, NST1 and NST3, are key regulators of the formation of secondary walls in woody tissues of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19:270–280. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.106.047043
Mochida K, Yoshida T, Sakurai T, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K, Tran LS (2009) Silico analysis of transcription factor repertoire and prediction of stress responsive transcription factors in soybean. DNA Res Int J Rapid Publ Rep Genes Genomes 16:353–369. https://doi.org/10.1093/dnares/dsp023
Mohanta TK et al (2020) Genomics, molecular and evolutionary perspective of NAC transcription factors. PLoS ONE 15:e0231425. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0231425
Nakashima K et al (2007) Functional analysis of a NAC-type transcription factor OsNAC6 involved in abiotic and biotic stress-responsive gene expression in rice. Plant J Cell Mol Biol 51:617–630. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03168.x
Nakashima K, Takasaki H, Mizoi J, Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2012) NAC transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochem Biophys Acta 1819:97–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.10.005
Okhuarobo A, Ehizogie Falodun J, Erharuyi O, Imieje V, Falodun A, Langer P (2014) Harnessing the medicinal properties of Andrographis paniculata for diseases and beyond: a review of its phytochemistry and pharmacology. Asian Pac J Trop Dis 4:213–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2222-1808(14)60509-0
Olsen AN, Ernst HA, Leggio LL, Skriver K (2005) NAC transcription factors: structurally distinct, functionally diverse. Trends Plant Sci 10:79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2004.12.010
Panzica GP (2016) The apparent understanding of traditional and alternative medicines by modern scientific medical culture. J Pharmacogn Phytochem 4:1
Patra B, Schluttenhofer C, Wu Y, Pattanaik S, Yuan L (2013) Transcriptional regulation of secondary metabolite biosynthesis in plants. Biochem Biophys Acta 1829:1236–1247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.09.006
Pattanayak P, Behera P, Das D, Panda SK (2010) Ocimum sanctum Linn. A reservoir plant for therapeutic applications: an overview. Pharmacogn Rev 4:95–105. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-7847.65323
Paul TGG, Basu S, Saha NC (2019) Anticancer effect of andrographis paniculata by suppression of tumor altered hypoxia signaling cascade in mouse melanoma cells. J Cancer Res Pract 6:117–123. https://doi.org/10.4103/JCRP.JCRP_9_19
Pearl IA, Darling SF (1971) Phenolic extractives of the leaves of Populus balsamifera and of P. trichocarpa. Phytochemistry 10:2844–2847. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0031-9422(00)97307-2
Prakash P, Gupta N (2005) Therapeutic uses of Ocimum sanctum Linn (Tulsi) with a note on eugenol and its pharmacological actions: a short review. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 49:125–131
Puranik S, Sahu PP, Srivastava PS, Prasad M (2012) NAC proteins: regulation and role in stress tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 17:369–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2012.02.004
Qi Y, Guo H, Li K, Liu W (2012) Comprehensive analysis of differential genes and miRNA profiles for discovery of topping-responsive genes in flue-cured tobacco roots. FEBS J 279:1054–1070. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08497.x
Quik M, O’Leary K, Tanner CM (2008) Nicotine and Parkinson’s disease: implications for therapy. Mov Disord off J Mov Disord Soc 23:1641–1652. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.21900
Rachmat A, Nugroho S, Sukma D, Aswidinnoor H, Sudarsono S (2014) Overexpression of OsNAC6 transcription factor from Indonesia rice cultivar enhances drought and salt tolerance. Emir J Food Agric 26:519. https://doi.org/10.9755/ejfa.v26i6.17672
Ramakrishna A, Ravishankar GA (2011) Influence of abiotic stress signals on secondary metabolites in plants. Plant Signal Behav 6:1720–1731. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.6.11.17613
Rastogi S et al (2014) De Novo sequencing and comparative analysis of holy and sweet basil transcriptomes. BMC Genom 15:588. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-588
Rastogi S et al (2019) Ocimum metabolomics in response to abiotic stresses: cold, flood, drought and salinity. PLoS ONE 14:e0210903. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0210903
Riechmann JL et al (2000) Arabidopsis transcription factors: genome-wide comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Science 290:2105–2110. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.290.5499.2105
Romero MR, Serrano MA, Vallejo M, Efferth T, Alvarez M, Marin JJ (2006) Antiviral effect of artemisinin from Artemisia annua against a model member of the Flaviviridae family, the bovine viral diarrhoea virus (BVDV). Planta Med 72:1169–1174. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2006-947198
Sharma SN, Jha Z, Sinha RK, Geda AK (2015) Jasmonate-induced biosynthesis of andrographolide in Andrographis paniculata. Physiol Plant 153:221–229. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12252
Singh V, Amdekar S, Verma O (2010) Ocimum Sanctum (tulsi): bio-pharmacological activities. WebmedCentral Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.9754/journal.wmc.2010.001046
Singh AK, Kumar SR, Dwivedi V, Rai A, Pal S, Shasany AK, Nagegowda DA (2017) A WRKY transcription factor from Withania somnifera regulates triterpenoid withanolide accumulation and biotic stress tolerance through modulation of phytosterol and defense pathways. New Phytol 215:1115–1131. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14663
Soltani Howyzeh M, Sadat Noori SA, Shariati JV, Amiripour M (2018) Comparative transcriptome analysis to identify putative genes involved in thymol biosynthesis pathway in medicinal plant Trachyspermum ammi L. Sci Rep 8:13405. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-31618-9
Tajidin NE, Shaari K, Maulidiani M, Salleh NS, Ketaren BR, Mohamad M (2019) Metabolite profiling of Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) Nees. young and mature leaves at different harvest ages using (1)H NMR-based metabolomics approach. Sci Rep 9:16766. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-52905-z
Takasaki H et al (2010) The abiotic stress-responsive NAC-type transcription factor OsNAC5 regulates stress-inducible genes and stress tolerance in rice. Mol Genet Genom MGG 284:173–183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-010-0557-0
Turner NJ, Hebda RJ (1990) Contemporary use of bark for medicine by two salishan native elders of Southeast Vancouver Island, Canada. J Ethnopharmacol 29:59–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-8741(90)90098-e
Utzinger J, Xiao S-H, Tanner M, Keiser J (2007) Artemisinins for schistosomiasis and beyond. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 8:105–116
Wang X, Bennetzen JL (2015) Current status and prospects for the study of Nicotiana genomics, genetics, and nicotine biosynthesis genes. Mol Genet Genom MGG 290:11–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-015-0989-7
Wang W, Jiang X, Zhang L, Chen P, Shen Y, Huang L (2011) Isolation and characteristic of SmbHLH1 gene in Salvia miltiorrhiza. China J Chinese Materia Medica 36:3416–3420
Wang J, Qi MD, Guo J, Shen Y, Lin HX, Huang LQ (2017) Cloning, subcellular localization, and heterologous expression of ApNAC1 gene from Andrographis paniculata. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi = Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi = China J Chinese Materia Medica 42:890–895. https://doi.org/10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20170217.005
Wang WL, Wang YX, Li H, Liu ZW, Cui X, Zhuang J (2018) Two MYB transcription factors (CsMYB2 and CsMYB26) are involved in flavonoid biosynthesis in tea plant [Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze]. BMC Plant Biol 18:288. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-018-1502-3
Wang H, Wang D, Jiang H (2019) Expression analysis of the NAC transcription factor family of populus in response to salt stress. Forests 10:688. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10080688
Welner DH et al (2012) DNA binding by the plant-specific NAC transcription factors in crystal and solution: a firm link to WRKY and GCM transcription factors. Biochem J 444:395–404. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20111742
Wu Y et al (2009) Dual function of Arabidopsis ATAF1 in abiotic and biotic stress responses. Cell Res 19:1279–1290. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2009.108
Xu B et al (2014) Contribution of NAC transcription factors to plant adaptation to land. Science 343:1505–1508. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1248417
Xu X, Yao X, Lu L, Zhao D (2018) Overexpression of the transcription factor NtNAC2 confers drought tolerance in tobacco. Plant Mol Biol Rep 36:543–552. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-018-1096-9
Xue GP, Way HM, Richardson T, Drenth J, Joyce PA, McIntyre CL (2011) Overexpression 2of TaNAC69 leads to enhanced transcript levels of stress up-regulated genes and dehydration tolerance in bread wheat. Mol Plant 4:697–712. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssr013
Yamaguchi M, Kubo M, Fukuda H, Demura T (2008) Vascular-related NAC-DOMAIN7 is involved in the differentiation of all types of xylem vessels in Arabidopsis roots and shoots. Plant J Cell Mol Biol 55:652–664. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03533.x
Yamani HA, Pang EC, Mantri N, Deighton MA (2016) Antimicrobial activity of tulsi (Ocimum tenuiflorum) essential oil and their major constituents against three species of bacteria. Front Microbiol 7:681. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00681
Yamasaki K, Kigawa T, Seki M, Shinozaki K, Yokoyama S (2013) DNA-binding domains of plant-specific transcription factors: structure, function, and evolution. Trends Plant Sci 18:267–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2012.09.001
Yogendra KN, Dhokane D, Kushalappa AC, Sarmiento F, Rodriguez E, Mosquera T (2017) StWRKY8 transcription factor regulates benzylisoquinoline alkaloid pathway in potato conferring resistance to late blight. Plant Sci Int J Exp Plant Biol 256:208–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2016.12.014
Yu ZX, Li JX, Yang CQ, Hu WL, Wang LJ, Chen XY (2012) The jasmonate-responsive AP2/ERF transcription factors AaERF1 and AaERF2 positively regulate artemisinin biosynthesis in Artemisia annua L. Mol Plant 5:353–365. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssr087
Yuan Y, Qi L, Yang J, Wu C, Liu Y, Huang L (2014) Erratum to: a Scutellaria baicalensis R2R3-MYB gene, SbMYB8, regulates flavonoid biosynthesis and improves drought stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture (PCTOC) 120:973–973. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-014-0686-y
Yuan X, Wang H, Cai J, Li D, Song F (2019) NAC transcription factors in plant immunity. Phytopathol Res. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42483-018-0008-0
Zhang H et al (2020) Molecular and functional characterization of CaNAC035, an NAC transcription factor from pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Front Plant Sci 11:14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00014
Zheng X, Chen B, Lu G, Han B (2009) Overexpression of a NAC transcription factor enhances rice drought and salt tolerance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 379:985–989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.12.163
Zhong R, Richardson EA, Ye ZH (2007) Two NAC domain transcription factors, SND1 and NST1, function redundantly in regulation of secondary wall synthesis in fibers of Arabidopsis. Planta 225:1603–1611. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-007-0498-y
Zhong R, Lee C, Ye ZH (2010) Functional characterization of poplar wood-associated NAC domain transcription factors. Plant Physiol 152:1044–1055. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.148270
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to Director, ICAR-NBPGR New Delhi for providing facility. RK is grateful to University Grant Commission (UGC), New Delhi for SRF fellowship. We are also thankful to Welner et al. (2012) for the protein structure of ANAC019 (PDB ID: 4DUL).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RS conceived review article topic; RK and SD did the literature review and wrote the first draft of the manuscript; RS and AK evaluated critically the literature review and edited manuscript; DRC, MM, KS were associated with the edition of the manuscript; All authors have agreed with present draft of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in the publication.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, R., Das, S., Mishra, M. et al. Emerging roles of NAC transcription factor in medicinal plants: progress and prospects. 3 Biotech 11, 425 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02970-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02970-x