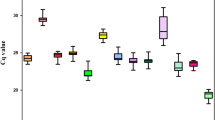
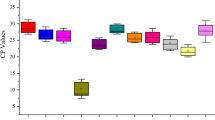
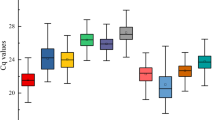
Abstract
Gene expression valuated by reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) are often applied to study the gene function. To obtain accurate and reliable results, the usage of stable reference genes is essential for RT-qPCR analysis. The traditional southern Chinese medicinal herb, Desmodium styracifolium Merr is well known for its remarkable effect on the treatment of urination disturbance, urolithiasis, edema and jaundice. However, there are no ready-made reference genes identified for D. styracifolium. In this study, 13 novel genes retrieved from transcriptome datasets of four different tissues were reported according to the coefficient of variation (CV) and maximum fold change (MFC) of gene expression. The expression stability of currently used Leguminosae ACT6 was compared to the 13 candidate reference genes in different tissues and 7-day-old seedlings under different experimental conditions, which was evaluated by five statistical algorithms (geNorm/NormFinder/BestKeeper/ΔCT/RefFinder). Our results indicated that the reference gene combinations of PP + UFM1, CCRP4 + BRM and NFD6 + NCLN1 were the most stable reference genes in leaf, stem and root tissues, respectively. The most stable reference gene combination for all tissues was CCRP4 + CUL1. In addition, the most stable reference genes for different experimental conditions were distinct, for instance SMUP1 for MeJA treatment, ERDJ2A + SMUP1 for SA treatment, NCLN1 + ERDJ2A for ABA treatment and SF3B + VAMP721d for salt stress, respectively. Our results lay a foundation for achieving accurate and reliable RT-qPCR results so as to correctly understand the function of genes in D. styracifolium.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bansal R, Mittapelly P, Cassone BJ, Mamidala P, Redinbaugh MG, Michel A (2015) Recommended reference genes for quantitative PCR analysis in soybean have variable stabilities during diverse biotic stresses. PLoS ONE 10(8):e0134890. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0134890
Borges A, Tsai SM, Caldas DG (2012) Validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR normalization in common bean during biotic and abiotic stresses. Plant Cell Rep 31(5):827–838. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1204-x
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Mueller R, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW, Shipley GL, Vandesompele J, Wittwer CT (2009) The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem 55(4):611–622. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2008.112797
Cheng X-x, Tang X-m, Guo C-c, Zhang C-r, Yang Q (2018) New flavonol glycosides from the seeds of Desmodium styracifolium. Chem Nat Compd 54(5):846–850. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10600-018-2496-7
Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Ørntoft TF (2004) Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Can Res 64:5245–5250
Committee CP (2020) Pharmacopoeia of the people’s Republic of China Part I. Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, p 46
de Jonge HJ, Fehrmann RS, de Bont ES, Hofstra RM, Gerbens F, Kamps WA, de Vries EG, van der Zee AG, te Meerman GJ, ter Elst A (2007) Evidence based selection of housekeeping genes. PLoS ONE 2(9):e898. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0000898
Gao M, Liu Y, Ma X, Shuai Q, Gai J, Li Y (2017) Evaluation of reference genes for normalization of gene expression using quantitative RT-PCR under aluminum, cadmium, and heat stresses in soybean. PLoS ONE 12(1):e0168965. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0168965
Gimeno J, Eattock N, Van Deynze A, Blumwald E (2014) Selection and validation of reference genes for gene expression analysis in switchgrass (Panicum virgatum) using quantitative real-time RT-PCR. PLoS ONE 9(3):e91474. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0091474
Guo P, Yan W, Han Q, Wang C, Zhang Z (2015) Simultaneous quantification of 25 active constituents in the total flavonoids extract from Herba Desmodii Styracifolii by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci 38(7):1156–1163. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201401360
Gutierrez L, Mauriat M, Guenin S, Pelloux J, Lefebvre JF, Louvet R, Rusterucci C, Moritz T, Guerineau F, Bellini C, Van Wuytswinkel O (2008) The lack of a systematic validation of reference genes: a serious pitfall undervalued in reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis in plants. Plant Biotechnol J 6(6):609–618. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7652.2008.00346.x
Hamilton ML, Kuate SP, Brazier-Hicks M, Caulfield JC, Rose R, Edwards R, Torto B, Pickett JA, Hooper AM (2012) Elucidation of the biosynthesis of the di-C-glycosylflavone isoschaftoside, an allelopathic component from Desmodium spp. that inhibits Striga spp. development. Phytochemistry 84:169–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2012.08.005
Hirayama H, Ikegami K, Irino N, Kajimoto T, Kubo T, Nohara T, Ou S (1989) Preventive of kidney stone containing flavonoid as active ingredient and production thereof. Japan patent JAH01305080(A)
Hirayama H, Ikegami K, Irino N, Kajimoto T, Kubo T, Nohara T, Ou S (1989) Triterpenoidalsaponin, production thereof and preventive for renal litiasis containing above-mentioned saponin derivative as active ingredient. Japan patent JPH63131390(A)
Hong SY, Seo PJ, Yang MS, Xiang F, Park CM (2008) Exploring valid reference genes for gene expression studies in Brachypodium distachyon by real-time PCR. BMC Plant Biol 8:112. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-8-112
Vandesompele Jo, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3(7):00341–003411
Joseph JT, Poolakkalody NJ, Shah JM (2018) Plant reference genes for development and stress response studies. J Biosci 43(1):173–187. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-017-9728-z
Kozera B, Rapacz M (2013) Reference genes in real-time PCR. J Appl Genet 54(4):391–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-013-0173-x
Kubista M, Andrade JM, Bengtsson M, Forootan A, Jonak J, Lind K, Sindelka R, Sjoback R, Sjogreen B, Strombom L, Stahlberg A, Zoric N (2006) The real-time polymerase chain reaction. Mol Aspects Med 27(2–3):95–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2005.12.007
Li D, Hu B, WangWu QW (2017a) The research on reference genes in medicinal plant. Mol Plant Breed 15(3):903–910. https://doi.org/10.13271/j.mpb.015.000903
Li T, Wang J, Lu M, Zhang T, Qu X, Wang Z (2017b) Selection and validation of appropriate reference genes for qRT-PCR analysis in Isatis indigotica Fort. Front Plant Sci 8:1139. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01139
Liang L, He Z, Yu H, Wang E, Zhang X, Zhang B, Zhang C, Liang Z (2020) Selection and validation of reference genes for gene expression studies in Codonopsis pilosula based on transcriptome sequence data. Sci Rep 10(1):1362. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-58328-5
Liu J, Wang Q, Sun M, Zhu L, Yang M, Zhao Y (2014) Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR normalization in Panax ginseng at different stages of growth and in different organs. PLoS ONE 9(11):e112177. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0112177
Liu M, Liu C, Chen H, Huang X, Zeng X, Zhou J, Mi S (2017) Prevention of cholesterol gallstone disease by schaftoside in lithogenic diet-induced C57BL/6 mouse model. Eur J Pharmacol 815:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.10.003
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2[-Delta Delta C(T)] method. Methods 25(4):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Nicot N, Hausman JF, Hoffmann L, Evers D (2005) Housekeeping gene selection for real-time RT-PCR normalization in potato during biotic and abiotic stress. J Exp Bot 56(421):2907–2914. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eri285
Pfaffl MW, Tichopad A, Prgomet C, Neuvians TP (2004) Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity, BestKeeper-Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotech Lett 26(6):509–515. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:bile.0000019559.84305.47
Silver N, Best S, Jiang J, Thein SL (2006) Selection of housekeeping genes for gene expression studies in human reticulocytes using real-time PCR. BMC Mol Biol 7:33. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2199-7-33
Stanton KA, Edger PP, Puzey JR, Kinser T, Cheng P, Vernon DM, Forsthoefel NR, Cooley AM (2017) A whole-transcriptome approach to evaluating reference genes for quantitative gene expression studies: a case study in mimulus. G3 7(4):1085–1095. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.116.038075
Wan H, Zhao Z, Qian C, Sui Y, Malik AA, Chen J (2010) Selection of appropriate reference genes for gene expression studies by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in cucumber. Anal Biochem 399(2):257–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2009.12.008
Wang H, Zhang X, Liu Q, Liu X, Ding S (2017) Selection and evaluation of new reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis in Epinephelus akaara based on transcriptome data. PLoS ONE 12(2):e0171646. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0171646
Wang X, Fu Y, Ban L, Wang Z, Feng G, Li J, Gao H (2015) Selection of reliable reference genes for quantitative real-time RT-PCR in alfalfa. Genes Genet Syst 90(3):175–180
Wang Y, Zhang Y, Liu Q, Tong H, Zhang T, Gu C, Liu L, Huang S, Yuan H (2021) Selection and validation of appropriate reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis of flowering stages and different genotypes of Iris germanica L. Sci Rep 11(1):9901. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-89100-y
Wang Z, Gong H, Xu X, Wei X, Wang Y, Zeng S (2020a) Transcriptome and small RNAome facilitate to study schaftoside in Desmodium styracifolium Merr. Ind Crops Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112352
Wang ZL, Gao HM, Wang S, Zhang M, Chen K, Zhang YQ, Wang HD, Han BY, Xu LL, Song TQ, Yun CH, Qiao X, Ye M (2020b) Dissection of the general two-step di-C-glycosylation pathway for the biosynthesis of (iso)schaftosides in higher plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117(48):30816–30823. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2012745117
Xie F, Xiao P, Chen D, Xu L, Zhang B (2012) miRDeepFinder: a miRNA analysis tool for deep sequencing of plant small RNAs. Plant Mol Biol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-012-9885-2
Xiong Y, Wang J, Deng J (2015) Comparison between Lysimachiae Herba and Desmodii Styracifolii Herba in pharmacological activities. China J Chin Materia Med 40(11):2106–2111
Yan H, Zhang Y, Xiong Y, Chen Q, Liang H, Niu M, Guo B, Li M, Zhang X, Li Y, Teixeira da Silva JA, Ma G (2018) Selection and validation of novel RT-qPCR reference genes under hormonal stimuli and in different tissues of Santalum album. Sci Rep 8(1):17511. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-35883-6
Zhang K, Fan W, Chen D, Jiang L, Li Y, Yao Z, Yang Y, Qiu D (2020) Selection and validation of reference genes for quantitative gene expression normalization in Taxus spp. Sci Rep 10(1):22205. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-79213-1
Zhang Y, Zhao L, Zeng Y (2014) Selection and application of reference genes for gene expression studies. Plant Physiol J. https://doi.org/10.13592/j.cnki.ppj.2014.0201
Zhou X, Wang J, Shi H, Xu H (2016) The exploration of 18S rRNA for quantitative RT-PCR as reference gene. Jilin Normal University 37(2):115–119
Funding
This work was partially supported by Grants from Key Area R&D Project of Guangdong Province (2020B020221001), Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Applied Botany (AB2018017), Guangdong Provincial Special Fund for Modern Agriculture Industry Technology Innovation Teams, China (NO.2019KJ148), Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (2015286).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This research was designed by FX, SZ and YW; ZW, FY and DS carried out the experiments; ZW performed data analysis; ZW prepared the hormonal treatment and salt stress samples; ZW drafted the manuscript; FX, SZ and YW revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
13205_2021_2954_MOESM1_ESM.docx
Supplementary file 1: Supplementary tables. Table S1 The rough candidate genes whose CV was lower than 12%. Table S2 The candidate reference genes selected according to RNA-seq data. Supplementary figures. Figure S1 Electrophoresis analysis of the specificity of primer pairs for RT-PCR amplification (a) and the RNA quality (b). In the Fig. S1(a), ‘1–16’ represent VAMP721d, PP, CCRP4, SF3B, ARI7, BRM, UFM1, NFD6, UN, SMUP1, CUL1, NCLN1, ERDJ2A, ACT6, DsCHS and 2000 bp marker, respectively. In the Fig. S1(b), ‘0’ represent the 1kb ladder marker, and ‘1–21’ represent the RNA from tissues (root, stem and leaf), MeJA, ABA, SA and salt treatment, each sample has three biological repeats. Figure S2 Dissociation curves for the reference genes tested in this study. The dissociation curves for each candidate gene showed a single peak indicated that the primers of each tested gene were specific. (DOCX 297 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Yu, F., Shi, D. et al. Selection and validation of reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis in Desmodium styracifolium Merr. 3 Biotech 11, 403 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02954-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-021-02954-x