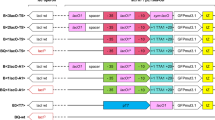
Abstract
In the area of microbial production of valuable chemicals, plasmids have been widely applied for overexpressing rate-limiting enzymes with high yields. However, the effect of antibiotic concentrations on the transcription of target genes in E. coli is less involved in previous reports. In this study, we constructed E. coli strains expressing the reporter gene and the kanamycin resistant gene in an operon, and analyzed the transcription levels of the reporter gene and the fluorescent intensity of the recombinant E. coli under different kanamycin concentrations. We found that the growth and gene transcription of the recombinant strain were affected obviously by the concentration of kanamycin, indicating the importance of fine-tuning of antibiotic concentrations in microbial fermentation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bentley WE, Mirjalili N, Andersen DC, Davis RH, Kompala DS (1990) Plasmid-encoded protein: the principal factor in the "metabolic burden" associated with recombinant bacteria. Biotechnol Bioeng 35:668–681
Chen J, Li W, Zhang ZZ, Tan TW, Li ZJ (2018) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the synthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates using acetate as a main carbon source. Microb Cell Fact 17:102
Datsenko KA, Wanner BL (2000) One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6640–6645
Einsfeldt K, Severo Junior JB, Correa Argondizzo AP, Medeiros MA, Alves TL, Almeida RV, Larentis AL (2011) Cloning and expression of protease ClpP from Streptococcus pneumoniae in Escherichia coli: study of the influence of kanamycin and IPTG concentration on cell growth, recombinant protein production and plasmid stability. Vaccine 29:7136–7143
Friehs K (2004) Plasmid copy number and plasmid stability. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 86:47–82
Glick BR (1995) Metabolic load and heterologous gene expression. Biotechnol Adv 13:247–261
Lerner CG, Inouye M (1990) Low copy number plasmids for regulated low-level expression of cloned genes in Escherichia coli with blue/white insert screening capability. Nucleic Acids Res 18:4631
Li M, Gu P, Kang J, Wang Y, Wang Q, Qi Q (2012) Extending homologous sequence based on the single gene mutants by one-step PCR for efficient multiple gene knockouts. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 57:209–214
Li Y, Huang B, Wu H, Li Z, Ye Q, Zhang YP (2016) Production of succinate from acetate by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. ACS Synth Biol 5:1299–1307
Li Y et al (2017) Current status on metabolic engineering for the production of L-aspartate family amino acids and derivatives. Bioresour Technol 245:1588–1602
Li ZJ, Qiao K, Che XM, Stephanopoulos G (2017) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the synthesis of the quadripolymer poly(glycolate-co-lactate-co-3-hydroxybutyrate-co-4-hydroxybutyrate) from glucose. Metab Eng 44:38–44
Lim HN, Lee Y, Hussein R (2011) Fundamental relationship between operon organization and gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:10626–10631
Lin XM, Yang MJ, Li H, Wang C, Peng XX (2014) Decreased expression of LamB and Odp1 complex is crucial for antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli. J Proteom 98:244–253
Marini G et al (2014) Experimental design approach in recombinant protein expression: determining medium composition and induction conditions for expression of pneumolysin from Streptococcus pneumoniae in Escherichia coli and preliminary purification process. BMC Biotechnol 14:1
Oldiges M, Eikmanns BJ, Blombach B (2014) Application of metabolic engineering for the biotechnological production of L-valine. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:5859–5870
Semenkov YuP, Katunin VI, Makarov EM, Kirillov SV (1982) Quantitative study of kanamycin action on different functions of Escherichia coli ribosomes. FEBS Lett 144:121–124
Trondle J, Trachtmann N, Sprenger GA, Weuster-Botz D (2018) Fed-batch production of L-tryptophan from glycerol using recombinant Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Bioeng 115:2881–2892
Zhu LW, Tang YJ (2017) Current advances of succinate biosynthesis in metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Adv 35:1040–1048
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31600066, 31870105, 31741007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Li, N., Jia, M. et al. The effects of kanamycin concentration on gene transcription levels in Escherichia coli. 3 Biotech 10, 93 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-2100-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-2100-2