Abstract
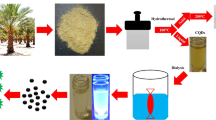
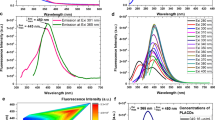
Fluorescent carbon dots (C-dots) were fabricated from Anogeissus latifolia (Gum ghatti) gum extract using direct microwave pyrolysis method. The C-dots are fine-tuned concerning three parameters, viz., NaOH addition (presence and absence), microwave power, and irradiation time. C-dots optical properties were investigated through UV–visible (UV–Vis) and fluorescence spectroscopy. Using field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and Raman Spectroscopy, physiochemical properties of synthesized C-dots were inspected. The average size of C-dots was estimated to be 4.8 ± 2 nm and is amorphous. These C-dots displayed high solubility in an aqueous medium due to oxygen functionality, and showed good fluorescence stability to high-ionic concentration and varied pH. The fluorescence spectra outcomes specified that C-dots exhibited excitation-dependent emission behavior. Furthermore, the C-dots biological function was tested for cell biocompatibility and bioimaging. The cytotoxicity studies were performed on Vero cell lines and compared with THP-1 human monocyte cell lines at different concentrations. The results revealed good biocompatibility app. 80 and 90% for Vero and THP-1 cell lines even after 24 h incubation with the C-dots. Finally, by employing C-dots as the fluorescent tool, THP-1 cells were imaged successfully via a Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (CLSM) in a concentration-dependent manner.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed GHG, Laíño RB, Calzón JAG, García MED (2016) Facile synthesis of water-soluble carbon nano-onions under alkaline conditions. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 7:758–766. https://doi.org/10.3762/bjnano.7.67
Alam AM, Park BY, Ghouri ZK et al (2015) Synthesis of carbon quantum dots from cabbage with down- and up-conversion photoluminescence properties: excellent imaging agent for biomedical applications. Green Chem 17(7):3791–3797. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5gc00686d
Atchudan R, Edison TNJI, Chakradhar D et al (2017a) Facile green synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon dots using Chionanthus retusus fruit extract and investigation of their suitability for metal ion sensing and biological applications. Sensors Actuators B Chem 393:276–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.02.119
Atchudan R, Edison TNJI, Perumal S, Lee YR (2017b) Green synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphitic carbon sheets with use of Prunus persica for supercapacitor applications. Appl Surf Sci 246:497–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.10.030
Baker SN, Baker GA (2010) Luminescent carbon nanodots: emergent nanolights. Angew Chem Int Ed 49(38):6726–6744. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn406628s
Bao L, Zhang ZL, Tian ZQ et al (2011) Electrochemical tuning of luminescent carbon nanodots: from preparation to luminescence mechanism. Adv Mater 23(48):5801–5806. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201102866
De B, Karak N (2013) A green and facile approach for the synthesis of water soluble fluorescent carbon dots from banana juice. RSC Adv 3(22):8286–8290. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ra00088e
Edison TNJI, Atchudan R, Sethuraman MG et al (2016) Microwave assisted green synthesis of fluorescent N-doped carbon dots: cytotoxicity and bio-imaging applications. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 161:154–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.05.017
Han B, Wang W, Wu H et al (2012) Polyethyleneimine modified fluorescent carbon dots and their application in cell labeling. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 100:209–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2012.05.016
Hu SL, Niu KY, Sun J et al (2009) One-step synthesis of fluorescent carbon nanoparticles by laser irradiation. J Mater Chem 19(4):484–488. https://doi.org/10.1039/b812943f
Jiang J, He Y, Li S, Cui H (2012) Amino acids as the source for producing carbon nanodots: microwave assisted one-step synthesis, intrinsic photoluminescence property and intense chemiluminescence enhancement. Chem Commun 48(77):9634–9636. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cc34612e
Kora AJ, Rastogi L (2018) Green synthesis of palladium nanoparticles using gum ghatti (Anogeissus latifolia) and its application as an antioxidant and catalyst. Arab J Chem 11(7):1097–1106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2015.06.024
Li CL, Ou CM, Huang CC et al (2014) Carbon dots prepared from ginger exhibiting efficient inhibition of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. J Mater Chem B 2(28):4564–5457. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4tb00216d
Li H, He X, Liu Y et al (2011) One-step ultrasonic synthesis of water-soluble carbon nanoparticles with excellent photoluminescent properties. Carbon 49(2):605–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2010.10.004
Liao J, Cheng Z, Zhou L (2016) Nitrogen-doping enhanced fluorescent carbon dots: green synthesis and their applications for bioimaging and label-free detection of Au3+ ions. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:3053–3061. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b00018
Liu C, Zhang P, Zhai X et al (2012) Nano-carrier for gene delivery and bioimaging based on carbon dots with PEI-passivation enhanced fluorescence. Biomaterials 33(13):3604–3613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.01.052
Liu W, Diao H, Chang H et al (2017) Green synthesis of carbon dots from rose-heart radish and application for Fe3+ detection and cell imaging. Sensors Actuators B Chem B241:190–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.10.068
Meng W, Bai X, Wang B et al (2019) Biomass-derived carbon dots and their applications. Energy Environ Mater 2:172–192. https://doi.org/10.1002/eem2.12038
Philippidis A, Stefanakis D, Anglos D, Ghanotakis D (2013) Microwave heating of arginine yields highly fluorescent nanoparticles. J Nanoparticle Res 15:1414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1414-3
Qu S, Wang X, Lu Q et al (2012) A biocompatible fluorescent ink based on water-soluble luminescent carbon nanodots. Angew Chemie 51(49):12381–12384. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.201206791
Raveendran V, Suresh Babu AR, Renuka NK (2019) Mint leaf derived carbon dots for dual analyte detection of Fe(iii) and ascorbic acid. RSC Adv 9:12070–12077. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ra02120e
Rizvi SB, Ghaderi S, Keshtgar M, Seifalian AM (2010) Semiconductor quantum dots as fluorescent probes for in vitro and in vivo bio-molecular and cellular imaging. Nano Rev 1(1):5161. https://doi.org/10.3402/nano.v1i0.5161
Roy M, Kusurkar TS, Maurya SK et al (2014) Graphene oxide from silk cocoon: a novel magnetic fluorophore for multi-photon imaging. 3 Biotech 4:67–75. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-013-0128-2
Sahu S, Behera B, Maiti TK, Mohapatra S (2012) Simple one-step synthesis of highly luminescent carbon dots from orange juice: application as excellent bio-imaging agents. Chem Commun 48(70):8835–8837. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cc33796g
Samak DH, El-Sayed YS, Shaheen HM et al (2018) In-ovo exposed carbon black nanoparticles altered mRNA gene transcripts of antioxidants, proinflammatory and apoptotic pathways in the brain of chicken embryos. Chem Biol Interact 295:133–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2018.02.031
Samak DH, El-Sayed YS, Shaheen HM et al (2020) Developmental toxicity of carbon nanoparticles during embryogenesis in chicken. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:19058–19072. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-3675-6
Singh R (2019) Nanotechnology based therapeutic application in cancer diagnosis and therapy. 3 Biotech 9:415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1940-0
Song L, Cui Y, Zhang C et al (2016) Microwave-assisted facile synthesis of yellow fluorescent carbon dots from o-phenylenediamine for cell imaging and sensitive detection of Fe3+ and H2O2. RSC Adv 6:17704–17712. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra02554d
Sun YP, Zhou B, Lin Y et al (2006) Quantum-sized carbon dots for bright and colorful photoluminescence. J Am Chem Soc 128(24):7756–7757. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja062677d
Tripathi KM, Tran TS, Tung TT et al (2017) Water soluble fluorescent carbon nanodots from biosource for cells imaging. J Nanomater 2017:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7029731
Vallabani NVS, Singh S (2018) Recent advances and future prospects of iron oxide nanoparticles in biomedicine and diagnostics. 3 Biotech 8:279. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-018-1286-z
Wang D, Wang X, Guo Y et al (2014) Luminescent properties of milk carbon dots and their sulphur and nitrogen doped analogues. RSC Adv 4(93):51658–516665. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra11158c
Wang L, Bi Y, Hou J et al (2016) Facile, green and clean one-step synthesis of carbon dots from wool: application as a sensor for glyphosate detection based on the inner filter effect. Talanta 160:268–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.07.020
Wang Q, Liu X, Zhang L, Lv Y (2012) Microwave-assisted synthesis of carbon nanodots through an eggshell membrane and their fluorescent application. Analyst 137(22):5392–5397. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2an36059d
Wei J, Liu B, Yin P (2014) Dual functional carbonaceous nanodots exist in a cup of tea. RSC Adv 4(108):63414–63419. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra11152d
Wu ZL, Zhang P, Gao MX et al (2013) One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of highly luminescent nitrogen-doped amphoteric carbon dots for bioimaging from Bombyx mori silk-natural proteins. J Mater Chem B 1(22):2868–2873. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3tb20418a
Yang Y, Cui J, Zheng M et al (2012) One-step synthesis of amino-functionalized fluorescent carbon nanoparticles by hydrothermal carbonization of chitosan. Chem Commun 48(3):380–382. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1cc15678k
Zhang J, Yu SH (2016) Carbon dots: large-scale synthesis, sensing and bioimaging. Mater Today 19(7):382–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2015.11.008
Zhang X, Lu J, Zhou X et al (2017) Rapid microwave synthesis of N-doped carbon nanodots with high fluorescence brightness for cell imaging and sensitive detection of iron (III). Opt Mater (Amst) 64:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2016.11.026
Acknowledgements
Author Anithadevi sincerely thank Dr. L. Sujatha and Dr. Suresh, MEMS Department, Raja Lakshmi Engineering College for providing analytical facility. We honor Madras Christian College, Chennai, Tamil Nadu for providing the facilities. We acknowledge our Principal Dr. P. Wilson and Head of Chemistry Department Dr. E. Iyyappan, for their encouragement.
Funding
No funds, grants, or other support was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors have contributed to the structural formation of this work. Anithadevi Sekar designed and participated in all experimental procedures, performed data analysis, and drafted the manuscript. Ganesh Munuswamy-Ramanujam provided help in performing biological studies. Rakhi Yadav and Pandian Kannaiyan supervised the study and revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in the publication.
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sekar, A., Yadav, R., Kannaiyan, P. et al. Evaluation of biopolymer-derived carbon dots as cancer diagnostic biomarkers for human monocyte cell lines (THP-1). 3 Biotech 11, 31 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02568-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02568-9