Abstract
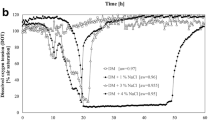
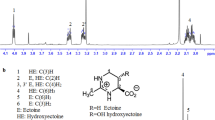
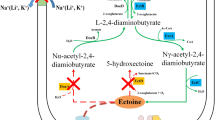
In the present study, the growth conditions and accumulation of ectoines (ectoine and hydroxyectoine) by Paludifilum halophilum DSM 102817T under salt stress conditions have been investigated. The productivity assay of this strain for ectoines revealed that the highest cellular content was reached in the minimal glucose sea water medium (SW-15) within 15% salinity. The addition of 0.1% (w/v) aspartic acid to the medium allowed an average of four times higher biomass production, and a dry mycelial biomass of 1.76 g L−1 was obtained after 6 days of growth in shake flasks at 40 °C and 200 rpm. Among the inorganic cations supplemented to the glucose SW-15 medium, the addition of 1 mM Fe2+ yielded the highest amount of mycelial biomass (3.45 g L−1) and total ectoines content (119 mg g−1), resulting in about 410 mg L−1 of products at the end of exponential growth phase. After 1 h of incubation in an osmotic downshock solution containing 2% NaCl, 70% of this content was released by the mycelium, and recovering cells maintained a high survival, with a maximal growth rate (µmax) of about 93% of the control population exposed to 15% NaCl. During growth at optimal salinity and temperature (15% NaCl and 40 °C), P. halophilum developed a compact and circular pellets that were easy to separate by simple decantation from both fermentation media and after hypoosmotic shock. Overall, the ectoines excreting P. halophilum could be a promising resource for ectoines production in a commercially valuable culture medium and at a large-scale fermentation process.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Argandona M, Nieto JJ, Iglesias-Guerra F, Calderon MI, Garcia-Estepa R, Vargas C (2010) Interplay between iron homeostasis and the osmotic stress response in the halophilic bacterium Chromohalobacter salexigens. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:3575–3589
Barth S, Huhn M, Matthey B, Klimka A, Galinski EA, Engert A (2000) Compatible-solute-supported periplasmic expression of functional recombinant proteins under stress conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:1572–1579
Ben Abdallah M, Karray F, Kallel N, Armougom F, Mhiri N, Quéméneur M, Cayol JL, Erauso G, Sayadi S (2018) Abundance and diversity of prokaryotes in ephemeral hypersaline lake Chott El Jerid using Illumina Miseq sequencing, DGGE and qPCR assays. Extremophiles 22:811–823
Borges N, Ramos A, Raven NDH, Sharp RJ (2002) Comparative study of the thermostabilizing properties of mannosylglycerate and other compatible solutes on model enzymes. Extremophiles 6:209–216
Boujelben I, Martínez-García M, van Pelt J, Maalej S (2015) Diversity of cultivable halophilic archaea and bacteria from superficial hypersaline sediments of Tunisian solar salterns. Antony van Leeuwenhoeck 106:675–692
Brands S, Schein P, Castro-Ochoa KF, Galinski EA (2019) Hydroxyl radical scavenging of the compatible solute ectoine generates two N-acetimides. Arch Biochem Biophys 674:108097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2019.108097
Bünger J, Driller H (2004) Ectoine: an effective natural substance to prevent UVA-induced premature photoaging. Skin Pharmacol Physiol 17:232–237
Bursy J, Pierik AJ, Pica N, Bremer E (2007) Osmotically induced synthesis of the compatible solute hydroxyectoine is mediated by an evolutionarily conserved ectoine hydroxylase. J Biol Chem 282:31147–31155
Bursy J, Kuhlmann AU, Pittelkow M, Hartmann H, Jebbar M, Pierik AJ, Bremer E (2008) Synthesis and uptake of the compatible solutes ectoine and 5-hydroxyectoine by Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) in response to salt and heat stresses. Appl Environ Bacteriol 74:7286–7296
Da Costa MS, Santos H, Galinski EA (1998) An overview of the role and diversity of compatible solutes in Bacteria and Archaea. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 61:117–153
Deng Y, Huang L, Zhang C, Xie P, Cheng J, Wang X (2019) Physicochemical and functional properties of water soluble gum from Chaenomeles speciosa seeds. J Bioresour Bioprod 4:222–230
Detkova EN, Boltyanskaya YV (2007) Osmoadaptation of haloalkaliphilic bacteria: role of osmoregulators and their possible practical application. Microbiology 76:511–522
Eiberweiser A, Nazet A, Kruchinin SE, Fedotova MV, Buchner R (2015) Hydration and ion binding of the osmolyte ectoine. J Phys Chem B 119:15203–15211
Frikha-Dammak D, Fardeau ML, Cayol JL, Ben Fguira-Fourati L, Najeh S, Ollivier B, Maalej S (2016) Paludifilum halophilum gen. nov. sp. nov. a thermoactinomycete isolated from superficial sediment of a solar saltern. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:1–8
Galinski EA, Pfeiffer HP, Trüper HG (1985) 1,4,5,6-Tetrahydro-2-methyl-4-pyrimidinecarboxylic acid. A novel cyclic amino acid from halophilic phototrophic bacteria of the genus Ectothiorhodospira. Eur J Biochem 149:135–139
Graf R, Anzali S, Buenger J, Pfluecker F, Driller H (2008) The multifunctional role of ectoine as a natural cell protectant. Clin Dermatol 26:326–333
Guzmán H, Van-Thuoc D, Martín J, Hatti-Kaul R, Quillaguamán J (2009) A process for the production of ectoine and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) by Halomonas boliviensis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 84:1069–1077
Han J, Gao Q-X, Zhang Y-G, Li L, Mohamad OAA, Narsing Rao MP, Xiao M, Hozzein WN, Alkhalifah DHM, Tao Y, Li W-J (2018) Transcriptomic and ectoine analysis of halotolerant Nocardiopsis gilva YIM 90087T under salt stress. Front Microbiol 9:618
Harishchandra RK, Wulff S, Lentzen G, Neuhaus T, Galla HJ (2010) The effect of compatible solute ectoines on the structural organization of lipid monolayer and bilayer membranes. Biophys Chem 150:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpc.2010.02.007
He YZ, Gong J, Yu HY, Tao Y, Zhang S, Dong ZY (2015) High production of ectoine from aspartate and glycerol by use of whole-cell biocatalysis in recombinant Escherichia coli. Microb Cell Fact 14:55
Hille A, Neu TR, Hempel DC, Horn H (2005) Oxygen profiles and biomass distribution in biopellets of Aspergillus niger. Biotechnol Bioeng 92:614–623
Ignatova Z, Gierasch LM (2006) Inhibition of protein aggregation in vitro and in vivo by a natural osmoprotectant. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:13357–13361
Ikeda H, Ishikawa J, Hanamoto A, Shinose M, Kikuchi H, Shiba T, Sakaki Y, Hattori M, Omura S (2003) Complete genome sequence and comparative analysis of the industrial microorganism Streptomyces avermitilis. Nat Biotechnol 21:526–531
Inbar L, Lapidot A (1988) The structure and biosynthesis of new tetrahydropyrimidine derivatives in actinomycin D producer Streptomyces parvulus. Use of 13C- and 15N-labeled L-glutamate and 13C and 15N NMR spectroscopy. J Biol Chem 263:16014–16022
Jorge CD, Borges N, Bagyan I, Bilstein A, Santos H (2016) Potential applications of stress solutes from extremophiles in protein folding diseases and healthcare. Extremophiles 20:251–259
Kempf B, Bremer E (1998) Uptake and synthesis of compatible solutes as microbial stress responses to high osmolality environments. Arch Microbiol 170:319–330
Klauck E, Typas A, Hengge R (2007) The sigmaS subunit of RNA polymerase as a signal integrator and network master regulator in the general stress response in Escherichia coli. Sci Prog 90:103–127
Kolp S, Pietsch M, Galinski EA, Gutschow M (2006) Compatible solutes as protectants for zymogens against proteolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1764:1234–1242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2006.04.015
Kunte HJ, Galinski EA, Trüper HG (1993) A modified FMOC-method for the detection of aminoacid type osmolytes and tetrahydropyrimidines (ectoines). J Microbiol Methods 17:129–136
Kunte HJ, Lentzen G, Galinski E (2014) Industrial production of the cell protectant ectoine: protection, mechanisms, processes, and products. Curr Biotechnol 3:10–25
Lentzen G, Schwarz T (2006) Extremolytes: natural compounds from extremophiles for versatile applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 72:623–634
León MJ, Hoffmann T, Sánchez-Porro C, Heider J, Ventosa A, Bremer E (2018) Compatible solute synthesis and import by the moderate halophile Spiribacter salinus: physiology and genomics. Front Microbiol 9:108
Liu KH, Ding XW, Narsing Rao MP, Zhang B, Zhang YG, Liu FH (2017) Morphological and transcriptomic analysis reveals the osmoadaptive response of endophytic fungus Aspergillus montevidensis ZYD4 to high salt stress. Front Microbiol 8:1789
Malin G, Lapidot A (1996) Induction of synthesis of tetrahydropyrimidine derivatives in Streptomyces strains and their effect on Escherichia coli in response to osmotic and heat stress. J Bacteriol 178:385–395
Motta A, Romano I, Gambacorta A (2004) Rapid and sensitive NMR method for osmolyte determination. J Microbiol Methods 58:289–294
O’Cleirigh C, Casey JT, Walsh PK, O’Shea DG (2005) Morphological engineering of Streptomyces hygroscopicus var.geldanus: regulation of pellet morphology through manipulation of broth viscosity. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:305–310
Ono H, Sawada K, Khunajakr N, Tao T, Yamamoto M, Hiramoto M, Shinmyo A, Takano M, Murooka Y (1999) Characterization of biosynthetic enzymes for ectoine as a compatible solute in a moderately halophilic eubacterium, Halomonas elongata. J Bacteriol 181:91–99
Onraedt AE, Walcarius BA, Soetaert WK, Vandamme EJ (2005) Optimization of ectoine synthesis through fed-batch fermentation of Brevibacterium epidermis. Biotechnol Prog 21:1206–1212
Oren A (2002) Intracellular salt concentration and ion metabolism in halophilic microorganisms. In: Seckbach J (ed) Halophilic microorganisms and their environments, 5th edn. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 207–231
Oren A (2013) Life at high salt concentrations, intracellular KCl concentrations, and acidic proteomes. Front Microbiol 4:315
Öztürk HU, Sariyar Akbulut B, Ayan B, Poli A (2015) Moderately halophilic bacterium Halomonas sp. AAD12: a promising candidate as a hydroxyectoine producer. J Microb Biochem Technol 7:262–268
Pastor JM, Salvador M, Argandona M, Bernal V, Reina-Bueno M, Csonka LN, Iborra JL, Vargas C, Nieto JJ, Canovas M (2010) Ectoines in cell stress protection: uses and biotechnological production. Biotechnol Adv 28:782–801
Prabhu J, Schauwecker F, Grammel N, Keller U, Bernhard M (2004) Functional expression of the ectoine hydroxylase gene (thpD) from Streptomyces chrysomallus in Halomonas elongata. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:3130–3132
Rani A, Venkatesu P (2018) Changing relations between proteins and osmolytes: a choice of nature. Phys Chem Chem Phys 20:20315–20333
Reshetnikov AS, Khmelenina VN, Mustakhimov II, Trotsenko YA (2011) Genes and enzymes of ectoine biosynthesis in halotolerant methanotrophs. Methods Enzymol 495:15–30
Reuter K, Pittelkow M, Bursy J, Heine A, Craan T, Bremer E (2010) Synthesis of 5-hydroxyectoine from ectoine: crystal structure of the non-heme iron(II) and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase EctD. PLoS ONE 5(5):e10647. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0010647
Richter AA, Mais C-N, Czech L, Geyer K, Hoeppner A, Smits SHJ, Erb TJ, Bange G, Bremer E (2019) Biosynthesis of the stress-protectant and chemical chaperon ectoine: biochemistry of the transaminase EctB. Front Microbiol 10:2811. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02811
Roberts MF (2005) Organic compatible solutes of halotolerant and halophilic microorganism. Saline Syst 1:5
Sadeghi A, Soltani BM, Nekouei MK, Jouzani GS, Mirzaei HH, Sadeghizadeh M (2014) Diversity of the ectoines biosynthesis genes in the salt tolerant Streptomyces and evidence for inductive effect of ectoines on their accumulation. Microbiol Res 169:699–708
Sauer T, Galinski EA (1998) Bacterial milking: a novel bioprocess for production of compatible solutes. Biotechnol Bioeng 57:306–313
Schröter MA, Meyer S, Hahn MB, Solomun T, Sturm H, Kunte HJ (2017) Ectoine protects DNA from damage by ionizing radiation. Sci Rep 7:15272. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-15512-4
Sinha J, Bae JT, Park JP, Kim KH, Song CH, Yun JW (2001) Changes in morphology of Paecilomyces japonika and their effect on broth reology during production of exo-biopolymers. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:88–92
Tao P, Li H, Yu Y, Gu J, Liu Y (2016) Ectoine and 5-hydroxyectoine accumulation in the halophile Virgibacillus halodenitrificans PDB-F2 in response to salt stress. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100:6779–6789
Tesche S, Rösemeier-Scheumann R, Lohr J, Hanke R, Büchs J, Krull R (2019) Salt-enhanced cultivation as a morphology engineering tool for filamentous actinomycetes: increased production of labyrinthopeptin A1 in Actinomadura namibiensis. Eng Life Sci 19:781–794
Van Dissel D, Claessen D, van Wezel GP (2014) Morphogenesis of Streptomyces in submerged cultures. Adv Appl Microbiol 89:1–45
Van-Thuoc D, Guzmán H, Quillaguamán J, Hatti-Kaul R (2010) High productivity of ectoines by Halomonas boliviensis using a combined twostep fed-batch culture and milking process. J Biotechnol 147:46–51
Van-Thuoc D, Hashim SO, Hatti-Kaul R, Mamo G (2013) Ectoine mediated protection of enzyme from the effect of pH and temperature stress: a study using Bacillus halodurans xylanase as a model. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:6271–6278
Van-Thuoc D, Thi Hien T, Sudesh K (2019) Identification and characterization of ectoine-producing bacteria isolated from Can Gio mangrove soil in Vietnam. Ann Microbiol 69:819–828
Vargas C, Jebbar M, Carrasco R, Blanco C, Calderon M, Iglesias-guerra F, Nieto JJ (2005) Ectoines as compatible solutes and carbon and energy sources for the halophilic bacterium Chromohalobacter salexigens. J Appl Microbiol 100:98–107
Vyrides I, Stuckey DC (2017) Compatible solute addition to biological systems treating waste/wastewater to counteract osmotic and other environmental stresses: a review. Crit Rev Biotechnol 37:865–879
Wei-Chuan C, Ching-Cha H, John Chi-Wei L, Yu-Kaung C, Li-Fen W, Yu-Hong W (2017) Production and characterization of ectoine using a moderately halophilic strain Halomonas salina BCRC17875. J Biosci Bioeng 125:1–7
Werkhäuser N, Bilstein A, Sonnemann U (2014) Treatment of allergic rhinitis with ectoine containing nasal spray and eye drops in comparison with azelastine containing nasal spray and eye drops or with cromoglycic acid containing nasal spray. J Allergy. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/176597
Widderich N, Kobus S, Höppner A, Riclea R, Seubert A, Dickschat JS, Heider J, Smits SHJ, Bremer E (2016) Biochemistry and crystal structure of ectoine synthase: a metal-containing member of the cupin superfamily. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0151285
Wucherpfennig T, Kiep KA, Driouch H, Wittmann C, Krull R (2010) Morphology and rheology in filamentous cultivations. Adv Appl Micobiol 72:89–136
Zhang Y, Li Y, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Zhao M, Su N et al (2016) Quantitative proteomics reveals membrane protein-mediated hypersaline sensitivity and adaptation in halophilic Nocardiopsis xinjiangensis. J Proteome Res 15:68–85
Zhao Q, Shannan L, Peiwen L, Simian S, Cuiqing M, Ping X, Haijun S, Chunyu Y (2019) High ectoine production by an engineered Halomonas hydrothermalis Y2 in a reduced salinity medium. Microb Cell Fact 18:184
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the General Direction of Scientific Research (DGRS) of Tunisia for financial support through the project PRF No PRF2019-D1P1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ayadi, H., Frikha-Dammak, D., Fakhfakh, J. et al. The saltern-derived Paludifilum halophilum DSM 102817T is a new high-yield ectoines producer in minimal medium and under salt stress conditions. 3 Biotech 10, 533 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02512-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02512-x