Abstract
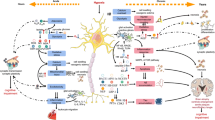
The aim of this study was to explore the underlying mechanism and function of dexmedetomidine (Dex)-regulated long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in improving postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD) in rats. The established POCD model, Dex treatment model in rats, Morris water maze testing, and HE staining assays were used to evaluate the efficacy of Dex in POCD treatment in rats. Hippocampus samples of rats from the POCD group and the Dex group were used for lncRNA sequencing. The expression of five differentially expressed lncRNAs (DElncRNAs) was verified by quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR). Competing endogenous RNAs (ceRNA) network was constructed using Cytoscape. The concentration of inflammatory cytokines were measured by ELISA. Microglia proliferation and apoptosis were assessed using CCK-8 assay and flow cytometry, respectively. In the Dex group, the escape latency was shorter, neuron cell injury levels were alleviated, and the expression levels of TNF-α and IL-1β were significantly down-regulated compared with the POCD group. A total of 60 DE lncRNAs were identified, including 16 up- and 44 down-regulated lncRNAs in the Dex group. KEGG pathway analysis revealed that DElncRNAs were significantly enriched in cytokine–cytokine receptor interactions, the p53 signaling pathway, and the NF-kappa B signaling pathway. The qRT-PCR results and ceRNA network suggested that the lncRNA LOC102546895 may play a key role in POCD. LOC102546895 inhibited proliferation while promoting apoptosis in microglial cells and promoted the mRNA and protein expression of the target gene Npas4. Our findings showed that Dex alleviated POCD in rats and regulated lncRNAs expression profile in the hippocampus tissues of rats with POCD. In conclusion, our study outcome proposes that Dex-regulated lncRNA LOC102546895 may play a role in rats with POCD through targeting Npas4.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bharadwaj S, Kamath S (2019) Postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Textb Neuroanesthesia Neurocrit Care. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-3387-3_34
Blasi E, Barluzzi R, Bocchini V, Mazzolla R, Bistoni F (1990) Immortalization of murine microglial cells by a v-raf/v-myc carrying retrovirus. J Neuroimmunol 27(2):229–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-5728(90)90073-v
Carr ZJ, Cios TJ, Potter KF, Swick JT (2018) Does dexmedetomidine ameliorate postoperative cognitive dysfunction? A brief review of the recent literature. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 18(10):64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-018-0873-z
Choy FC, Klaric TS, Koblar SA, Lewis MD (2015) The role of the neuroprotective factor Npas4 in cerebral ischemia. Int J Mol Sci 16(12):29011–29028. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226144
Choy FC, Klaric TS, Leong WK, Koblar SA, Lewis MD (2016) Reduction of the neuroprotective transcription factor Npas4 results in increased neuronal necrosis, inflammation and brain lesion size following ischaemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 36(8):1449–1463. https://doi.org/10.1177/0271678X15606146
Coutellier L, Beraki S, Ardestani PM, Saw NL, Shamloo M (2012) Npas4: a neuronal transcription factor with a key role in social and cognitive functions relevant to developmental disorders. PLoS ONE 7(9):e46604. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0046604
Dawson LF, Phillips JK, Finch PM, Inglis JJ, Drummond PD (2011) Expression of α 1-adrenoceptors on peripheral nociceptive neurons. Neuroscience 175:300–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.11.064
Deiner S, Luo X, Silverstein JH, Sano M (2015) Can intraoperative processed EEG predict postoperative cognitive dysfunction in the elderly? Clin Ther 37(12):2700–2705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.11.004
Dresselhaus EC, Meffert MK (2019) Cellular specificity of NF-kappaB function in the nervous system. Front Immunol 10:1043. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01043
Fang Q, Qian X, An J, Wen H, Cope DK, Williams JP (2014) Higher dose dexamethasone increases early postoperative cognitive dysfunction. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 26(3):220–225. https://doi.org/10.1097/ANA.0000000000000024
Green CM, Schaffer SD (2019) Postoperative cognitive dysfunction in noncardiac surgery: a review. Trends Anaesth Crit Care 24:40–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tacc.2018.08.003
Hem S, Albite R, Loresi M, Rasmussen J, Ajler P, Yampolsky C, Chabot JD, Gerszten PC, Goldschmidt E (2016) Pathological changes of the hippocampus and cognitive dysfunction following frontal lobe surgery in a rat model. Acta Neurochir 158(11):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-016-2938-6
Huang Y, Wang JP, Yu XL, Wang ZB, Xu TS, Cheng XC (2013) Non-coding RNAs and diseases. Mol Biol+ 47(4):465–475. https://doi.org/10.1134/s0026893313040171
Hudetz JA, Iqbal Z, Gandhi SD, Patterson KM, Byrne AJ, Hudetz AG, Pagel PS, Warltier DC (2009) Ketamine attenuates post-operative cognitive dysfunction after cardiac surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 53(7):864–872. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-6576.2009.01978.x
Huupponen E, Maksimow A, Lapinlampi P, Särkelä M, Saastamoinen A, Snapir A, Scheinin H, Scheinin M, Meriläinen P, Himanen SL, Jääskeläinen S (2010) Electroencephalogram spindle activity during dexmedetomidine sedation and physiological sleep. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 52(2):289–294. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-6576.2007.01537.x
Jacob S, Karl Bang C, Thomas L, Nicolai L, Rasmussen LS (2009) Long-term consequences of postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Anesthesiology 110(3):548–555. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0b013e318195b569
Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Beals J, Benshoff N, Olney JW (2003) Prolonged exposure to inhalational anesthetic nitrous oxide kills neurons in adult rat brain. Neuroscience 122(3):609–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2003.07.012
Li L, Zhang Y, Luo H, Huang C, Li S, Liu A, Jiang Y (2019) Systematic identification and analysis of expression profiles of mRNAs and incrnas in macrophage inflammatory response. Shock 51(6):770–779. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0000000000001181
Liu Y, Ma L, Gao M, Guo W, Ma Y (2016) Dexmedetomidine reduces postoperative delirium after joint replacement in elderly patients with mild cognitive impairment. Aging Clin Exp Res 28(4):729–736. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-015-0492-3
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25(4):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lu J, Chen G, Zhou H, Zhou Q, Zhu Z, Wu C (2017) Effect of parecoxib sodium pretreatment combined with dexmedetomidine on early postoperative cognitive dysfunction in elderly patients after shoulder arthroscopy: a randomized double blinded controlled trial. J Clin Anesth 41:30–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinane.2017.06.004
Mario C, Antonio Rei F, Niccolò T, Daqing M, Claudia M, Marc F, Masao T, Lever IJ, Jagdeep N, Fanselow MS (2010) Role of interleukin-1β in postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Ann Neurol 68(3):360–368. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22082
Qian XL, Zhang W, Liu MZ, Zhou YB, Zhang JM, Han L, Peng YM, Jiang JH, Wang QD (2015) Dexmedetomidine improves early postoperative cognitive dysfunction in aged mice. Eur J Pharmacol 746:206–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.11.017
Ramamoorthi K, Fropf R, Belfort GM, Fitzmaurice HL, McKinney RM, Neve RL, Otto T, Lin Y (2011) Npas4 regulates a transcriptional program in CA3 required for contextual memory formation. Science 334(6063):1669–1675. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1208049
Ren S, Peng Z, Mao JH, Yu Y, Yin C, Gao X, Cui Z, Zhang J, Yi K, Xu W, Chen C, Wang F, Guo X, Lu J, Yang J, Wei M, Tian Z, Guan Y, Tang L, Xu C, Wang L, Gao X, Tian W, Wang J, Yang H, Wang J, Sun Y (2012) RNA-seq analysis of prostate cancer in the Chinese population identifies recurrent gene fusions, cancer-associated long noncoding RNAs and aberrant alternative splicings. Cell Res 22(5):806–821. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2012.30
Stegh AH (2012) Targeting the p53 signaling pathway in cancer therapy - the promises, challenges and perils. Expert Opin Ther Targets 16(1):67–83. https://doi.org/10.1517/14728222.2011.643299
Sui J, Li YH, Zhang YQ, Li CY, Shen X, Yao WZ, Peng H, Hong WW, Yin LH, Pu YP, Liang GY (2016) Integrated analysis of long non-coding RNAassociated ceRNA network reveals potential lncRNA biomarkers in human lung adenocarcinoma. Int J Oncol 49(5):2023–2036. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2016.3716
Terrando N, Monaco C, Ma D, Foxwell BM, Feldmann M, Maze M (2010) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha triggers a cytokine cascade yielding postoperative cognitive decline. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(47):20518–20522. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1014557107
Vousden KH, Lane DP (2007) p53 in health and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8(4):275–283. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm2147
Walsh CM, Booth V, Poe GR (2011) Spatial and reversal learning in the Morris water maze are largely resistant to six hours of REM sleep deprivation following training. Learn Mem 18(7):422–434. https://doi.org/10.1101/lm.2099011
Wang WX, Wu Q, Liang SS, Zhang XK, Hu Q, Chen QH, Huang HJ, Xu L, Lou FQ (2018) Dexmedetomidine promotes the recovery of neurogenesis in aged mouse with postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Neurosci Lett 677:110–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2018.03.043
Xiang H, Hu B, Li Z, Li J (2014) Dexmedetomidine controls systemic cytokine levels through the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Inflammation 37(5):1763–1770. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9906-1
Yan Y, Ye W, Chen Q, Yang L, Zhang L, Liu Y, Zhou X, Wang G (2018) Differential expression profile of long non-coding RNA in the stenosis tissue of arteriovenous fistula. Gene 664:127–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.04.028
Zhang L, Fang Y, Cheng X, Lian YJ, Xu HL (2019) Silencing of long noncoding RNA SOX21-AS1 relieves neuronal oxidative stress injury in mice with alzheimer’s disease by upregulating FZD3/5 via the Wnt signaling pathway. Mol Neurobiol 56(5):3522–3537. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1299-y
Zywiel MG, Prabhu A, Perruccio AV, Gandhi R (2014) The influence of anesthesia and pain management on cognitive dysfunction after joint arthroplasty: a systematic review. Clin Orthop Related Res 472(5):1453–1466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-013-3363-2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: ZZ and GX. Data curation: ZZ and GX. Formal analysis: FD and LC. Funding acquisition: ZZ and GX. Investigation: FD, LC and BZ. Methodology: FD, LC and BZ. Software: FD. Writing—original draft: FD and LC. Writing—review and editing: FD, LC and BZ. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All rat experiments completely adhered to the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (National Institutes of Health). All the experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the second affiliated hospital of Nanchang university.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplement Table 4.
The specific information detailing DE lncRNAs (XLSX 15 kb)
Supplement Table 5.
The specific information detailing DE mRNAs (XLSX 57 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, F., Cai, L., Zhou, B. et al. Whole transcriptome sequencing reveals dexmedetomidine-improves postoperative cognitive dysfunction in rats via modulating lncRNA. 3 Biotech 10, 202 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02190-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02190-9