Abstract
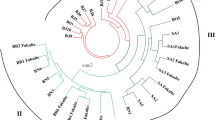
Genetic variation and diversity are prerequisites for improvement of buffalograss breeding. To assess the within-population genetic diversity of buffalograss, seven morphological traits were evaluated to confirm the variations at the morphological level. The principal component analysis revealed that leaf length, leaf width and stolon branches had a significant contribution to the total variation. The first three principle components showed 72.55% variation. The DNA analysis performed using SRAP primers was used for deducing the diversity at the DNA level. A total of 125 bands were obtained with 8 selected SRAP primer pairs, of which 119 (95.2%) were polymorphic. The polymorphic information content ranged from 0.94 to 0.97 with a mean of 0.96; the marker index ranged from 10.34 to 18.43 with an average value of 14.28. The individuals were successfully assigned to two major groups according to sex in the PCoA and UPGMA dendrogram based on SRAP data, while the individuals could not be grouped based on morphological traits, and the two markers were not significantly correlated (r = 0.0753, P = 0.8489 > 0.05). The molecular data revealed that sex is a critical factor and that female and monoecious plants could be chosen as parents to breed new varieties.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed MS (2017) Molecular characterization of locally adopted sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) varieties using microsatellite markers. J Anim Plant Sci 27(1):164–174
Aliyu B, Akoroda M, Padulosi S (2000) Variation within Vigna reticulata Hooke FII Nig. J Gene:1–8
Allen P, Bennett K, Heritage B (2014) SPSS statistics version 22: a practical guide. Cengage Learning Australia, Australia
Beetle AA (1950) Buffalograss-native of the shortgrass plains. Wyoming Agr Expt Sta Bull (293):1–31
Bisht IS, Mahajan RK, Loknathan TR, Agrawal RC (1998) Diversity in Indian sesame collection and stratification of germplasm accessions in different diversity groups. Genet Resour Crop Ev 45(4):325–335
Boczkowska M, Nowosielski J, Nowosielska D, Podyma W (2014) Assessing genetic diversity in 23 early Polish oat cultivars based on molecular and morphological studies. Genet Resour Crop Ev 61(5):927–941
Budak H, Shearman R, Parmaksiz I, Dweikat I (2004a) Comparative analysis of seeded and vegetative biotype buffalograsses based on phylogenetic relationship using ISSRs, SSRs, RAPDs, and SRAPs. Theor Appl Genet 109(2):280–288
Budak H, Shearman RC, Parmaksiz I, Gaussoin RE, Riordan TP, Dweikat I (2004b) Molecular characterization of Buffalograss germplasm using sequence-related amplified polymorphism markers. Theor Appl Genet 108(2):328–334
Budak H, Shearman RC, Gulsen O, Dweikat I (2005) Understanding ploidy complex and geographic origin of the Buchloe dactyloides genome using cytoplasmic and nuclear marker systems. Theor Appl Genet 111(8):1545–1552
Cheng Y, Ma X, Zhou K, Humphreys MW, Zhang XQ (2016) Phylogenetic analysis of Festuca–Lolium complex using SRAP markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 63(1):7–18
Deepa N, Rakesh S, Sreenivasa MY (2018) Morphological, pathological and mycotoxicological variations among Fusarium verticillioides isolated from cereals. 3 Biotech 8(2):105
Diederichsen A (2009) Duplication assessments in Nordic Avena sativa accessions at the Canadian national genebank. Genet Resour Crop Evol 56(4):587–597
Ferriol M, Pico B, Nuez F (2003) Genetic diversity of a germplasm collection of Cucurbita pepo using SRAP and AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 107(2):271–282
Grover A, Sharma PC (2014) Development and use of molecular markers: past and present. Crit Rev Biotechnol 36(2):1–13
Gulsen O, Shearman RC, Vogel KP, Lee DJ, Baenziger PS, Heng-Moss TM, Budak H (2005) Nuclear genome diversity and relationships among naturally occurring buffalograss genotypes determined by sequence-related amplified polymorphism markers. HortScience 40(3):537–541
Huff DR, Peakall R, Smouse PE (1993) RAPD variation within and among natural populations of outcrossing buffalograss [Buchloë dactyloides (Nutt.) Engelm.]. Theor Appl Genet 86(8):927–934
Jain JR, Timsina B, Satyan KB, Manohar SH (2017) A comparative assessment of morphological and molecular diversity among Sechium edule (Jacq.) Sw. accessions in India. 3 Biotech 7(2):106
Jia S, Yan Z, Wang Y, Wei Y, Xie Z, Zhang F (2017) Genetic diversity and relatedness among ornamental purslane (Portulaca L.) accessions unraveled by SRAP markers. 3 Biotech 7(4):241
Jones N, Ougham H, Thomas H, Pašakinskienė I (2009) Markers and mapping revisited: finding your gene. New Phytol 183(4):935–966
Kumar A, Singh P, Rai N, Bhaskar G, Datta D (2014) Genetic diversity of French bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) genotypes on the basis of morphological traits and molecular markers. Indian J Biotechnol 13:207–213
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):1870–1874
Li G, Quiros CF (2001) Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction: its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica. Theor Appl Genet 103(2):455–461
Liu CJ (1997) Geographical distribution of genetic variation in Stylosanthes scabra revealed by RAPD analysis. Euphytica 98(1):21–27
Liu L, Deng CT, Bao MZ (2008) Analysis of genetic diversity within the population of buffalo grass by morphological traits and ISSR markers. Pratacultural Sci 25(1):100–106
Liu Y, Zhang J-m, Wang X-g, Liu F, Shen Z-b (2013) Genetic diversity in Vicia amoena (Fabaceae) germplasm resource in China using SRAP and ISSR markers. Biochem Syst Ecol 51:86–93
Liu L, Chen W, Zheng X, Li J, Yan D-T, Liu L, Liu X, Wang Y-L (2016) Genetic diversity of Ulmus lamellosa by morphological traits and sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) markers. Biochem Syst Ecol 66:272–280
Mohammadi SA, Prasanna BM (2003) Analysis of genetic diversity in crop plants—salient statistical tools and considerations. Crop Sci 43(4):1235–1248
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2012) GenAlEx 6.5: genetic analysis in excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research—an update. Bioinformatics 28(19):2537–2539
Powell W, Morgante M, Andre C, Hanafey M, Vogel J, Tingey S, Rafalski A (1996) The comparison of RFLP, RAPD, AFLP and SSR (microsatellite) markers for germplasm analysis. Mol Breeding 2(3):225–238
Pradeep Reddy M, Sarla N, Siddiq E (2002) Inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) polymorphism and its application in plant breeding. Euphytica 128(1):9–17
Prevost A, Wilkinson MJ (1999) A new system of comparing PCR primers applied to ISSR fingerprinting of potato cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 98(1):107–112
Reeder JR (1971) Notes on Mexican grasses IX. Miscellaneous chromosome numbers—3. Brittonia 23(2):105–117
Rohlf FJ (2002) NTSYS-pc: numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system (version 2.1). Exeter Publishing Ltd 2.1, Setauket
Roodt R, Spies J, Burger T (2002) Preliminary DNA fingerprinting of the turf grass Cynodon dactylon (Poaceae: Chloridoideae). Bothalia 32(1):117–122
Rostamiahmadvandi H, Cheghamirza K, Kahrizi D, Bahraminejad S (2013) Comparison of morpho-agronomic traits versus RAPD and ISSR markers to evaluate genetic diversity among Cuminum cyminum L. accessions. Aust J Crop Sci 7(3):361–367
Sedeh MS (2017) Assessment genetic diversity landraces in Onobrychis sativa using SSR, RAPD and SRAP markers. J AgrIC Biotechnol 2(1):6–10
Serba DD (2009) Buffalograss genetic linkage mapping, chinch bug resistance characteristics and turfgrass performance. University of Nebraska, Omaha
Seyedimoradi H, Talebi R, Hassani D, Karami F (2012) Comparative genetic diversity analysis in Iranian local grapevine cultivars using ISSR and DAMD molecular markers. Environ Exp Biol 10:125–132
Taylor EB, Boughman JW, Groenenboom M, Sniatynski M, Schluter D, Gow JL (2006) Speciation in reverse: morphological and genetic evidence of the collapse of a three-spined stickleback (Gasterosteus aculeatus) species pair. Mol Ecol 15(2):343–355
Turchetto C, Segatto AL, Telles MP, Diniz-Filho JA, Freitas LB (2014) Infraspecific classification reflects genetic differentiation in the widespread Petunia axillaris complex: a comparison among morphological, ecological, and genetic patterns of geographic variation. Perspect Plant Ecol 16(2):75–82
Verma KS, ul Haq S, Kachhwaha S, Kothari SL (2017) RAPD and ISSR marker assessment of genetic diversity in Citrullus colocynthis (L.) Schrad: a unique source of germplasm highly adapted to drought and high-temperature stress. 3 Biotech 7(5):288
Voigt P, Kneebone W, Harlan J, Ahring R (1975) Registration of Texoka Buffalograss1 (Reg. No. 35). Crop Sci 15(6):885–885
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, Lee TV, Hornes M, Friters A, Pot J, Paleman J, Kuiper M, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23(21):4407–4414
Zhou Y-j, Wang X-g, Zhang X-q (2011) Development and application of a SRAP marker for the identification of sex in Buchloe dactyloides. Euphytica 181(2):261–266
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, F., Chen, J., Wang, J. et al. Intra-population genetic diversity of Buchloe dactyloides (Nutt.) Engelm (buffalograss) determined using morphological traits and sequence-related amplified polymorphism markers. 3 Biotech 9, 97 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1632-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-019-1632-9