Abstract
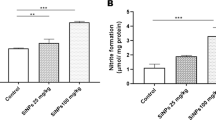
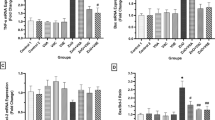
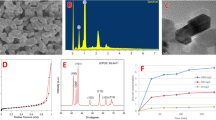
In this study, the toxic effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnONPs) at different doses and periods were evaluated, and the histopathological changes and caspase-9 and -8 expression levels in liver and lung tissues of thirty-three male mice model, were determined. The mice model was divided into the treatment groups which were injected intraperitoneally with 0.5 ml of ZnONPs (100 and 300 mg/kg) for 15, 20, and 25 days; and a control group that was injected with 0.5 ml of 0.9% physiological solution for 15, 20, and 25 days. The ZnONPs were shown to cause histopathological effects in the liver and lung tissues which include reversible changes such as hypertrophy, degeneration, and others that were diagnostic in histological sections; and irreversible changes like necrosis. The ZnONPs at 300 mg/kg after 25 days had caused a significant decrease in caspase-9 expression levels (two–fourfold lower than Control) in both liver and lung tissues. However, there was no significant difference in caspase-8 in both liver and lung tissues, suggesting that the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis, rather than the extrinsic pathway, may be inhibited. ZnONPs were, therefore, exhibited to inhibit programmed cell death, and also induced irreversible phenotypic necrosis, in a dose- and time-dependent manner.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
AlMaliki SJ (2000) A behavior and some physiological effect of (Apium graveolens) seeds in albino mice. J Sci Bas 18(2):77–88
Alferah MA (2018) Histological changes of male westar rats liver following the ingestion of zinc oxide nanoparticles with special emphasis on the histochemical alterations. J Histol Histopathol 5(4):1−6
Almansour M, Alferah M, Shraideh Z, Jarrar B (2017) Zinc oxide nanoparticles hepatotoxicity: histological and histochemical study. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 51:124–130
Attia H, Nounou H, Shalaby M (2018) Zinc oxide nanoparticles induced oxidative DNA damage, inflammation and apoptosis in rat’s brain after oral exposure. Toxics 6(2):29
Böhm I, Schild H (2003) Apoptosis: the complex scenario for a silent cell death. Mol Imag Biolog 5(1):2–14
Brentnall M, Rodriguez-Menocal L, De Guevara RL, Cepero E, Boise LH (2013) Caspase-9, caspase-3 and caspase-7 have distinct roles during intrinsic apoptosis. BMC Cell Biol 14:32
Danial NN, Korsmeyer SJ (2004) Cell death: critical control points. Cell 116(2):205–219
Denning DP, Hatch V, Horvitz HR (2013) Both the caspase CSP-1 and a caspase-independent pathway promote programmed cell death in parallel to the canonical pathway for apoptosis in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Genet 9(3):e1003341
Ding WX et al (2000) Critical role of reactive oxygen species and mitochondria permeability transition in microcystic induced rapid apoptosis in rat hepatocytes. Hepatol 32(3):547–555
Elbakary RH, Okasha EF, Ragab AMH, Ragab MH (2018) Histological effects of gold nanoparticles on the lung tissue of adult male albino rats. J Microsc Ultrastruct 6(2):116–122
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35(4):495–516
Hall AP et al (2012) Liver hypertrophy: a review of adaptive (adverse and non-adverse) changes—conclusions from the 3rd international ESTP expert workshop. Toxicol Pathol 40(7):971–994
Han Z, Yan Q, Ge W, Liu ZG, Gurunathan S et al (2016) Cytotoxic effects of ZnO nanoparticles on mouse testicular cells. Int J Nanomed 11:5187–5203
Hegazy AA, Ahmed MM, Shehata MA, Abdelfattah MM (2018) Changes in rats’ liver structure induced by zinc oxide nanoparticles and the possible protective role of vitamin E. Int J Human Anat 1(3):1–16
Hosseini SM, Amani R, Moshrefi AH, Razavimehr SV, Aghajanikhah MH, Sokouti Z (2020) Chronic zinc oxide nanoparticles exposure produces hepatic and pancreatic impairment in female rats. Iran J Toxicol 14(3):145–154
Hu LS, George J, Wang JH (2013) Current concepts on the role of nitric oxide in portal hypertension. World J Gastroenterol 19(11):1707–1717
Humason GL (1972) Animal tissue techniques, 3rd edn., W H Freeman, San Francisco
Hussein HA, Abdullah MA (2021) Novel drug delivery systems based on silver nanoparticles, hyaluronic acid, lipid nanoparticles and liposomes for cancer treatment. Appl Nanosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-02018-9
Hussein HA, Maulidiani M, Abdullah MA (2020a) Microalgal metabolites as anti-cancer/anti-oxidant agents reduce cytotoxicity of elevated silver nanoparticle levels against non-cancerous vero cells. Heliyon 6:e05263. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05263
Hussein HA, Mohamad H, Ghazaly MM, Laith AA, Abdullah MA (2020b) Cytotoxic effects of Tetraselmis suecica chloroform extracts with silver nanoparticle co-application on MCF-7, 4 T1, and vero cell lines. J Appl Phycol 32:127–143
Hussein HA, Mohamad H, Ghazaly MM, Laith AA, Abdullah MA (2020c) Anticancer and antioxidant activities of Nannochloropsis oculata and Chlorella sp. extracts in co-application with silver nanoparticle. J King Saud Univ Sci 32(8):3486–3494. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2020.10.011
Jia L et al (2017) Ion-shedding zinc oxide nanoparticles induce microglial BV2 cell proliferation via the ERK and Akt signaling pathways. Toxicol Sci 156(1):167–178
Jiang J, Pi J, Cai J (2018) The advancing of zinc oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Bioinorg Chem Appl 2(3):1–18
Jorgensen I, Rayamajhi M, Mioa EA (2017) Programmed cell death as a defence against infection. Nat Rev Immunol 17(3):151–164
Khalaf AA, Hassanen E, Azouz RA, Zaki AR, Ibrahim MA, Farroh KY, Galal MK (2019) Ameliorative effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles against dermal toxicity induced by lead oxide In rats. Int J Nanomed 14:7729–7741
Khan I, Saeed K, Khan I (2019) Nanoparticles: properties, applications and toxicities. Arabian J Chem 12(7):908–931
Kim SJ, Kim HS, Seo YR (2019) Understanding of ROS-inducing strategy in anticancer therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:5381692
Locksley RM, Killeen N, Lenardo MJ (2001) The TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: integrating mammalian biology. Cell 104:487–501
Loreto C, La Rocca G, Anzalone R, Caltabiano R (2014) The role of intrinsic pathway in apoptosis activation and progression in Peyronie’s disease. J Biomed Biotechnol 2014:616149
Mitra S, Nguyen LN, Akter M, Park G et al (2019) Impact of ROS generated by chemical, physical, and plasma techniques on cancer attenuation. Cancers (Basel) 11(7):1030
Mobarak YM, Sharaf MM (2011) Lead acetate-induced histopathological changes in the gills and digestive system of silver Sailfin molly (Poecilia latipinna). Int J Zoolog Res 7(1):1–18
Neyrinck A (2004) Modulation of Kupffer cell activity: physio-pathological consequences on hepatic metabolism. Bull Mem Acad R Med Belg 159(5–6):358–366
Nicholson DW, Ali A, Thornberry NA, Vaillancourt JP, Ding CK, Gallant M, Gareau Y, Griffin PR, Labelle M, Lazebnik YA, Munday NA, Raju SM, Smulson ME, Yamin TT, Yu VL, Miller DK (1995) Identification and inhibition of the ICE/CED-3 protease necessary for mammalian apoptosis. Nature 376:37–43
Noori A, Karimi F, Soheil F, Fereshteh Y (2014) Effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles on renal function in mice. Int J Biosci 5(9):140–146
Norbury CJ, Hickson ID (2001) Cellular responses to DNA damage. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 41(1):367–401
Parrish AB, Freel CD, Kornbluth S (2013) Cellular mechanisms controlling caspase activation and function. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 5(6):008672
Perillo B, Di Donato M, Pezone A, Di Zazzo E et al (2020) ROS in cancer therapy: the bright side of the moon. Exp Mol Med 52:192–203
Ping L, Libin Z, Ting Z, Xiongxiong L, Pengcheng Z, Yan L, Xiaogang Z, Qiang L (2017) Caspase-9: structure, mechanisms and clinical application. Oncotarget 8(14):23996–24008
Pinho AR, Martins F, Costa MEV et al (2020) In Vitro cytotoxicity effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles on spermatogonia cells. Cells 9(5):1081
Raducka-Jaszul O, Bogusławska DM, Jedruchniewicz N, Sikorski AF (2020) Role of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway during definitive erythropoiesis in normal patients and in patients with β-thalassemia. Int J Mol Sci 21(9):3325
Reddy ARN, Srividya L (2018) Evaluation of In Vitro cytotoxicity of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles using human cell lines. J Toxicol Risk Assess 4:009
Saadi S, Hooshmandi Z (2016) The effect of short-term intraperitoneal injection of Fe2O4Zn nanoparticle on liver enzymes and tissue in male wistar laboratory rats. Int J Med Res Health Sci 5(12):92–100
Salman RA (2018) Histopathological effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles on kidney and liver tissues in albino male mice. Ibn Al-Haitham J Pure Appl Sci 31(1):9–14
Saman S, Saeed M, Attaollah S, Masoud G (2013) Histopathological effects of ZnO nanoparticles on liver and heart tissues in wistar rats. Adv Biores 4(2):83–88
Scherzad A, Meyer T, Kleinsasser N, Hackenberg S (2017) Molecular mechanisms of zinc oxide nanoparticle—induced genotoxicity. Mater 10(12):1427
Shapiro SD (2003) Proteolysis in the lung. Eur Respir J Suppl 44:30s–32s
Shen J, Yang D, Zhou X, Wang Y, Tang S, Yin H, Wang J, Chen R, Chen J (2019) Role of autophagy in zinc oxide nanoparticles-induced apoptosis of mouse LEYDIG cells. Int J Mol Sci 20(16):4042
Shih WW, Chien HL, Ming SL, Chih WC, Yung SH (2020) ZnO nanoparticles induced caspase-dependent apoptosis in gingival squamous cell carcinoma through mitochondrial dysfunction and p70S6K signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci 21(5):1612
Singh A, Singh NB, Afzal S, Singh T, Hussain I (2018) Zinc oxide nanoparticles: a review of their biological synthesis, antimicrobial activity, uptake, translocation and biotransformation in plants. J Mater Sci 53(1):185–201
Tang HQ et al (2016) The effect of ZnO nanoparticles on liver function in rats. Int J Nanomed 11:4275–4285
Wang D et al (2017) Acute toxicological effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles in mice after intratracheal instillation. Int J Occup Environ Health 23(1):11–19
Wang L, Xu H, Qiu Y, Liu X, Huang W, Yan N, Qu Z (2020) Utilization of Ag nanoparticles anchored in covalent organic frameworks for mercury removal from acidic wastewater. J Hazard Mater 389:121824
Wilhelmi V et al (2013) Zinc oxide nanoparticles induce necrosis and apoptosis in macrophages in a p47phox- and Nrf2-independent manner. PLoS One 8(6):e65704
Wu MH, Jin XK, Yu AQ, Zhu YT, Li D, Li WW et al (2014) Caspase-mediated apoptosis in crustaceans: cloning and functional characterization of EsCaspase-3-like protein from Eriocheir. Fish Shellfish Immunol 41(2):625–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fsi.2014.10.017
Wu Y, Zhao D, Zhuang J, Zhang F, Xu C (2016) Caspase-8 and caspase-9 functioned differently at different stages of the cyclic stretch-induced apoptosis in human periodontal ligament cells. PLoS One 11(12):e0168268
Xiao M (2018) Senescence and cell death in chronic liver injury: roles and mechanisms underlying hepatocarcinogenesis. Oncotarget 9(9):8772–8784
Yang H, Villani RM, Wang H, Simpson MJ et al (2018) The role of cellular reactive oxygen species in cancer chemotherapy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37:266
Zhao Y et al (2015) Differential regulation of gene and protein expression by zinc oxide nanoparticles in hen’s ovarian granulosa cells: specific roles of nanoparticles. PLoS One 10(10):e0140499
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the University of Basrah for the research facilities to carry out the experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Ali, A.A.A., Al-Tamimi, S.Q., Al-Maliki, S.J. et al. Toxic effects of zinc oxide nanoparticles and histopathological and caspase-9 expression changes in the liver and lung tissues of male mice model. Appl Nanosci 12, 193–203 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-02248-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-02248-x