Abstract
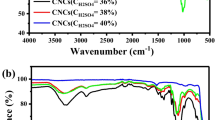
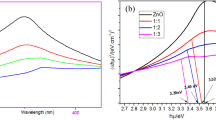
Cellulose, zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO NPs) and a new composite of crystalline cellulose–ZnO nanoparticles (ZnO/CNC) have been prepared by simple hydrothermal treatment using Hibiscus leaf extract. The cellulose which was isolated from corn cobs and the nanomaterials were characterised using different analytical techniques including Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), X-ray diffraction (XRD) measurements and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). These techniques explained the structure, crystallinity and purity of the extracted cellulose, ZnO NPs and the ZnO/CNC nanocomposite. The TEM image showed the rod like shape of the synthesized ZnO NPs with approximate width size of about 90.83 nm and length 546.97 nm, whereas the ZnO/CNC nanocomposite is of 4.89 nm spheroidal shape. The antibacterial properties of the as-synthesized nanomaterials showed good properties but the cellulose did not.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalkarim SYH, Yu H-Y, Wang C, Yang L, Guan Y, Huang L, Yao J (2018a) Sheet-like cellulose nanocrystal-ZnO nanohybrids as multifunctional reinforcing agents in biopolyester composite nanofibers with ultrahigh UV-shielding and antibacterial performances. ACS Appl Bio Mater 1:727
Abdalkarim SYH, Yu H-Y, Wang C, Huang L-X, Yao J (2018b) Green synthesis of sheet-like cellulose nanocrystal–zinc oxide nanohybrids with multifunctional performance through one-step hydrothermal method. Cellulose 25(11):6446
Abderrahim B, Abderrahman E, Mohamed A, Fatima T, Abdesselam T, Krim O (2015) Kinetic thermal degradation of cellulose, polybutylene succinate and a green composite: comparative study. World J Environ Eng 3(4):110
Abubakar US, Yusuf KM, Safiyanu I, Abdullahi S, Saidu SR, Abdu GT, Indee AM (2016) Proximate and mineral composition of corn cob, banana and plantain peels. Int J food Sci Nutr 1:27
Adeyemi JO, Elemike EE, Onwudiwe DC (2019) ZnO nanoparticles mediated by aqueous extracts of Dovyalis caffra fruits and the photocatalytic evaluations. Mater Res Express 6:125091
Agrawal R, Espinosa HD (2011) Giant piezoelectric size effects in Zinc Oxide and Gallium Nitride nanowires. A first principles investigation. Nano Lett 11:790
Al-Snafi AE (2018) Chemical constituents, pharmacological effects and therapeutic importance of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis- A review. IOSR J Pharm 8:119
Awan F, Islam MS, Ma Y, Yang C, Shi Z, Berry RM, Tam KC (2018) Cellulose nanocrystal-ZnO nanohybrids for controlling photocatalytic activity and UV protection in cosmetic formulation. ACS Omega 3:12411
Azizi S, Ahmad MB, Hussein MZ, Ibrahim NA (2013) Synthesis, antibacterial and thermal studies of cellulose nanocrystal stabilized ZnO-Ag heterostructure nanoparticles. Molecules 18:6280
Börjesson M, Westman G (2015) Cellulose—fundamental aspects and current trends. Intech Books, London, pp 160–169
Chaudhuri SK, Malodia L (2017) Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using leaf extract of Calotropis gigantea: characterization and its evaluation on tree seedling growth in nursery stage. Appl Nanosci 7:512
Chen T, Zheng Y, Lin J-M, Chen G (2008) Study on the photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange in water using Ag/ZnO as catalyst by liquid chromatography electrospray ionization ion-trap mass spectrometry. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 19:1003
Crabbe-Mann M, Tsaoulidis D, Parhizkar M (2018) Ethyl cellulose, cellulose acetate and carboxymethyl cellulose microstructures prepared using electrohydrodynamics and green solvents. Cellulose 25:1703
Du Y, Huang Z, Wu S, Xiong K, Zhang X, Zheng B, Nadimicherla R, Fu R, Wu D (2018) Preparation of versatile yolk-shell nanoparticles with a precious metal yolk and a microporous polymer shell for high-performance catalysts and antibacterial agents. Polymer 137:200
Elemike EE, Fayemi OE, Ekennia AC, Onwudiwe DC, Ebenso EE (2017) Silver nanoparticles mediated by costus afer leaf extract: synthesis, antibacterial, antioxidant and electrochemical properties. Molecules 22:701
Elemike EE, Onwudiwe DC, Wei L, Chaogang L, Zhiwei Z (2019) Synthesis of nanostructured ZnO, AgZnO and the composites with reduced graphene oxide (rGO-AgZnO ) using leaf extract of Stigmaphyllon ovatum. J Environ Chem Eng 7:103190
Food Standards Agency. Current EU approved additives and their E Numbers 2014. www.food.gov.uk/science/additives/enumberlist
Fu F, Li L, Liu L, Cai J, Zhang Y, Zhou J, Zhang L (2015) Construction of cellulose based ZnO nanocomposite films with antibacterial properties through one-step coagulation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:2606
Gunalan S, Rajeswari S, Venckatesh R (2012) Green synthesized ZnO nanoparticles against bacterial and fungal pathogens. Prog Nat sci Mater Int 22(6):700
Hu X, Xu X, Fu F, Yang B, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Touhid SSB, Liu L, Dong Y, Liu X, Yao J (2020) Synthesis of bimetallic silver-gold nanoparticle composites using a cellulose dope: tunable nanostructure and its biological activity. Carbohydr Polym 248:116777
Jawada AH, Mohammed SA, Mastuli MS, Abdullah MF (2018) Carbonization of corn (Zea mays) cob agricultural residue by onestep activation with sulfuric acid for methylene blue adsorption. Desalin Water Treat 118:351
Kalia S, Kaith BS, Kaur I (2009) Pretreatments of natural fibers and their application as reinforcing material in polymer composites—A review. Polym Eng Sci 49(7):1272
Kim J, Yun S, Ounaies Z (2006) Discovery of cellulose as a smart material. Macromolecules 39:4206
Lefatshe K, Muiva CM, Kebaabetswe LP (2017) Extraction of nanocellulose and in-situ casting of ZnO/cellulose nanocomposite with enhanced photocatalytic and antibacterial activity. Carbohyd Polym 164:308
Lennholm H, Henriksson G (2007) In: Ek M, Gellerstedt G, Henriksson G (eds) Fiber and polymer technology, Ljungberg Textbook Stockholm, KTH, pp 72–102
Li R, Zhang L, Xu M (2012) Novel regenerated cellulose films prepared by coagulating with water: structure and properties. Carbohydr Polym 87:100
Martins NCT, Freire CSR, Neto CP, Silvestre AJD, Causio J, Baldi G, Sadocco P, Trindade T (2013) Antibacterial paper based on composite coatings of nanofibrillated cellulose and ZnO. Colloids Surf A 417:119
Matharu RK, Ciric L, Edirisinghe M (2018) Nanocomposites: suitable alternatives as antimicrobial agents. Nanotechnol 29:282001
Morawski AW, Kusiak-Nejman E, Przepiórski J, Kordala R, Pernak J (2013) Cellulose-TiO2 nanocomposite with enhanced UV–Vis light absorption. Cellulose 20:1300
Mun S, Ko H-U, Zhai L, Min S-K, Kim H-C, Kim J (2016) Enhanced electromechanical behavior of cellulose film by zinc oxide nanocoating and its vibration energy harvesting. Acta Mater 114:6
Naseer M, Aslam U, Khalid B, Chen B (2020) Green route to synthesize Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles using leaf extracts of Cassia fistula and Melia azadarach and their antibacterial potential. Sci Rep 10:9055
Padmavathy N, Vijayaraghavan R (2008) Enhanced bioactivity of ZnO nanoparticles—an antimicrobial study. Sci Technol Adv Mat 9(3):35010
Rayung M, Ibrahim NA, Zainuddin N, Saad WZ, Razak NIA, Chieng BW (2014) The effect of fiber bleaching treatment on the properties of poly(lactic acid)/oil palm empty fruit bunch fiber composites. Int J Mol Sci 15:14742
Ruban P, Gajalakshmi K (2012) In vitro antibacterial activity of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis flower extract against human pathogens. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2(5):403
Sawai J, Kawada E, Kanou F, Igarashi H, Hashimoto A, Kokugan T, Shimizu M (1996) Detection of active Oxygen generated from ceramic powders having antibacterial activity. J Chem EngJpn 29(4):633
Sharma ND, Landis CM, Sharma P (2010) Piezoelectric thin-film superlattices without using piezoelectric materials. J Appl Phys 108:024304
Siddiqi KS, Rahman AU, Tajuddin AH (2018) Properties of Zinc Oxide nanoparticles and their activity against microbes. Nanoscale Res Lett 13:141
Sirelkhatim A, Mahmud S, Seeni A, Kaus NHM, Ann LC, Bakhori SKM, Hasan H, Mohamad D (2015) Review on Zinc Oxide nanoparticles: antibacterial activity and toxicity mechanism. Nano-Micro Lett 7(3):242
Sirviö JA, Visanko M, Hildebrandt NC (2017) Rapid preparation of all-cellulose composites by solvent welding based on the use of aqueous solvent. Eur Polymer J 97:298
Trilokesh C, Uppulur KB (2019) Isolation and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from jackfruit peel. Sci Rep 9:16709
Ul-Islam M, Khattak WA, Ullah MW, Khan S, Park JK (2014) Synthesis of regenerated bacterial cellulose-zinc oxide nanocomposite films for biomedical applications. Cellulose 21:447
Vartiainen J, Pöhler T, Sirola K, Pylkkänen L, Alenius H, Hokkinen J (2011) Health and environmental safety aspects of friction grinding and spray drying of microfibrillated cellulose. Cellulose 18:786
Wang C, Shaw LL (2014) On synthesis of Fe2SiO4/SiO2 and Fe2O3/SiO2 composites through sol–gel and solid-state reactions. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 72:614
Wang TY, Libardo MDJ, Angelesoza AM, Pellois JP (2017) Membrane oxidation in cell delivery and cell killing applications. ACS Chem Biol 12(5):1182
Wang D-C, Yang X, Yu H-Y, Gu J, Qi D, Yao J, Ni Q (2020) Smart nonwoven fabric with reversibly dual-stimuli responsive wettability for intelligent oilwater separation and pollutants removal. J Haz Mater 383:121123
Yusof HM, Mohamad R, Zaidan UH, Rahman NAA (2019) Microbial synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles and their potential application as an antimicrobial agent and a feed supplement in animal industry: a review. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 10:57
Zheng J, Choo K, Bradt C, Lehou R, Rehmann L (2014) Enzymatic hydrolysis of steam exploded corncob residues after pretreatment in a twin-screw extruder. Biotechnol Rep 3:107
Zou W, Chen Y, Zhang X, Li J, Sun L, Gui Z, Du B, Chen S (2018) Cytocompatible chitosan based multi-network hydrogels with antimicrobial, cell antiadhesive and mechanical properties. Carbohydr Polym 202:257
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the management of Federal University of Petroleum resources Effurun for the platform that enabled this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no clash of interest associated with this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elemike, E.E., Onwudiwe, D.C. & Mbonu, J.I. Facile synthesis of cellulose–ZnO-hybrid nanocomposite using Hibiscus rosa-sinensis leaf extract and their antibacterial activities. Appl Nanosci 11, 1349–1358 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-01774-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-01774-y