Abstract
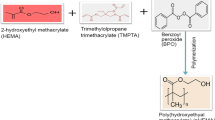
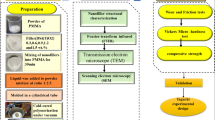
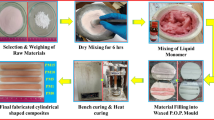
In the last two decades, polymer matrix nanocomposites have been drawing great attention among research communities owing to their superior properties, such as being lightweight, stiffness, and having better specific strength in comparison to base polymer and traditional materials. However, limited work was targeted for biomedical applications. Thus, the development of biocompatible polymer composites is most promising research topic in the field of material science. Poly(2-hydroxyethylmethacrylate) (pHEMA) is one of the favorable biomaterial due to high water content, nontoxicity, and tissue compatibility. This article encompasses the synthesis of pHEMA nanocomposites and their characterization targeting for dental material. The pHEMA nanocomposites were fabricated through blending and an extrusion dispersion technique. In this process, a twin-screw extruder machine was used. The appropriate amounts of nanoclay and TiO2 nanoparticles were dispersed in pHEMA and the machine was operated at a shear rotation of 10 rpm for 10 min to ensure the homogeneous dispersion of nanoparticles in the matrix. The thermal analyses were performed by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) analyses were performed for studying the structural, morphological, and microstructural behavior of the nanocomposites. A multi-cycle indentation test and micro-scratch analysis was performed. A considerable transformation in the microstructural behavior with improved thermo-mechanical properties was observed in pHEMA/1 wt% nanoclay and pHEMA/2 wt% nanoclay nanocomposites.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alamgir M, Nayak GC, Mallick A, Tiwari SK, Mondal S, Gupta M (2018) Processing of PMMA nanocomposites containing biocompatible GO and TiO2 nanoparticles. Mater Manuf Process 33:291–1298. https://doi.org/10.1080/10426914.2018.1424996
Al-Amin M, Dey SC, Rashid TU, Ashaduzzaman M, Shamsuddin SM (2016) Solar assisted photocatalytic degradation of reactive azo dyes in presence of anatase titanium dioxide. Int J Latest Res EngTechnol 2:14–21
Ali F, Waseem M, Khurshid R, Afzal A (2020) TiO2 reinforced high-performance epoxy-co-polyamide composite coatings. Prog Org Coat 146:105726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2020.105726
Arya A, Sadiq M, Sharma AL (2018) Effect of variation of different nanofillers on structural, electrical, dielectric, and transport properties of blend polymer nanocomposites. Ionics 24:2295–2319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2364-7
Bari SS, Mishra S (2017) Calcium silicate nanowires—an effective alternative for improving mechanical properties of chitosan–hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) copolymer nanocomposites. CarbohydrPolym 169:426–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.04.023
Calabi-Floody M, Bendall JS, Jara AA, Welland ME, Theng BK, Rumpel C, de la Luz MM (2011) Nanoclays from an Andisol: extraction, properties and carbon stabilization. Geoderma 161:159–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.12.013
Ding R, Wu H, Thunga M, Bowler N, Kessler MR (2016) Processing and characterization of low-cost electrospun carbon fibers from organosolv lignin/polyacrylonitrile blends. Carbon 100:126–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2015.12.078
Frounchi M, Dadbin S, Salehpour Z, Noferesti M (2006) Gas barrier properties of PP/EPDM blend nanocomposites. J Membrsci 282:142–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2006.05.016
Gul S, Kausar A, Muhammad B, Jabeen S (2016) Research progress on properties and applications of polymer/clay nanocomposite. Polym Plast Technol Eng 55:684–703
Hashim A, Al-Attiyah KHH, Obaid SF (2019) Fabrication of novel (biopolymer blend-lead oxide nanoparticles) nanocomposites: structural and optical properties for low-cost nuclear radiation shielding. Ukr J Phys 64:157–157. https://doi.org/10.15407/ujpe64.2.157
Jarrar R, Mohsin MA, Haik Y (2012) Alteration of the mechanical and thermal properties of nylon 6/nylon 6, 6 blends by nanoclay. J ApplPolymSci 124:1880–1890. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.35215
Kharismadewi D, Haldorai Y, Nguyen VH, Tuma D, Shim JJ (2016) Synthesis of graphene oxide–poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) composite by dispersion polymerization in supercritical CO2: adsorption behavior for the removal of organic dye. Compos Interfaces 23:719–739. https://doi.org/10.1080/09276440.2016.1169707
Kodama Y, Barsbay M, Güven O (2014) Radiation-induced and RAFT-mediated grafting of poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate)(PHEMA) from cellulose surfaces. RadiatPhysChem 94:98–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radphyschem.2013.07.016
Kujur MS, Manakari V, Parande G, Prasadh S, Wong R, Mallick A, Gupta M (2021) Development of rare-earth oxide reinforced magnesium nanocomposites for orthopedic applications: a mechanical/immersion/biocompatibility perspective. J MechBehav Biomed Mater 114:104162
Kumar P, Skotnicova K, Mallick A, Gupta M, Cegan T, Jurica J (2021) Mechanical characterization of graphene nanoplatelets-reinforced Mg-3Sn alloy synthesized by powder metallurgy. Metals 11:62
Munhoz T, Fredholm Y, Rivory P, Balvay S, Hartmann D, da Silva P, Chenal JM (2017) Effect of nanoclay addition on physical, chemical, optical and biological properties of experimental dental resin composites. Dent Mater 33:271–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2016.11.016
Niaki MH, Fereidoon A, Ahangari MG (2018) Experimental study on the mechanical and thermal properties of basalt fiber and nanoclay reinforced polymer concrete. Compos Struct 191:231–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.02.063
Osorio R, Cabello I, Medina-Castillo AL, Osorio E, Toledano M (2016) Zinc-modified nanopolymers improve the quality of resin–dentin bonded interfaces. Clin Oral Investig 20:2411–2420. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-016-1738-y
Passos MF, Fernández-Gutiérrez M, Vázquez-Lasa B, San Román J, MacielFilho R (2016) PHEMA-PLLA semi-interpenetrating polymer networks: a study of their swelling kinetics, mechanical properties and cellular behavior. EurPolym J 85:150–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2016.10.023
Scionti G, Rodriguez-Arco L, Lopez-Lopez MT, Medina-Castillo AL, Garzón I, Alaminos M, Toledano M, Osorio R (2018) Effect of functionalized PHEMA micro-and nano-particles on the viscoelastic properties of fibrin–agarose biomaterials. J Biomed Mater Res Part A106:738–745. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.36275
Sepet H, Tarakcioglu N, Misra RDK (2016) Investigation of mechanical, thermal and surface properties of nanoclay/HDPE nanocomposites produced industrially by melt mixing approach. J Compos Mater 50:3105–3116. https://doi.org/10.1177/0021998315615653
Siafaka P, Achilias DS (2013) Polymerization kinetics and thermal degradation of poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacylate)/organo-modified montmorillonite nanocomposites prepared by in situ bulk polymerization. MacromolSymp 331:166–172. https://doi.org/10.1002/masy.201300065
Sui Y, Wang Z, Gao X, Gao C (2012) Antifouling PVDF ultrafiltration membranes incorporating PVDF-g-PHEMA additive via atom transfer radical graft polymerizations. J MembrSci 413:38–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2012.03.055
Tian H, Wang K, Liu D, Yan J, Xiang A, Rajulu AV (2017) Enhanced mechanical and thermal properties of poly(vinyl alcohol)/corn starch blends by nanoclay intercalation. Int J BiolMacromol 101:314–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.03.111
Tiwari RR, Khilar KC, Natarajan U (2008) New poly(phenylene oxide)/polystyrene blend nanocomposites with clay: intercalation, thermal and mechanical properties. J ApplPolymSci 108:1818–1828. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.27743
Usal TD, Yucel D, Hasirci V (2019) A novel GelMA-pHEMA hydrogel nerve guide for the treatment of peripheral nerve damages. Int J BiolMacromol 121:699–706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.060
Ussia M, Mecca T, Cunsolo F, Nicotra G, Spinella C, Cerruti P, Impellizzeri G, Privitera V, Carroccio SC (2018) ZnO–pHEMA nanocomposites: an ecofriendly and reusable material for water remediation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:40100–40110. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b13029
Vargün E, Usanmaz A (2010) Degradation of poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) obtained by radiation in aqueous solution. J MacromolSci Part A Pure ApplChem 47:882–891. https://doi.org/10.1080/10601325.2010.501304
Wang X, Chen X (2018) Novel nanomaterials for biomedical environmental and energy applications. Elsevier, Amsterdam (Google Scholar)
Wu Y, Pang H, Liu Y, Wang X, Yu S, Fu D, Chen J, Wang X (2019) Environmental remediation of heavy metal ions by novel-nanomaterials: a review. Environ Pollut 246:608–620
Zhang Z, Huo F, Zhang X, Guo D (2012a) Fabrication and size prediction of crystalline nanoparticles of silicon induced by nanogrinding with ultrafine diamond grits. Scr Mater 67:657–660
Zhang Z, Song Y, Xu C, Guo D (2012b) A novel model for undeformed nanometer chips of soft-brittle HgCdTe films induced by ultrafine diamond grits. Scr Mater 67:197–200
Zhang Z, Wang B, Kang R, Zhang B, Guo D (2015a) Changes in surface layer of silicon wafers from diamond scratching. CIRP Ann ManufTechnol 64:349–352
Zhang Z, Guo D, Wang B, Kang R, Zhang B (2015b) A novel approach of high speed scratching on silicon wafers at nanoscale depths of cut. Sci Rep 5:16395
Zhang Z, Wang B, Zhou P, Kang R, Zhang B, Guo D (2016a) A novel approach of chemical mechanical polishing for cadmium zinc telluride wafers. Sci Rep 6:26891. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep26891
Zhang Z, Wang B, Zhou P, Guo D, Kang R, Zhang B (2016b) A novel approach of chemical mechanical polishing using environment-friendly slurry for mercury cadmium telluride semiconductors. Sci Rep 6:22466
Zhang Z, Cui J, Wang B, Wang Z, Kang R, Guo D (2017) A novel approach of mechanical chemical grinding. J Alloys Compd 726:514–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.08.024
Zhang Z, Cui J, Zhang J, Liu D, Yu Z, Guo D (2019) Environment friendly chemical mechanical polishing of copper. Appl Surf Sci 467:5–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.10.133
Zhang Z, Liao L, Wang X, Xie W, Guo D (2020) Development of a novel chemical mechanical polishing slurry and its polishing mechanisms on a nickel alloy. Appl Surf Sci 506:144670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144670
Zhao W, Li X, Gao S, Feng Y, Huang J (2017) Understanding mechanical characteristics of cellulose nanocrystals reinforced PHEMA nanocomposite hydrogel: in aqueous cyclic test. Cellulose 24:2095–2110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1244-7
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to DST, Govt. of India and TQUIP-2 to carry out this work. This work has been carried out under the R&D project entitled Synthesis and Characterization of Dental Polymeric Nanocomposite Materials vide sanction order no. SB/EMEQ-020/2013 dated 04.11.2013 supported by SERB, DST, Govt. of India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alamgir, M., Mallick, A. & Nayak, G.C. Mechanical and thermal behavior of pHEMA and pHEMA nanocomposites targeting for dental materials. Appl Nanosci 11, 1257–1265 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-01767-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-021-01767-x