Abstract
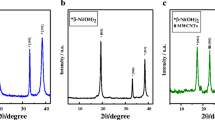
The article considers the effect of multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) modification with nickel and cobalt in different amounts on their electrochemical properties. For this purpose, several composites were synthesized by simple low-temperature method, characterized by XRD and thermal analysis and investigated as anodes for lithium-ion batteries. The composites with 40% of nickel and 40% of cobalt display a stable capacity of 550 mAh/g and 700 mAh/g, respectively, at a current density of 200 mA/g for the 60 cycles. The exhibited capacity is higher than the theoretical capacity of carbon. A comparison of nickel and cobalt composites shows that Co/CNT composite has better electrochemical characteristics: higher capacity, more flat discharge curve and resistant to texture changes structure.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Casas C, Li W (2012) A review of application of carbon nanotubes for lithium ion battery anode material. J Power Sour 208:74–85
Cuia X, Wanga Y, Chenb Z et al (2015) Preparation of pompon-like MnO/carbon nanotube composite microspheres as anodes for lithium ion batteries. Electrochim Acta 180:858–865
Diao G, Li H, Liang H et al (2018) CVD synthesis of multi-walled carbon nanotubes onto different catalysts at low temperature. NANO 13(4):1850036
Elizabetha I, Naird AK, Singhb BP et al (2017) Multifunctional Ni–NiO–CNT composite as high performing free standing anode for li ion batteries and advanced electro catalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. Electrochim Acta 230:98–105
Goriparti S, Miele E, Angeliset FD et al (2014) Review on recent progress of nanostructured anode materials for Li-ion batteries. J Power Sour 257:421–443
Huang J, Zhu N, Yang T et al (2015) Nickel oxide and carbon nanotube composite (NiO/CNT) as a novel cathode non-precious metal catalyst in microbial fuel cells. Biosens Bioelectron 72:332–339
Jafari SM, Khosravi M, Mollazadeh M (2016) Nanoporous hard carbon microspheres as anode active material of lithium ion battery. Electrochim Acta 203:9–20
Kamali AR, Fray DJ (2011) Tin-based materials as advanced anode materials for lithium ion batteries: a review. Rev Adv Mater Sci 27:14–24
Kawasaki S, Hara T, Iwai Y et al (2008) Metallic and semiconducting single-walled carbon nanotubes as the anode material of Li ion secondary battery. Mater Lett 62:2917–2920
Klink S, Ventosa E, Xia W et al (2012) Tailoring of CNT surface oxygen groups by gas-phase oxidation and its implications for lithium ion batteries. Electrochem Commun 15:10–13
Lee J, Zhang R, Liu Z (2000) Dispersion of Sn and SnO on carbon anodes. J Power Sour 90:70–75
Noel M, Suryanarayanan V (2002) Role of carbon host lattices in Li-ion intercalation/de-intercalation processes. J Power Sour 111:193–209
Sehrawat P, Julien C, Islam SS (2016) Carbon nanotubes in Li-ion batteries: a review. Mat Sci Eng 213:12–40
Shen Y, Wang X, Hu H et al (2016) A reversible conversion and intercalation reaction material for Li ion battery cathode. Mater Lett 180:260–263
Shi L, Wang Q, Li H et al (2001) Electrochemical performance of Ni-deposited graphite anodes for lithium secondary batteries. J Power Sour 102:60–67
Shi Y, Pan X, Li B et al (2018) Co3O4 and its composites for high-performance Li-ion batteries: review. Chem Eng J 343:427–446
Shouman MA, Fathy NA (2018) Microporous nanohybrids of carbon xerogels and multi-walled carbon nanotubes for removal of rhodamine B dye. J Water Process Eng 23:165–173
Takamura T, Sumiya K, Suzuki J et al (1999) Enhancement of Li doping/undoping reaction rate of carbonaceous materials by coating with an evaporated metal film. J Power Sour 81(82):368–372
Thirumal V, Pandurangan A, Jayavel R et al (2016) Synthesis of nitrogen doped coiled double walled carbon nanotubes by chemical vapor deposition method for supercapacitor applications. Curr Appl Phys 16:816–825
Wang Q, Li H, Chen L et al (2002) Novel spherical microporous carbon as anode material for Li-ion batteries. Sol State Ion 153:43–50
Wang X, Wang J, Su L (2009) Preparation and electrochemical performance of ultra-short carbon nanotubes. J Power Sour 18:194–200
Wang J, Wu H, Cui Y et al (2018) A new class of ternary compound for lithium-ion battery: from composite to solid solution. ACS Appl Mater Interface 10:5125–5132
Wu YP, Wan C, Jiang C et al (1999) Mechanism of lithium storage in low temperature carbon. Carbon 37:1901–1908
Wu YP, Rahm E, Huolze R (2003) Carbon anode materials for lithium ion batteries. J Power Sour 114:228–236
Xiong Z, Yun YS, Jin H-J (2013) Applications of carbon nanotubes for lithium ion battery anodes. Materials 6:1138–1158
Xua Z-L, Kimb J-K, Kanga K (2018) Carbon nanomaterials for advanced lithium sulfur batteries: review. Nano Today 19:84–107
Yang S, Song H, Chen X (2006) Electrochemical performance expanded mesocarbon microbeads as anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochem Commun 8:137–142
Yanga Z, Lib Z, Wuc H et al (2003) Effects of doped copper on electrochemical performance of the raw carbon nanotubes anode. Mater Lett 57:3160–3166
Zhang Y, Chen T, Wang J (2012) The study of multi-walled carbon nanotubes with different diameter as anodes for lithium-ion batteries. Appl Surf Sci 258:4729–4732
Zhang Q, Wang J, Yu P et al (2018) Porous carbon electrocatalyst with exclusive metal-coordinate active sites for acidic oxygen reduction reaction. Carbon 132:85–94
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the support provided by the Science and Technology platform project (China–Ukraine, 2014C050012001), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong (2014A030310130 and 2014A030313642), Natural Science Foundation of Huizhou University (no. 2015JB004 156020026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diao, G., Li, H., Ivanenko, I. et al. Nickel and cobalt effect on properties of MWCNT-based anode for Li-ion batteries. Appl Nanosci 10, 4839–4845 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01310-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01310-4