Abstract
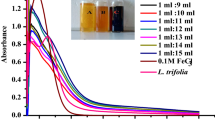
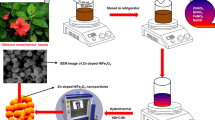
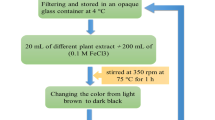
The green synthesis of nanoparticles allows for obtaining nanomaterials using plant extracts, avoiding the use of toxic and dangerous chemical compounds. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of phenolic compounds in plant extracts on the synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles (FexOy-NPs) with photocatalytic activity. Accordingly, the phenolic content in 11 plant extracts was evaluated by the Folin–Ciocalteu (F–C) method, and the iron-reducing capacity was evaluated by the ferric-reducing antioxidant power method (FRAP). From the F–C and FRAP analyses, the Luma apiculata (LAL), Phragmites australis (PAL) and Eucalyptus globulus (EGL) extracts were selected and analyzed by HPLC coupled with a diode array detector (DAD) to identify and quantify the phenolic compounds. Using the three selected extracts, FexOy-NPs were synthesized, which were then characterized by UV–Vis spectroscopy, FTIR, DLS, zeta potential, SEM-EDX, and Raman and diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. The SEM-EDX, DLS and zeta potential analyses showed that the FexOy-NPs were spherical, stable and nanosized. The FRAP, F–C and FTIR analyses indicated the role of phenolic compounds in the formation and stabilization of FexOy-NPs. It was possible to establish a direct relationship between the composition of the phenolic compounds and the reducing capacity of the extracts. In addition, it was found that phenolic compounds and their concentrations are associated with the size and type of FexOy-NPs obtained. Furthermore, it was proposed that types of phenolic compounds influence the formation of different phases of FexOy-NPs. The photocatalytic activity of the FexOy-NPs was demonstrated by diffuse reflectance spectroscopy and decolorization of a dye under visible radiation.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida I, Fernandes E, Lima J, Valentão P, Andrade P, Seabra R, Costa P, Bahia M (2009) Oxygen and nitrogen reactive species are effectively scavenged by eucalyptus globulus leaf water extract. J Med Food 12:175–183. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2008.0046
Anouar EH, Gierschner J, Duroux J-L, Trouillas P (2012) UV/Visible spectra of natural polyphenols: a time-dependent density functional theory study. Food Chem 131:79–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.08.034
Berker KI, Guclu K, Demirata B, Apak R (2010) A novel antioxidant assay of ferric reducing capacity measurement using ferrozine as the colour forming complexation reagent. Anal Methods 2:1770–1778. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0AY00245C
Bersani D, Lottici P, Montenero A (1999) Micro-Raman investigation of iron oxide films and powders produced by sol–gel syntheses. J Raman Spectrosc 30:355–360. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4555(199905)30:5%3C355::AID-JRS398%3E3.0.CO;2-C
Bishnoi S, Kumar A, Selvaraj R (2018) Facile synthesis of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles using inedible Cynometra ramiflora fruit extract waste and their photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue dye. Mater Res Bull 97:121–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2017.08.040
Burgos V, Araya F, Reyes-Contreras C, Vera I, Vidal G (2017) Performance of ornamental plants in mesocosm subsurface constructed wetlands under different organic sewage loading. Ecol Eng 99:246–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.11.058
Calheiros CSC, Bessa VS, Mesquita RBR, Brix H, Rangel AOSS, Castro PML (2015) Constructed wetland with a polyculture of ornamental plants for wastewater treatment at a rural tourism facility. Ecol Eng 79:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2015.03.001
Castillo RdP, Araya J, Troncoso E, Vinet S, Freer J (2015) Fourier transform infrared imaging and microscopy studies of Pinus radiata pulps regarding the simultaneous saccharification and fermentation process. Anal Chim Acta 866:10–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.01.032
Cornell RM, Schwertmann U (2003) The iron oxides: structure, properties, reactions, occurrences and uses. Wiley, New York
Davis EA, Mott NF (1970) Conduction in non-crystalline systems V. Conductivity, optical absorption and photoconductivity in amorphous semiconductors. Philos Mag 22:0903–0922. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786437008221061
Devatha CP, Thalla AK, Katte SY (2016) Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles using different leaf extracts for treatment of domestic waste water. J Clean Prod 139:1425–1435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.09.019
Durán N, Cuevas R, Cordi L, Rubilar O, Diez MC (2014) Biogenic silver nanoparticles associated with silver chloride nanoparticles (Ag@AgCl) produced by laccase from Trametes versicolor. SpringerPlus 3:645. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-3-645
El-Moslamy SH, Elkady MF, Rezk AH, Abdel-Fattah YR (2017) Applying Taguchi design and large-scale strategy for mycosynthesis of nano-silver from endophytic Trichoderma harzianum SYA.F4 and its application against phytopathogens. Sci Rep 7:45297. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep45297
Fazlzadeh M, Rahmani K, Zarei A, Abdoallahzadeh H, Nasiri F, Khosravi R (2017) A novel green synthesis of zero valent iron nanoparticles (NZVI) using three plant extracts and their efficient application for removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions. Adv Powder Technol 28:122–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2016.09.003
Fuentes N, Pauchard A, Sánchez P, Esquivel J, Marticorena A (2013) A new comprehensive database of alien plant species in Chile based on herbarium records. Biol Invasions 15:847–858. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-012-0334-6
Iravani S (2011) Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem 13:2638–2650. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1GC15386B
Kähkönen MP, Hopia AI, Vuorela HJ, Rauha J-P, Pihlaja K, Kujala TS, Heinonen M (1999) Antioxidant activity of plant extracts containing phenolic compounds. J Agric Food Chem 47:3954–3962. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf990146l
Lin J, Weng X, Dharmarajan R, Chen Z (2017) Characterization and reactivity of iron based nanoparticles synthesized by tea extracts under various atmospheres. Chemosphere 169:413–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.11.092
Lu W, Shen Y, Xie A, Zhang W (2010) Green synthesis and characterization of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 322:1828–1833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2009.12.035
Machado S, Pinto SL, Grosso JP, Nouws HPA, Albergaria JT, Delerue-Matos C (2013) Green production of zero-valent iron nanoparticles using tree leaf extracts. Sci Total Environ 445–446:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.12.033
Martínez-Cabanas M, López-García M, Barriada JL, Herrero R, Sastre de Vicente ME (2016) Green synthesis of iron oxide nanoparticles. Development of magnetic hybrid materials for efficient As(V) removal. Chem Eng J 301:83–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.04.149
Mondal P, Purkait MK (2018) Green synthesized iron nanoparticles supported on pH responsive polymeric membrane for nitrobenzene reduction and fluoride rejection study: Optimization approach. J Clean Prod 170:1111–1123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.222
Nidheesh PV, Gandhimathi R, Velmathi S, Sanjini NS (2014) Magnetite as a heterogeneous electro Fenton catalyst for the removal of Rhodamine B from aqueous solution. RSC Adv 4:5698–5708. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3RA46969G
Nieuwoudt MK, Comins JD, Cukrowski I (2011) The growth of the passive film on iron in 0.05 M NaOH studied in situ by Raman micro-spectroscopy and electrochemical polarisation. Part I: near-resonance enhancement of the Raman spectra of iron oxide and oxyhydroxide compounds. J Raman Spectrosc 42:1335–1339. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrs.2837
Pang YL, Lim S, Ong HC, Chong WT (2016) Research progress on iron oxide-based magnetic materials: synthesis techniques and photocatalytic applications. Ceram Int 42:9–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.08.144
Perron NR, Brumaghim JL (2009) A review of the antioxidant mechanisms of polyphenol compounds related to iron binding. Cell Biochem Biophys 53:75–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-009-9043-x
Prior RL, Wu X, Schaich K (2005) Standardized methods for the determination of antioxidant capacity and phenolics in foods and dietary supplements. J Agric Food Chem 53:4290–4302. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0502698
Rabbani M, Rafiee F, Ghafuri H, Rahimi R (2016) Synthesis of Fe3O4 nonoparticles via a fast and facile mechanochemicl method: modification of surface with porphyrin and photocatalytic study. Mater Lett 166:247–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.12.087
Rengasamy M, Anbalagan K, Kodhaiyolii S, Pugalenthi V (2016) Castor leaf mediated synthesis of iron nanoparticles for evaluating catalytic effects in transesterification of castor oil. RSC Adv 6:9261–9269. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA15186D
Salgado P, Melin V, Contreras D, Moreno Y, Mansilla HD (2013) Fenton reaction driven by iron ligands. J Chil Chem Soc 58:2096–2101. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0717-97072013000400043
Sarkar J, Mollick MMR, Chattopadhyay D, Acharya K (2017) An eco-friendly route of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles formation and investigation of the mechanical properties of the HPMC-γ-Fe2O3 nanocomposites. Bioproc Biosyst Eng 40:351–359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00449-016-1702-x
Sepúlveda-Mardones M, López D, Vidal G (2017) Methanogenic activity in the biomass from horizontal subsurface flow constructed wetlands treating domestic wastewater. Ecol Eng 105:66–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.04.039
Shahwan T, Abu Sirriah S, Nairat M, Boyacı E, Eroğlu AE, Scott TB, Hallam KR (2011) Green synthesis of iron nanoparticles and their application as a Fenton-like catalyst for the degradation of aqueous cationic and anionic dyes. Chem Eng J 172:258–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.05.103
Shamaila S, Sajjad AKL, Ryma N-u-A, Farooqi SA, Jabeen N, Majeed S, Farooq I (2016) Advancements in nanoparticle fabrication by hazard free eco-friendly green routes. Appl Mater Today 5:150–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2016.09.009
Sharma P, Kumar R, Chauhan S, Singh D, Chauhan M (2014) Facile growth and characterization of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles for photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange. J Nanosci Nanotechno 14:6153–6157. https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2014.8734
Sherman DM (2005) Electronic structures of iron(III) and manganese(IV) (hydr)oxide minerals: thermodynamics of photochemical reductive dissolution in aquatic environments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69:3249–3255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2005.01.023
Shi A, Chen X, Liu L, Hu H, Liu H, Wang Q, Agyei D (2017) Synthesis and characterization of calcium-induced peanut protein isolate nanoparticles. RSC Adv 7:53247–53254. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA07987G
Simirgiotis MJ, Bórquez J, Schmeda-Hirschmann G (2013) Antioxidant capacity, polyphenolic content and tandem HPLC–DAD–ESI/MS profiling of phenolic compounds from the South American berries Luma apiculata and L. chequén. Food Chem 139:289–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.01.089
Szymczycha-Madeja A, Welna M, Zyrnicki W (2013) Multi-element analysis, bioavailability and fractionation of herbal tea products. J Brazil Chem Soc 24:777–787. https://doi.org/10.5935/0103-5053.20130102
Tauc J, Grigorovici R, Vancu A (1966) Optical properties and electronic structure of amorphous germanium. Phys Status Solidi B 15:627–637. https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.19660150224
Teja AS, Koh P-Y (2009) Synthesis, properties, and applications of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Prog Cryst Growth Charact Mater 55:22–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcrysgrow.2008.08.003
Vijayaraghavan K, Ashokkumar T (2017) Plant-mediated biosynthesis of metallic nanoparticles: a review of literature, factors affecting synthesis, characterization techniques and applications. J Environ Chem Eng 5:4866–4883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2017.09.026
Wang SY, Lin H-S (2000) Antioxidant activity in fruits and leaves of blackberry, raspberry, and strawberry varies with cultivar and developmental stage. J Agric Food Chem 48:140–146. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf9908345
Wang T, Lin J, Chen Z, Megharaj M, Naidu R (2014) Green synthesized iron nanoparticles by green tea and eucalyptus leaves extracts used for removal of nitrate in aqueous solution. J Clean Prod 83:413–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2014.07.006
Wu W, Changzhong J, Roy VAL (2015) Recent progress in magnetic iron oxide-semiconductor composite nanomaterials as promising photocatalysts. Nanoscale 7:38–58. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NR04244A
Xiao Z, Yuan M, Yang B, Liu Z, Huang J, Sun D (2016) Plant-mediated synthesis of highly active iron nanoparticles for Cr (VI) removal: Investigation of the leading biomolecules. Chemosphere 150:357–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.02.056
Xu P, Zeng GM, Huang DL, Feng CL, Hu S, Zhao MH, Lai C, Wei Z, Huang C, Xie GX, Liu ZF (2012) Use of iron oxide nanomaterials in wastewater treatment: a review. Sci Total Environ 424:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.02.023
Zanella D, Bossi E, Gornati R, Bastos C, Faria N, Bernardini G (2017) Iron oxide nanoparticles can cross plasma membranes. Sci Rep 7:11413. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-11535-z
Zhang Z, Hossain MF, Takahashi T (2010) Self-assembled hematite (α-Fe2O3) nanotube arrays for photoelectrocatalytic degradation of azo dye under simulated solar light irradiation. Appl Catal B Environ 95:423–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.01.022
Zhang H, Ji Z, Xia T, Meng H, Low-Kam C, Liu R, Pokhrel S, Lin S, Wang X, Liao Y-P, Wang M, Li L, Rallo R, Damoiseaux R, Telesca D, Madler L, Cohen Y, Zink J, Nel AE (2012) Use of metal oxide nanoparticle band gap to develop a predictive paradigm for oxidative stress and acute pulmonary inflammation. ACS Nano 6:4349–4368. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn3010087
Zvarec O, Purushotham S, Masic A, Ramanujan RV, Miserez A (2013) Catechol-functionalized chitosan/iron oxide nanoparticle composite inspired by mussel thread coating and squid beak interfacial chemistry. Langmuir 29:10899–10906. https://doi.org/10.1021/la401858s
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by CONICYT/FONDAP/15130015. Pablo Salgado would like to thank Project CONICYT FONDECYT/Postdoctorado 3180566. The authors would like to thank the Centro de Microscopía Avanzada, CMA BIO–BIO Proyecto CONICYT PIA ECM-12; Interdisciplinary Group of Advanced Nanocomposites of the School of Engineering, University of Concepción and its Project CONICYT FONDEQUIP/EQM 150139; Project CONICYT FONDEQUIP/EQM 140088; and the Laboratory of Organic Environmental Chemistry for its spectroscope of diffuse reflectance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salgado, P., Márquez, K., Rubilar, O. et al. The effect of phenolic compounds on the green synthesis of iron nanoparticles (FexOy-NPs) with photocatalytic activity. Appl Nanosci 9, 371–385 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-018-0931-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-018-0931-5