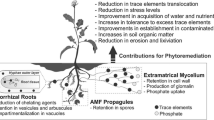
Abstract
Agricultural and industrial activity generates high concentrations of organic and inorganic pollutants, many of which are incorporated into the trophic chain, affecting ecosystems. There are several strategies for the remediation of polluted areas; we discuss one of them in the present review that shows the successful evidence of the use of arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis in phytoextraction (the removal of contaminants from soil and water sources with mycorrhizal plants), and in the process of phytostabilization (the reduction of the mobility of heavy metals in soil by mycorrhizal roots, absorption onto roots, or precipitation within the root zone). Mechanisms of action of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) including, altered uptake and distribution of heavy metals, improvement in the mineral nutrition and water availability, protection against oxidative stress and increment in the physical stability of the soil by producing glomalin has been discussed with reference to heavy metals (HMs) and persistent oxidative pollutants (POPs). We report plant species associated with species of mycorrhizal fungi as strategy for phytostabilizing heavy metals and reducing biotranslocation to the aerial parts of plants.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelhameed RE, Metwally RA (2019) Alleviation of cadmium stress by arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Int J Phytoremediation 21(7):663–671. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2018.1556584
Abdul K (2006) Mycorrhizoremediation-an enhanced form of phytoremediation. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 7(7):503–514. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.2006.B0503
Agarwal A, Singh J, Sing AP (2017) Review paper Arbuscular Mycorrhizal fungi and its role sequestration of heavy metal. Biosci Trends 10(21):4068–4077
Alarcón A, Davies F Jr, Autenrieth RL, Zuberer DA (2008) Arbuscular mycorrhiza and petroleum-degrading microorganisms enhance phytoremediation of petroleum-contaminated soil. Int J Phytorem 10:251–263. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226510802096002
Ali H, Khan E, Ilahi I (2019) Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: environmental persistence, toxicity and bioaccumulation. Hindawi J Chem 14:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6730305
Ali H, Khan E (2017) What are heavy metals? Long-standing controversy over the scientific use of the term ‘heavy metals’–proposal of a comprehensive definition. Toxicol Environ Chem 100(1):1–2. https://doi.org/10.1080/02772248.2017.1413652
Ambrosini VG, Voges JG, Canton L, Couto RR, Ferreira PAA, Comin JJ, Bastos de Melo GW, Brunetto G, Soares FCR (2015) Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on young vines in copper-contaminated soil. Braz J Microbiol 46(4):1045–1052. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1517-838246420140622
Andrade SAL, Silveira APD, Mazzafera P (2010) Arbuscular mycorrhiza alters metal uptake and the physiological response of Coffea arabica seedlings to increasing Zn and Cu concentrations in soils. Sci Total Environ 408:5381–5391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2010.07.064
Andrade SAL, Da Silveira APD, Jorge RA, De Abreu MF (2008) Cadmium accumulation in sunflower plants influenced by arbuscular mycorrhiza. Int J Phytoremediation 10(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/1522651070182700
Appenroth KJ (2010) Definition of “heavy metals” and their role in biological systems. In: Sherameti I, Varma A (eds) Soil heavy metals. Springer, pp 19–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-02436-8_2
Aprile A, De Bellis L (2020) Editorial for special issue: heavy metals accumulation, toxicity, and detoxification in plants. Int J Mol Sci 21(11):4103. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21114103
Arriagada C, Pereira G, García-Romera I, Ocampo JA (2010) Improved zinc tolerance in Eucalyptus globulus inoculated with Glomus deserticola and Trametes versicolor or Coriolopsis rigida. Soil Biol Biochem 42(1):118–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.10.011
Arriagada C, Aranda E, Sampedro I, García-Romera I, Ocampo JA (2009) Contribution of the saprobic fungi Trametes versicolor and Trichoderma harzianum and the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi Glomus deserticola and G. claroideum to arsenic tolerance of Eucalyptus globulus. Bioresour Technol 100(24):6250–6257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.07.010
Arriagada CA, Herrera MA, Ocampo JA (2007) Beneficial effect of saprobe and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth of Eucalyptus globulus co-cultured with Glycine max in soil contaminated with heavy metals. J Environ Manag 84:93–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2006.05.005
Arriagada CA, Herrera MA, García-Romera I, Ocampo JA (2004) Tolerance to cd of soybean (Glycine max) and eucalyptus (Eucalyptus globulus) inoculated with arbuscular mycorrhizal and saprobe fungi. Symbiosis 36:285–299
Audet P, Charest C (2007) Dynamics of arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis in heavy metal phytoremediation: meta-analytical and conceptual perspectives. Environ Pollut 147:609–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2006.10.006
Azcón R, Perálvarez MC, Biró B, Roldán A, Ruíz-Lozano JM (2009) Antioxidant activities and metal acquisition in mycorrhizal plants growing in a heavy-metal multicontaminated soil amended with treated lignocellulosic agrowaste. Appl Soil Ecol 41(2):168–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2008.10.008
Babadi M, Zalaghi R, Taghavi M (2019) A non-toxic polymer enhances sorghum-mycorrhiza symbiosis for bioremediation of cd. Mycorrhiza. 29:375–387. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-019-00902-5
Brundrett MC, Tedersoo L (2020) Resolving the mycorrhizal status of important northern hemisphere trees. Plant Soil 454:3–34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-020-04627-9
Brundrett MC, Tedersoo L (2018) Evolutionary history of mycorrhizal symbioses and global host plant diversity. New Phytol 220:1108–1115. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14976
Calonne-Salmon M, Plouznikoff K, Declerck S (2018) The arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Rhizophagus irregularis MUCL 41833 increases the phosphorus uptake and biomass of Medicago truncatula, a benzo[a]pyrene-tolerant plant species. Mycorrhiza 28:761–771. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-018-0861-9
Cao J, Wang C, Dou Z, Liu M, Ji D (2018) Hyphospheric impacts of earthworms and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on soil bacterial community to promote oxytetracycline degradation. J Hazard Mater 341:346–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.07.038
Cao J, Ji D, Wang C (2015) Interaction between earthworms and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the degradation of oxytetracycline in soils. Soil Biol Biochem 90:283–292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.08.020
Castillo OS, Dasgupta-Schubert N, Alvarado CJ, Zaragoza EM, Villegas HJ (2011) The effect of the symbiosis between Tagetes erecta L. (marigold) and Glomus intraradices in the uptake of copper (II) and its implications for phytoremediation. N Biotechnol 29(1):156–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2011.05.009
Cheng H, Wang J, Tu C, Lin S, Xing D, Hill P, Chadwick D, Jones DL (2021) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and biochar influence simazine decomposition and leaching. Glob Change Biol Bioenergy 13:708–718. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcbb.12802
Chen S, Zhou Z, Tsang DCW, Wang J, Odinga ES, Gao Y (2020) Glomalin-related soil protein reduces the sorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by soils. Chemosphere 260:105093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.127603
Chen S, Sheng X, Qin C, Waigi MG, Gao Y (2019) Glomalin-related soil protein enhances the sorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons on cation-modified montmorillonite. Environ Int 132:105093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.105093
Chen M, Arato M, Borghi L, Nouri E, Reinhardt D (2018a) Beneficial services of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi–from ecology to application. Front Plant Sci 9:1270. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01270
Chen BD, Nayuki K, Kuga Y, Zhang X, Wu S, Ohtomo R (2018b) Uptake and Intraradical immobilization of cadmium by Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi as revealed by stable isotope tracer and synchrotron radiation μX-ray fluorescence analysis. Microbes Environ 33(3):257–263. https://doi.org/10.1264/jsme2.ME18010
Chen XH, Zhao B (2007) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi mediated uptake of lanthanum in Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.). Chemosphere 68(8):1548–1555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.02.068
Chen BD, Zhu YG, Duan J, Xiao XY, Smith SE (2007) Effects of the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus mosseae on growth and metal uptake by four plant species in copper mine tailings. Environ Pollut 147(2):374–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2006.04.027
Chhabra ML, Jalali BL (2013) Impact of pesticides-mycorrhia interaction on growth and development of wheat. J Biopestic 6(2):129–132
Citterio S, Prato N, Pietro Fumagalli P, Aina R, Massa N, Santagostino A, Sgorbati S, Berta G (2005) The arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus mosseae induces growth and metal accumulation changes in Cannabis sativa L. Chemosphere 59:21–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.10.009
Cornejo P, Meier S, García S, Ferrol N, Durán P, Borie F, Seguel A (2017) Contribution of inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi to the bioremediation of a copper polluted soil using Oenothera picensis. Journal of soil science and plant nutrition. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 17(1):14–21. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0718-95162016005000070
Cornejo P, Meier S, Borie G, Rillig MC, Borie F (2008) Glomalin-related soil protein in a Mediterranean ecosystem affected by a copper smelter and its contribution to cu and Zn sequestration. Sci Total Environ 406(1–2):154–160
Csuros M, Csuros C (2002) Environmental sampling and analysis for metals, Lewis publishers, Boca Raton, FL, USA. 1st Edition CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420032345
De la Providencia IE, Stefani FOP, Labridy M, St-Arnaud M, Hijri M (2015) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal diversity associated with Eleocharis obtusa and Panicum capillare growing in an extreme petroleum hydrocarbon-polluted sedimentation basin. FEMS Microbiol Lett 362(12):fnv081. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnv081
Del Val C, Barea JM, Azcón-Aguilar C (1999) Diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus populations in heavy metal contaminated soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 99:718–723. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.65.2.718-723.1999
Dhalaria R, Kumar D, Kumar H, Nepovimova E, Kuča K, Torequl Islam M, Verma R (2020) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi as potential agents in ameliorating heavy metal stress in plants. Agronomy 10(6):815. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy10060815
Dietz KJ, Baier M, Kramer U (1999) Free radicals and reactive oxygen species as mediators of heavy metal toxicity in plants. In: Prasad H (ed) Heavy metal stress in plants. From Molecules to Ecosystem. Springer, Berlin, pp 73–97. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-07745-0_4
Dong J, Wang L, Ma F, Yang J, Qi S, Zhao T (2016) The effect of Funnelliformis mosseae inoculation on the phytoremediation of atrazine by the aquatic plant Canna indica L. var. flava Roxb. RSC Adv 6(27):22538–22549. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra23583a
Dua M, Singh A, Sethunathan N, Jhri AK (2002) Biotechnology and bioremediation: successes and limitations. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 59:143–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-002-1024-6
Dupré de Boulois H, Joner EJ, Leyval C, Jakobsen I, Chen BD, Roos P, Thiry Y, Rufyikiri G, Delvaux B, Declerck S (2008) Impact of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on uranium accumulation by plants. J Environ Radioact 99(5):775–784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2007.10.009
Fan X, Song F (2018) Responses of nonenzymatic antioxidants to atrazine in arbuscular mycorrhizal roots of Medicago sativa L. Mycorrhiza 28:567–571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-018-0848-6
Ferreira PA, Ceretta CA, Tiecher T, Facco DB, Garlet LP, Soares CRFS et al (2018) Rhizophagus Clarus and phosphorus in Crotalaria juncea: growth, Glomalin content and acid phosphatase activity in a copper-contaminated soil. Rev Bras Cienc Solo 42:e0170245. https://doi.org/10.1590/18069657rbcs20170245
Ferrol N, González-Guerrero M, Valderas A, Benabdellah K, Azcón-Aguilar C (2009) Survival strategies of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in cu-polluted environments. Phytochem Rev 8:551–559. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-009-9133-9
Gao WQ, Wang P, Wu QS (2019) Functions and application of glomalin-related soil proteins: a review. Sains Malaysiana 48(1):111–119. https://doi.org/10.17576/jsm-2019-4801-13
Gao Y, Zhou Z, Ling W, Hu X, Chen S (2017) Glomalin-related soil protein enhances the availability of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 107:129–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2017.01.002
Gao Y, Li Q, Ling W, Zhu X (2011) Arbuscular mycorrhizal phytoremediation of soils contaminated with phenanthrene and pyrene. J Hazard Mater 185:703–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.09.076
Gao Y, Cheng Z, Ling W, Huang J (2010) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal hyphae contribute to the uptake of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by plant roots. Bioresour Technol 101:6895–6901
Garg N, Aggarwal N (2012) Effect of mycorrhizal inoculations on heavy metal uptake and stress alleviation of Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp. Genotypes grown in cadmium and lead contaminated soils. Plant Growth Regul 66:9–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-011-9624-8
Garg N, Bhandari P (2012) International journal of phytoremediation influence of cadmium stress and Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi on nodule senescence in Cajanus Cajan (L.) MILLSP. Int J Phytoremediation 14(1):62–74. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2011.573822
Ghasemi NS, Fallah S, Pokhrel LR, Rostamnejadi A (2017) Natural amelioration of zinc oxide nanoparticle toxicity in fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-gracum) by arbuscular mycorrhizal (Glomus intraradices) secretion of glomalin. Plant Physiol Biochem 112:227–238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.01.001
Gil-Cardeza ML, Ferri A, Cornejo P, Gomez E (2014) Distribution of chromium species in a Cr-polluted soil: presence of Cr(III) in glomalin related protein fraction. Sci Total Environ 493:828–833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.06.080
Glick BR (2010) Using soil bacteria to facilitate phytoremediation. Biotechnol Adv 28:367–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2010.02.001
González-Chávez MC, Carrillo-González R, Wright SF, Nichols KA (2004) The role of glomalin, a protein produced by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, in sequestering potentially toxic elements. Environ Pollut 130:317–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2004.01.004
Goto BT, Jobim K. Laboratório de Biologia de Micorrizas. Disponible en: < http://glomeromycota.wixsite.com/lbmicorrizas >. Acesso em: 10/03/2020
Grant CA, Sheppard SC (2008) Fertilizer impacts on cadmium availability in agricultural soils and crops. Hum Ecol risk assess: an international Journal,14(2):210-228. 14:210–228. https://doi.org/10.1080/10807030801934895
Gu HH, Zhou Z, Gao YQ, Yuan XT, Ai YJ, Zhang JY, Li FP (2017) The influences of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus on phytostabilization of lead/zinc tailings using four plant species. Intl J Phytoremediation 19(8):739–745. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2017.1284751
Guo W, Zhao R, Zhao W, Fu R, Guo J, Bi N, Zhang J (2013) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on maize (Zea mays L.) and sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench) grown in rare earth elements of mine tailings. Appl. Soil Ecol 72:85–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2013.06.001
Gupta MM, Abbott LK (2020) Exploring economic assessment of the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Symbiosis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-020-00738
Gupta MM, Chourasiya D, Sharma MP (2019) Diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in relation to sustainable plant production systems. In: Microbial diversity in ecosystem sustainability and biotechnological applications. Springer, Singapore, pp 167–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-8487-5_7
Gupta MM, Aggarwal A, Asha (2018) From mycorrhizosphere to rhizo-sphere microbiome: the paradigm shift. In: Giri B, Prasad R, Varma A (eds) Root Biology Springer, Cham, pp. 487–500. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-75910-4_20
Gupta SC, Goldsbrough PB (1991) Phytochelatin accumulation and cadmium tolerance in selected tomato cell lines. Plant Physiol 97:306–312
Hancock LM, Ernst CL, Charneskie R, Ruane LG (2012) Effects of cadmium and mycorrhizal fungi on growth, fitness, and cadmium accumulation in flax (Linum usitatissimum; Linaceae). Am J Bot 99:1445–1452. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.1100497
Hashem A, Abd-Allah EF, Alqarawi AA, Egamberdieva D (2016) Bioremediation of adverse impact of cadmium toxicity on Cassia italica mill by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Saudi J Biol Sci 23(1):39–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.11.007
Hassan GR (2005) Contribution of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus to red kidney and wheat plants tolerance grown in heavy metal-polluted soil. Afr J Biotech 4(4):332–345
Hernández-Ortega HA, Alarcón A, Ferrera-Cerrato R, Zavaleta-Mancera HA, López-Delgado HA, Mendoza-López MR (2012) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth, nutrient status, and total antioxidant activity of Melilotus albus during phytoremediation of a diesel-contaminated substrate. J Environ Manag 95:S319–S324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman
Huang H, Zhang S, Shan X-Q, Chen BD, Zhu YG, Bell JNB (2007) Effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus (Glomus caledonium) on the accumulation and metabolism of atrazine in maize (Zea mays L.) and atrazine dissipation in soil. Environ. Pollut., 146(2), 452–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2006.07.001
Ibáñez SG, Medina MI, Agostini E (2011) Phenol tolerance, changes of antioxidative enzymes and cellular damage in transgenic tobacco hairy roots colonized by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Chemosphere 83(5):700–705. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.02.021
Jamal A, Ayub N, Usman M, Khan AG (2002) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi enhance zinc and nickel uptake from contaminated soil by soybean and lentil. Int J Phytoremediation 4(3):205–221. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226510208500083
Janeeshma E, Puthur JT (2020) Direct and indirect influence of arbuscular mycorrhizae on enhancing metal tolerance of plants. Arch microbiol 202(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-019-01730-z
Janousková M, Pavliková D, Vosátka M (2006) Potential contribution of arbuscular mycorrhiza to cadmium immobilisation in soil. Chemosphere 65:1959–1965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.07.007
Jiang QY, Zhuo F, Long SH, Zhao HD, Yang DJ, Ye ZH, Li SS, Jing YX (2016) Can arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi reduce cd uptake and alleviate cd toxicity of Lonicera japonica grown in cd-added soils? Sci Rep 6:21805. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep21805
Joner E, Leyval C (2003a) Phytoremediation of organic pollutants using mycorrhizal plants: a new aspect of rhizosphere interactions. Agronomie 23(5):495–502. https://doi.org/10.1051/agro:2003021
Joner EJ, Leyval C (2003b) Rhizospheric degradation of Phenanthrene is a funtion proximity to roots. Plant Soil 257:143–150. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026278424871
Joner EJ, Leyval C (2001) Influence of arbuscular mycorrhiza on clover and ryegrass grown together in a soil spiked with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Mycorrhiza 10:155–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s005720000071
Joner EJ, Briones R, Leyval C (2000) Metal-binding capacity of arbuscular mycorrhizal mycelium. Plant Soil 226:227–234. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026565701391
Leal LP, Varón-López M, de Gonçalves OPI, Valentim dos Santos J, Fonsêca SSCR, Siqueira JO, de Souza MFM (2016) Enrichment of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in a contaminated soil after rehabilitation. Braz J Microbiol 47(4):853–862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjm.2016.06.001
Lebeau T, Braud A, Jézequel K (2008) Performance of bioaugmentation.Assisted phytoextraction applied to metal contaminated soils: a review. Environ Pollut 153:497–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.09.015
Lenoir IA, Lounés-Hadj S, Fontaine J (2016a) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal-asssited phytoremediation of soil contaminated with persistente organic pollutants: a review. Eur J Soil Sci, September 67:624–640. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12375
Lenoir IA, Lounés-Hadj SA, Laruelle F, Dalpé Y, Fontaine J (2016b) Arbuscular mycorrhizal wheat inoculation promotes alkane and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon biodegradation: microcosm experiment on aged-contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 213:549–560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2016.02.056
Leyval C, Poner EJ, del Val C, Haselwandter K (2002) Potential or arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for bioremediation. In: Gianinazzi S, Schüepp H, Barea JM, Haselwandter K (eds) Mycorrhizal technology in agriculture. Birkhäuser, Base, pp 175–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-8117-3_14
Leyval C, Turnau K, Haselwandter K (1997) Effect of heavy metal pollution on mycorrhizal colonisation and function, physiological, ecological and applied aspects. Mycorrhiza 7:139–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/s005720050174
Liao JP, Lin XG, Cao ZH, Shi YQ, Wong MH (2003) Interactions between arbuscular mycorrhizae and heavy metals under sand culture experiment. Chemosphere 50:847–853. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0045-6535(02)00229-1
Liu L, Li J, Yue F, Yan X, Wang F, Bloszies S, Wang Y (2018) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal inoculation and biochar amendment on maize growth, cadmium uptake and soil cadmium speciation in cd-contaminated soil. Chemosphere 194:495–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.12.025
Lu YF, Lu M (2015) Remediation of PAH-contaminated soil by the combination of tall fescue, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and epigenic earthworms. J Hazard Mater 285:535–541. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.07.021
Lu YF, Lu M, Peng F, Wan Y, Liao MH (2014) Remediation of polychlorinated biphenyl-contaminated soil by using a combination of ryegrass, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and earthworms. Chemosphere 106:44–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.12.089
Ma Y, Rajkumar M, Oliveira RS, Zhang C, Freitas H (2019) Potential of plant beneficial bacteria and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in phytoremediation of metal-contaminated saline soils. J Hazard Mater 379:120813. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120813
Maiti RK, Hernández JL, González A, López D (2004) Plant based Biorremediation and mechanisms of heavy metal tolerance of plants: a review. Proc Indian natn Sci Acad B70(1):1–12
Malcová R, Vosátka M, Gryndler M (2003) Effects of inoculation with Glomus intraradices on lead uptake by Zea mays L. and Agrostis capillaris L. Appl Soil Ecol 23(1):55–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0929-1393(02)00160-9
Malekzadeh E, Aliasgharzad N, Majidi J, Abdolalizadeh J, Aghebati-Maleki L (2016) Contribution of glomalin to Pb sequestration by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus in a sand culture system with clover plant. Eur J Soil Biol 74:45–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2016.03.003
Miransari M (2011) Hyperaccumulators, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and stress of heavy metals. Biotechnol Adv 29(6):645–653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.04.006
Mohammad A, Mittra B (2013) Effects of inoculation with stress-adapted arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus deserticola on growth of Solanum melogena L. and Sorghum sudanese staph. Seedlings under salinity and heavy metal stress conditions. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 59(2):173–183. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2011.610029
Nkereuwem ME, Fagbola O, Okon IE, Adeleye AO, Nzamouhe M (2020) Bioremediation potential of mycorrhiza fungi in crude oil contaminated soil planted with Costus lucanusianus. Amazon J Plant Res 4(1):441–455. https://doi.org/10.26545/ajpr.2020.b00053x
Ogar A, Sobczyk Ł, Turnau K (2015) Effect of combined microbes on plant tolerance to Zn–Pb contaminations. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(23):19142–19156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-5094-2
Orłowska E, Godzik B, Turnau K (2012) Effect of different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal isolates on growth and arsenic accumulation in Plantago lanceolate L. Environ Poll 168:121–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2012.04.026
Oyetibo GO, Miyauchi K, Huang Y, Chien MF, Ilori MO, Amund OO, Endo G (2017) Biotechnological remedies for the estuarine environment polluted with heavy metals and persistent organic pollutants. Intl Biodeterioration Biodegradation 119:614–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2016.10.005
Pedroso D, Barbosa MV, dos Santos JV, Pinto FA, Siqueira JO, Carneiro MAC (2018) Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi favor the initial growth of Acacia mangium, Sorghum bicolor, and Urochloa brizantha in soil contaminated with Zn, cu, Pb, and cd. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 101(3):386–391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2405-6
Pongrac P, Soniak S, Vogel-Mikus K, Kump P, Neemer M, Regvar M (2009) Roots of metal hyperaccumulating population of Thlaspipraecox (Brassicacear) harbour arbuscular mycorrhizal and other fungi under experimental conditions. Int J Phytoremediation 11:4,347–4,359. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226510802565527
Qin H, Brookes PCXJ, Feng Y (2014) Bacterial degradation of Aroclor 1242 in the mycorrhizosphere soils of zucchini (Cucurbita pepo L.) inoculated with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:12790–12799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3231-y
Riaz M, Kamran M, Fang Y, Wang Q, Cao H, Yang G, Deng L, Wang Y, Zhou Y, Anastopoulos I, Wang X (2020) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi-induced mitigation of heavy metal phytotoxicity in metal contaminated soils: a critical review. J Hazard Mater 402:123919. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123919
Rilling MC, Steinberg PD (2002) Glomalin production by an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus: a mechanism of habitat modification? Short communication. Soil Biol Biochem. 34:1371–1374. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(02)00060-3
Rivera-Becerril F, van Tuinen D, Martin-Laurent F, Metwally A, Dietz KJ, Gianinazzi S (2005) Gianinazzi-Pearson V (2005) molecular changes in Pisum sativum L. roots during arbuscular mycorrhizal buffering of cadmium stress. Mycorrhiza 16:51–60.77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-005-0016-7
Ross IS (1975) Some effects of heavy metals on fungal cells. Trans Br Mycol Soc 64(2):175–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-1536(75)80101-X
Ruscitti M, Arango M, Ronco M, Beltrano J (2011) Inoculation with mycorrhizal fungi modifies praline metabolism and increases chromium tolerance in pepper plants (Capsicum annuum L.). Brazilian. J Plant Physiol 23(1):15–25. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1677-04202011000100004
Sainz MJ, González-Penalta B, Vilariño A (2006) Effects of hexachlorocyclohexane on rhizosphere fungal propagules and root colonization by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in Plantago lanceolata. European Eur J Soil Sci 57(1):83–90. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.2005.00775.x
Schutzendubel A, Polle A (2002) Plant responses to abiotic stresses: heavy metal-induced oxidative stress and protection by mycorrhization. J. Exp. Bot. 53(372):1351–1365. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/53.372.1351
Schüßler A, Schwarzott D, Walker C (2001) A new fungal phylum, the Glomeromycota: phylogeny and evolution. Mycol Res 105:1413–1421. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0953756201005196
Setyorini D, Prihatini T, Kurnia U (2002) Pollution of soil by agricultural and industrial waste. Food and Fertelizer Technology Center, Indonesia
Shahabivand S, Maivan HZ, Goltapeh EM, Sharifi M, Aliloo AA (2012) The effects of root endophyte and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on growth and cadmium accumulation in wheat under cadmium toxicity. Plant Physiol Biochem 60:53–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2012.07.018
Sharma V, Parmar P, Kumari N (2016) Differential cadmium stress tolerance in wheat genotypes under mycorrhizal association. J Plant Nutr 39(14):2025–2036. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2016.1170851
Singh G, Pankaj U, Chand S, Kumar RV (2019) Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi-assisted Phytoextraction of toxic metals by Zea mays L. from tannery sludge. Soil Sediment Contam 28(8):729–746. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2019.165738
Singh J, Kumar M, Vyas A (2014) Healthy response from chromium survived Pteridophytic plant-Ampelopteris prolifera with the interaction of Mycorrhizal fungus Glomus deserticola. Intl J Phytoremediation 16(5):524–535. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2013.798619
Singh PK (2015) In vitro cu-sequestration by Glomalin from Acaulospora spinosa Walker and Trappe. Natl Acad Sci Lett 38:183–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40009-014-0309-5
Singh PK (2012) Role of Glomalin related soil protein produced by Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi : a review. J Agric Res Sci 2(3):119–125
Smith SE, Read DJ (1997) Mycorrhizal Symbiosis, 2nd edn. Academic Press, San Diego
Sodango TH, Li X, Sha J, Bao Z (2018) Review of the spatial distribution, source and extent of heavy metal pollution of soil in China: impacts and mitigation approaches. J Health Pollut 8(17):53–70. https://doi.org/10.5696/2156-9614-8.17.53
Solís-Ramos LY, Andrade-Torres A (2020) Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi in tropical ecosystems towards its management? Agri res & Tech: Open Access J. 24(4):556279. https://doi.org/10.19080/ARTOAJ.2020.24.556279
Souza AL, Andrade SAL, Souza CS, Schiavinato AM (2012) Arbuscular mycorrhiza confers Pb tolerance in Calopogonium mucunoides. Acta Physiol Plant 34:523–531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-011-0849-y
Spatafora JW, Chang Y, Benny GL, Lazarus K, Smith ME, Berbee ML, Bonito G, Corradi N, Grigoriev I, Gryganskyi A, James TY, O’Donnell K, Roberson RW, Taylor TN, Uehling J, Vilgalys R, White MM, Stajich JE (2016) A phylum-level phylogenetic classification of zygomycete fungi based on genome-scale data. Mycologia 108:1028–1046. https://doi.org/10.3852/16-042
Sudová R, Vosátka M (2007) Differences in the effects of three arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal strains on P and Pb accumulation by maize plants. Plant Soil 296:77–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-007-9291-8
Sut M, Boldt-Burisch K, Raab T (2016) Possible evidence for contribution of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) in phytoremediation of iron–cyanide (Fe–CN) complexes. Ecotoxicology 25(6):1260–1269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-016-1678-y
Sytar O, Kumar A, Latowski D, Kuczynska P, Strzalka K, Prasad MNV (2013) Heavy metal-induced oxidative damage, defense reactions, and detoxification mechanism in plants. Acta Physiol Plant 35:985–999. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-012-1169-6
Tang M, Chen H, Huang JC, Tian ZQ (2009) AM fungi effects on the growth and physiology of Zea mays seedlings under diesel stress. Soil Biol Biochem 41(5):936–940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.11.007
Tchounwou PB, Yedjou CG, Patlolla AK, Sutton DJ (2014) Heavy metals toxicity and the environment, A. Luch (ed.), molecular, clinical and environmental toxicology, 133-166. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7643-8340-4_6
Tedersoo L, Sánchez-Ramírez S, Koljalg U, Bahram M, Döring M, Schigel D, May T, Ryberg M, Abarenkov K (2018) High-level classification of the Fungi and a tool for evolutionary ecological analyses. Fungal Divers 90:135–159
Teng Y, Luo Y, Sun X, Tu C, Xu L, Liu W, Li Z, Christie P (2010) Influence of arbuscular mycorrhiza and Rhizobium on phytoremediation by alfalfa of an agricultural soil contaminated with weathered PCBs: a field study. Int J Phytoremediation 12(5):516–533. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226510903353120
Toler HD, Morton JB, Cumming JR (2005) Growth and metal accumulation of mycorrhizal sorghum exposed to elevated copper and zinc. Water Air Soil Pollut 164:155–172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-005-2718-z
Tonin C, Vandenkoornhuyse P, Joner EJ, Straczek J, Leyval C (2001) Assessment of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi diversity in the rhizosphere of Viola calaminaria and effect of these fungi on heavy metal uptake by clover. Mycorrhiza 10:161–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s005720000072
Turnau K, Mesjasz-Przybylowicz J (2003) Arbuscular mycorrhiza of Berkheya coddii and other Ni-hyperaccumulating members of Asteraceae from ultramafic soils in South Africa. Mycorrhiza 13:185–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-002-0213-6
Verdin A, Sahraoui ALH, Fontaine J, Grandmoungin-Ferjani A, Durand R (2006) Effects of anthracene on development of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus and contribution of the symbiotic association to pollutant dissipation. Mycorrhiza 16:397–405
Vodnik D, Grčman H, Maček I, van Elteren JT, Kovačevič M (2008) The contribution of glomalin-related soil protein to Pb and Zn sequestration in polluted soil. Sci Total Environ 392(1):130–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.11.016
Vogel-Mikus K, Pongrac P, Kump P, Necemer M, Regvar M (2006) Colonisation of a Zn, cd and Pb hyperaccumulator Thlaspi praecox Wulfen with indigenous arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal mixture induces changes in heavy metal and nutrient uptake. Environ Pollut 139:362–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2005.05.005
Volante A, Lingua G, Cesaro P, Cresta A, Puppo M, Ariati L, Berta G (2005) Influence of three species of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the persistence of aromatic hydrocarbons in contaminated substrates. Mycorrhiza 16:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-005-0012-y
Wang B, Qiu YL (2006) Phylogenetic distribution and evolution of mycorrhizas in land plants. Mycorrhiza 16(5):299–363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-005-0033-6
Wang G, Wang L, Ma F, You Y, Wang Y, Yang D (2020) Integration of earthworms and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi into phytoremediation of cadmium-contaminated soil by Solanum nigrum L. J Hazard Mater 389:121873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121873
Wang Q, Chen J, Chen S, Qian L, Yuan B, Tian Y, Wang Y, Liu J, Yan C, Lu H (2020a) Terrestrial-derived soil protein in coastal water: metal sequestration mechanism and ecological function. J Hazard Mater 386:121655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121655
Wang Q, Lu H, Chen J, Jiang Y, Williams MA, Wu S, Li J, Liu J, Yang G, Yan C (2020b) Interactions of soil metals with glomalin-related soil protein as soil pollution bioindicators in mangrove wetland ecosystems. Sci Total Environ 709:105093. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.136051
Wang S, Zhang S, Huang H, Christie P (2011) Behavior of decabromodiphenyl ether (BDE-209) in soil: effects of rhizosphere and mycorrhizal colonization of ryegrass roots. Environ Pollut 159(3):749–753. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.11.035
Whitfield L, Richards AJ, Rimmer DL (2004) Relationships between soil heavy metal concentration and mycorrhizal colonization in Thymus polytrichus in northern England. Mycorrhiza. 14:55–62
Wijayawardene et al (2020) Outline of Fungi and fungi-like taxa. Micosphere 11:1060–1456
Wu JT, Wang L, Zhao L, Huang XC, Ma F (2020) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi effect growth and photosynthesis of Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin ex. Steudel under copper stress. Plant Biol 22(1):62–69. https://doi.org/10.1111/plb.13039
Wu N, Huang H, Zhang S, Zhu YG, Christie P, Zhang Y (2009) Phenanthrene uptake by Medicago sativa L. under the influence of an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus. Environ Pollut 157:1613–1618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2008.12.022
Wu N, Shuzhen Zhang S, Huang H, Shan X, Christie P, Wang Y (2008) DDT uptake by arbuscular mycorrhizal alfalfa and depletion in soil as influenced by soil application of a non-ionic surfactant. Environ Pollut 151:569–575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2007.04.005
Wu Z, McGrouther K, Huang J, Wu P, Wu W, Wang H (2014) Decomposition and the contribution of glomalin-related soil protein (GRSP) in heavy metal sequestration: field experiment. Soil Biol Biochem 68:283–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.10.010
Xavier IJ, Boyetchko SM (2002) Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi as biostimulants and bioprotectants of crops. In: Khachatourians, G.G., Arora, D.K. (Eds.), app. Mycol. And Biotechnol. Vol. 2: agriculture and food production. Elsevier, Amsterdam, p.311-330. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1874-5334(02)80015-6
Xu Z, Wu Y, Xiao Z, Ban Y, Belvett N (2019) Positive effects of Funneliformis mosseae inoculation on reed seedlings under water and TiO2 nanoparticles stresses. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 35:81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-019-2656-3
Xun F, Xie B, Liu S, Guo C (2015) Effect of plant growth-promoting bacteria (PGPR) and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) inoculation on oats in saline-alkali soil contaminated by petroleum to enhance phytoremediation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:598–608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3396-4
Yang Y, Han X, Liang Y, Ghosh A, Chen J, Tang M (2015) The combined effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) and lead (Pb) stress on Pb accumulation, plant growth parameters, photosynthesis, and antioxidant enzymes in robinia pseudoacacia L. PLoS One 10(12):e0145726. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0145726
Yu XZ, Wu SC, Wu FY, Wong M (2011) Enhanced dissipation of PAHs from soil using mycorrhizal ryegrass and PAH-degrading bacteria. J Hazard Mater 186(2–3):1206–1217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.11.116
Zhan F, Li B, Jiang M, Li T, He Y, Li Y, Wang Y (2019) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the growth and heavy metal accumulation of bermudagrass [Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers.] grown in a lead–zinc mine wasteland. Int J Phytoremediation 21(9):849–856. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2019.1577353
Zhang F, Liu M, Li Y, Che Y, Xiao Y (2019a) Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, biochar and cadmium on the yield and element uptake of Medicago sativa. Sci Total Environ 655:1150–1158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.317
Zhang X, Zhang H, Lou X, Tang M (2019b) Mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal Medicago truncatula roots exhibit differentially regulated NADPH oxidase and antioxidant response under Pb stress. Environ Exp Bot 164:10–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2019.04.01
Zhang XH, Zhu YG, Lin AJ, Chen BD, Smith SE, Smith FA (2006) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi can alleviate the adverse effects of chlorothalonil on Oryza sativa L. Chemosphere 64(10):1627–1632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2006.01.034
Zhou X, Zhou J, Xiang X, Cébron A, Béguiristain T, Leyval C (2013) Impact of four plant species and Arbuscular Mycorrhizal (AM) Fungi on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) dissipation in spiked soil. Pol J Environ Stud 22(4):1239–1245
Hu B, Hu S, Chen Z, Vymazal J (2020) Employ of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi for pharmaceuticals ibuprofen and diclofenac removal in mesocosm-scale constructed wetlands. J. Hazard. Mater., 409: 124524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124524.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to the Vice-Rectory of Research (University of Costa Rica) for research funding (project No. C0057). To Jenny Muñoz Valverde for feeding the database of some scientific articles. Thanks to Helena Ajuria and Nidia González Lara for the English language proofreading and José Salazar Ferrer for his assistance with the figure. Authors are grateful to anonymous referees and the Editor Manju M. Gupta for critical reading and improvement of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Authors declare that there is no conflict of interest of any kind.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solís-Ramos, L.Y., Coto-López, C. & Andrade-Torres, A. Role of arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis in remediation of anthropogenic soil pollution. Symbiosis 84, 321–336 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-021-00774-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-021-00774-4