Abstract
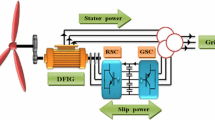
This paper deals with the power generation control in variable speed wind turbines. In this context, the wind energy conversion system is equipped with a doubly-fed induction generator (DFIG) and two back-to-back PWM voltage source converters in the rotor circuit. A vector control of the rotor side converter (RSC) provides an independent control of stator active and reactive power and optimal speed tracking for maximum energy capture. A vector control scheme for the grid side converter (GSC) gives an independent control of slip active and reactive power exchanged between the grid and the GSC, in order to ensure sinusoidal supply currents and to maintain DC-link voltage constant. In this paper, an intelligent fuzzy inference system is proposed as alternative of the conventional PI controller to overcome any disturbance, three fuzzy controllers are used in the RSC for the speed, active and reactive power control, another fuzzy inference system is proposed as PI gain tuner for the DC-link voltage control loop. Performances have been tested on 1.5 MW DFIG by using Matlab/Simulink software environment.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bezza M, Moussaoui B.EL, Fakkar A (2012) Sensorless MPPT fuzzy controller for DFIG wind turbine. egypro, Energy procedia. Elsevier proceedings, vol 18, pp 339–348. Elsevier, New York
Camblong H, de Alegria IM, Rodriguez M, Abad G (2006) Experimental evaluation of wind turbines maximum power point tracking controllers. Energy Conv Manage 47:2846–2858 (Elsevier)
El Aimani S, Francois B, Minne F, Robyns B (2003) Modelling and simulation of doubly fed induction generators for variable speed wind turbines integrated in a distribution network. In: 10th European conference on power electronics and applications (EPE 2003), Toulouse, France
Jabr HM, Kar NC (2005) Adaptive vector control for slip energy recovery in doubly-fed wind driven induction generator. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Canadian conference on electrical and computer engineering pp 759–762
Jabr HM, Kar NC (2006) Fuzzy gain tuner for vector control of doubly-fed wind driven induction generator. In: Proceedings of IEEE Canadian conference on electric and computer engineering, Ottawa, pp 2266–2269
Jabr HM, Lu D, Kar NC (2011) Design and implementation of neuro-fuzzy vector control for wind-driven doubly-fed induction generator. IEEE Trans Sust Energy 2(4):236–241
Lee HH, Dzung PQ, Phuong LM, Khoa LD, Nhan NH (2010) A new fuzzy logic approach for control system of wind turbine with doubly fed induction generator. In: IFOST proceedings, Ulsan 13–15 October, pp 134–139
Li H, Chen Z (2006) A new current control strategy of maximizing the generated power from a doubly fed induction generator system. In: Proceedings of the 12th international power electronics and motion control conference (EPE-PEMC 2006), Portoroz, pp 1557–1562
Li S, Haskew TA (2007) Analysis of decoupled d–q vector control in DFIG back-to-back PWM converter. In: IEEE Proceedings, Tampa, FL, 24–28 June, pp 1–7
Mohan N (2001) Advanced electric drives—analysis, control and modelling using Simulink. MNPERE, Minneapolis
Morren J, de Haan SWH, Bauer P, Pierik JTG (2003) Comparison of complete and reduced models of a wind turbine using doubly-fed induction generator. In: Proceedings of the 10th European conference on power electronics applications (EPE 2003), Toulouse, France
Narayan C, Kar NC, Jabr HM (2010) A novel PI gain scheduler for a vector controlled doubly-fed wind driven induction generator. In: Proceedings of the eighth IEEE international conference, vol 2, pp 948–953
Ren Y, Li H, Zhou J, An Z, Liu J, Hu H, Liu H (2009) Dynamic performance analysis of grid-connected DFIG based on fuzzy logic control. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on Mechatronics and Automation, Changchun, China, pp 719–723
Singh M, Chandra A (2009) Adaptive neuro-fuzzy control of renewable interfacing inverter to maintain smooth power flow and non-linear unbalanced load compensation simultaneously. In: IEEE electrical power and energy conference (EPEC) pp 1–6
Sorensen P, Hansen AD, Lund T, Bindner H (2006) Reduced models of doubly fed induction generator system for wind turbine simulations. Wind Energy 9:299–311
Vanilacomini R, Bim E (2011) Direct power control of a doubly fed induction generator by using a neuro-fuzzy controller. In: Power electronics conference (COBEP), Brazilian, pp 32–37
Zhao Y, Zou XD, Xu YN, Kang Y, Chen J (2006) Maximal power point tracking under speed-mode control for wind energy generation system with doubly fed introduction generator. In: Proceedings of the 5th international power electronics and motion control conference (IPEMC 2006), Shanghai, pp 1–5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dida, A., Ben Attous, D. Fuzzy logic control of grid connected DFIG system using back-to-back converters. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag 8 (Suppl 1), 129–136 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-014-0309-3
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-014-0309-3