Abstract
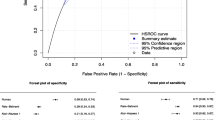
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has shown a great potential in the evaluation and management of prostate cancer. In this study, we would like to evaluate the benefit of multiparametric MRI in the detection and localization of prostate cancer by comparing it with the gold standard of histopathology from radical prostatectomy. In this single-centre prospective study, 90 consecutive patients underwent radical prostatectomy from November 2016 to May 2018. All patients first underwent multiparametric (mp)-MRI, and all suspicious regions of interest were delineated and recorded on a 5-point scale as defined in prostate imaging reporting and data system version 2 (PI-RADS V2) score. All radical prostatectomy specimens, acquired after robotic radical prostatectomy with extended pelvic lymphadenectomy, were sent for histopathological examination (HPE). The mean age of the 90 patients was 65.3 years, and the mean serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) was 16.9 ng/ml. The sensitivity and specificity of mp-MRI in the detection of the corresponding region of interest (ROI) on HPE were 67.4% and 89.3% respectively. Positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), and accuracy of mp-MRI in the detection of corresponding ROI on HPE were 86.3%, 73.3%, and 78.3% respectively. The mp-MRI detected 96.8% solitary lesions and 61.7% multifocal lesions on the corresponding ROI on HPE. Multiparametric MRI has an excellent specificity and reasonable sensitivity for the diagnosis of prostate cancer. It is a good modality for the detection of solitary tumours, higher-grade tumours, detection of seminal vesicle invasion and extracapsular extension and helps in the decision-making process before radical prostatectomy, focal therapy or selecting an appropriate candidate for active surveillance.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A (2014) Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin 64:9
Guneyli S, Erdem CZ, Erdem LO (2016) Magnetic resonance imaging of prostate cancer. Clin Imaging 40:601–609
Barentsz JO, Richenberg J, Clements R, Choyke P, Verma S, Villeirs G et al (2012) ESUR Prostate MR Guidelines 2012. Eur Radiol 22(4):746–757
Le JD, Tan N, Shkolyar E, Lu DY, Kwan L, Marks LS et al (2015) Multifocality and prostate cancer detection by multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging: correlation with whole-mount histopathology. Eur Urol 67:569–576
Sarkar D (2016) The role of multi-parametric MRI and fusion biopsy for the diagnosis of prostate cancer – a systematic review. J Pros Canc 1:2
Jesse DL, Nelly T, Eugene S, David YL, Lorna K, Leonard SM et al (2015) Multifocality and prostate cancer detection by multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging: correlation with whole-mount histopathology. Eur Urol 67:569–576
Moosavi B, Flood TA, Al-Dandan O, Breau RH, Cagiannos I, Morash C et al (2016) Multiparametric MRI of the anterior prostate gland: clinical-radiological-histopathological Correlation. Clin Radiol 71:405–417
Ghai S, Haider MA (2015) Multiparametric-MRI in diagnosis of prostate cancer. Indian J Urol 31(3):194–201
Turkbey B, Mani H, Shah V, Rastinehad AR, Bernardo M, Pohida T et al (2011) Multiparametric 3T prostate magnetic resonance imaging to detect cancer: histopathological correlation using prostatectomy specimens processed in customized magnetic resonance imaging based molds. J Urol 186:1818–1824
Turkbey B, Albert PS, Kurdziel K, Choyke PL (2009) Imaging localized prostate cancer: current approaches and new developments. AJR Am J Roentgenol 192:1471
Roethke MC, Kuru TH, Schultze S, Tichy D, Fenchel M, Schlemmer HP et al (2014) Evaluation of the ESUR PI-RADS scoring system for multiparametric MRI of the prostate with targeted MR/TRUS fusion-guided biopsy at 3.0 Tesla. Eur Radiol 24:344–352
Thompson JE, Van LPJ, Moses D, Shnier R, Brenner P, Delprado W et al (2016) The diagnostic performance of multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging to detect significant prostate cancer. J Urol 195:1428–1435
Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) [Internet] Reston (VA): American college of radiology; [cited 2015 Mar 5]. Available from: http://www.acr.org/Quality-Safety/Resources/PIRADS/
Huang S, Mann S, O’Sullivan R, Ryan A, Landau A, Snow R et al (2016) Correlation between multiparametric MRI findings and radical prostatectomy specimens in 162 patients. J Urol 185(4s):e393
Loggitsi D, Gyftopoulos A, Economopoulos N, Apostolaki A, Kalogeropoulos T, Thanos A et al (2017) Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging of the prostate for tumour detection and local staging: imaging in 1.5T and histopathologic correlation. Can Assoc Radiol J 68:379–386
Peuch P, Potiron E, Lemaitre L, Leroy X, Haber GP, Crouzet S et al (2009) Dynamic contrast-enhanced-magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of intraprostatic prostate cancer: correlation with radical prostatectomy specimens. J Urol 74(5):1094–1099
Grivas N, Hinnenb K, Jongc JD, Heemsbergend W, Moonend L, Witteveen T et al (2018) Seminal vesicle invasion on multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging: correlation with histopathology. Eur J Radiol 98:107–112
De Rooij M, Hamoen EH, Witjes JA, Barentsz JO, Rovers MM (2016) Accuracy of magnetic resonance imaging for local staging of prostate cancer: a diagnostic meta-analysis. Eur Urol 70:233
Hövels AM, Heesakkers RA, Adang EM, Jager GJ, Strum S, Hoogeveen YL et al (2008) The diagnostic accuracy of CT and MRI in the staging of pelvic lymph nodes in patients with prostate cancer: a meta-analysis. Clin Radiol 63:387
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vadher, R.K., Bansal, S., Yadav, R. et al. Evaluation of Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Correlation with Radical Prostatectomy Histopathology Specimen in Prostate Cancer. Indian J Surg Oncol 14, 603–608 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13193-023-01733-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13193-023-01733-9