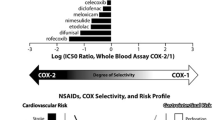
Abstract
Aspirin and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are associated with a reduced risk of gastrointestinal malignancies, which is thought to be mediated mainly through the inhibition of cyclooxygenases-2 (COX-2). Due to the severe side effects of aspirin/NSAIDs, selective COX-2 inhibitors may be a more ideal choice. The objective is to evaluate the association of selective COX-2 inhibitors with gastrointestinal (GI) malignancies and premalignant lesions. We searched for published manuscripts evaluating the association between COX-2 inhibitors and GI malignancies or precancerous lesion. Two investigators independently abstracted the data; then, we conducted the analysis by Review Manager V.5.0; evaluation of effectiveness was performed by an intention to treat (ITT) method. Selective COX-2 inhibitors had no beneficial effects on the progression or regression of esophageal and gastric dysplasia (OR = 1.06, 95% CI 0.63–1.78, P = 0.83 for regression of esophageal dysplasia; OR = 1.06, 95% CI 0.58–1.91, P = 0.86 for progression of esophageal dysplasia; OR = 1.95, 95%CI 0.92–4.17, P = 0.08 for regression of gastric dysplasia; and OR = 0.99, 95%CI 0.68–1.43, P = 0.94 for progression of gastric dysplasia). There is no protective effect on colorectal cancer (OR = 0.89, 95% CI 0.77–1.03, P = 0.11), and the use could not improve the effect of chemoradiation (OR = 1.20, 95% CI 0.46–3.19, P = 0.71). This pooled analysis indicates no meaningful association between selective COX-2 inhibitors and GI malignancies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61(2):69–90
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E (2010) Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 60(5):277–300
Liao LM, Vaughan TL, Corley DA, Cook MB, Casson AG, Kamangar F et al (2012) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use reduces risk of adenocarcinomas of the esophagus and esophagogastric junction in a pooled analysis. Gastroenterology 142(3):442–452
Xu J, Yu Y, He X, Niu N, Li X, Zhang R et al (2019) Tumor-associated macrophages induce invasion and poor prognosis in human gastric cancer in a cyclooxygenase-2/MMP9-dependent manner. Am J Transl Res 11(9):6040–6054
Macfarlane TV, Murchie P, Watson MC (2015) Aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug prescriptions and survival after the diagnosis of head and neck and oesophageal cancer. Cancer Epidemiol 39(6):1015–1022
Wilson LF, Green AC, Kendall BJ, Jordan SJ, Nagle CM, Bain CJ et al (2015) Cancers prevented in Australia in 2010 through the consumption of aspirin. Aust N Z J Public Health 39(5):414–417
Umezawa S, Higurashi T, Komiya Y, Arimoto J, Horita N, Kaneko T et al (2019) Chemoprevention of colorectal cancer: past, present, and future. Cancer Sci 110(10):3018–3026
Joanna B, Jolanta B, Agnieszka G, Diana HZ, Krystyna S (2019) Vitamin D, linoleic acid, arachidonic acid and COX-2 in colorectal cancer patients in relation to disease stage, tumour localisation and disease progression. Arab J Gastroenterol 20(3):121–126
Che XH, Chen CL, Ye XL, Weng GB, Guo XZ, Yu WY et al (2016) Dual inhibition of COX-2/5-LOX blocks colon cancer proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro. Oncol Rep 35(3):1680–1688
Zhang Y, Pan KF, Zhang L, Ma JL, Zhou T, Li JY et al (2015) Helicobacter pylori, cyclooxygenase-2 and evolution of gastric lesions: results from an intervention trial in China. Carcinogenesis 36(12):1572–1579
Venè R, Tosetti F, Minghelli S, Poggi A, Ferrari N, Benelli R (2015) Celecoxib increases EGF signaling in colon tumor associated fibroblasts, modulating EGFR expression and degradation. Oncotarget 6(14):12310–12325
Fujimura T, Ohta T, Oyama K, Miyashita T, Miwa K (2006) Role of cyclooxygenase-2 in the carcinogenesis of gastrointestinal tract cancers: a review and report of personal experience. World J Gastroenterol 12(9):1336–1345
Grover JK, Yadav S, Vats V, Joshi YK (2003) Cyclo-oxygenase 2 inhibitors: emerging roles in the gut. Int J Colorectal Dis 18(4):279–291
Sheng H, Shao J, Kirkland SC, Isakson P, Coffey RJ, Morrow J et al (1997) Inhibition of human colon cancer cell growth by selective inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2. J Clin Invest 99(9):2254–2259
Veettil SK, Nathisuwan S, Ching SM, Jinatongthai P, Lim KG, Kew ST et al (2019) Efficacy and safety of celecoxib on the incidence of recurrent colorectaladenomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Manag Res 11:561–571
Zheng J, Feng Z, Zhu J (2018) Effect of preintravenous injection of parecoxib, combined with transversus abdominis plane block in strategy of enhanced recovery after radical resection of colorectal cancer. J Cancer Res Ther 14(7):1583–1588
Macfarlane TV, Murchie P, Watson MC (2015) Aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug prescriptions and survival after the diagnosis ofhead and neck and oesophageal cancer. Cancer Epidemiol 39(6):1015–1022
Ng K, Meyerhardt JA, Chan AT, Sato K, Chan JA, Niedzwiecki D et al (2014) Aspirin and COX-2 inhibitor use in patients with stage III colon cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 107(1):345
Guo Q, Li Q, Wang J, Liu M, Wang Y, Chen Z et al (2019) A comprehensive evaluation of clinical efficacy and safety of celecoxibin combination with chemotherapy in metastatic or postoperative recurrent gastric cancer patients: a preliminary, three-center, clinical trial study. Medicine (Baltimore) 98(27):e16234
Altorki NK, Christos P, Port JL, Lee PC, Mirza F, Spinelli C et al (2011) Preoperative taxane-based chemotherapy and celecoxib for carcinoma of the esophagus and gastroesophageal junction: results of a phase 2 trial. J Thorac Oncol 6(6):1121–1127
Higgins JPT, Green S (2008) Cochrane Collaboration. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Chichester, England ; Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Blackwell.
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327(7414):557–560
Duval S, Tweedie R (2000) Trim and fill: a simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 56(2):455–463
Vinogradova Y, Coupland C, Hippisley-Cox J (2011) Exposure to cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors and risk of cancer: nested case-control studies. Br J Cancer 105(3):452–459
Midgley RS, McConkey CC, Johnstone EC, Dunn JA, Smith JL, Grumett SA et al (2010) Phase III randomized trial assessing rofecoxib in the adjuvant setting of colorectal cancer: final results of the VICTOR trial. J Clin Oncol 28(30):4575–4580
Jin CH, Wang AH, Chen JM, Li RX, Liu XM, Wang GP et al (2011) Observation of curative efficacy and prognosis following combination chemotherapy with celecoxib in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer. J Int Med Res 39(6):2129–2140
Debucquoy A, Roels S, Goethals L, Libbrecht L, Van Cutsem E, Geboes K et al (2009) Double blind randomized phase II study with radiation+5-fluorouracil+/-celecoxib for resectable rectal cancer. Radiother Oncol 93(2):273–278
Köhne CH, De Greve J, Hartmann JT, Lang I, Vergauwe P, Becker K et al (2008) Irinotecan combined with infusional 5-fluorouracil/folinic acid or capecitabine plus celecoxib or placebo in the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. EORTC study 40015. Ann Oncol 19(5):920–6
Maiello E, Giuliani F, Gebbia V, Di Renzo N, Pezzella G, Romito S et al (2006) FOLFIRI with or without celecoxib in advanced colorectal cancer: a randomized phase II study of the Gruppo Oncologico dell’Italia Meridionale (GOIM). Ann Oncol 17(Suppl 7):vii55-9
Harris RE, Beebe-Donk J, Alshafie GA (2008) Similar reductions in the risk of human colon cancer by selective and nonselective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors. BMC Cancer 8:237
Rahme E, Barkun AN, Toubouti Y, Bardou M (2003) The cyclooxygenase-2-selective inhibitors rofecoxib and celecoxib prevent colorectal neoplasia occurrence and recurrence. Gastroenterology 125(2):404–412
Lanas A, Ortego J, Sopena F, Alcedo J, Barrio E, Bujanda L et al (2007) Effects of long-term cyclo-oxygenase 2 selective and acid inhibition on Barrett’s oesophagus. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 26(6):913–923
Limburg PJ, Wei W, Ahnen DJ, Qiao Y, Hawk ET, Wang G et al (2005) Randomized, placebo-controlled, esophageal squamous cell cancer chemoprevention trial of selenomethionine and celecoxib. Gastroenterology 129(3):863–873
Heath EI, Canto MI, Piantadosi S, Montgomery E, Weinstein WM, Herman JG et al (2007) Secondary chemoprevention of Barrett’s esophagus with celecoxib: results of a randomized trial. J Natl Cancer Inst 99(7):545–557
Wong BC, Zhang L, Ma JL, Pan KF, Li JY, Shen L et al (2011) Effects of selective COX-2 inhibitor and Helicobacter pylori eradication on precancerous gastric lesions. Gut 61(6):812–818
Leung WK, Ng EK, Chan FK, Chan WY, Chan KF, Auyeung AC et al (2006) Effects of long-term rofecoxib on gastric intestinal metaplasia: results of a randomized controlled trial. Clin Cancer Res 12(15):4766–4772
Yang HB, Cheng HC, Sheu BS, Hung KH, Liou MF, Wu JJ (2007) Chronic celecoxib users more often show regression of gastric intestinal metaplasia after Helicobacter pylori eradication. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 25(4):455–461
Zhang LJ, Wang SY, Huo XH, Zhu ZL, Chu JK, Ma JC et al (2009) Anti-Helicobacter pylori therapy followed by celecoxib on progression of gastric precancerous lesions. World J Gastroenterol 15(22):2731–2738
Yang YH, Yang YH, Cheng CL, Ho PS, Ko YC (2012) The role of chemoprevention by selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors in colorectal cancer patients - a population-based study. BMC Cancer 12:582
Corley DA, Kerlikowske K, Verma R, Buffler P (2003) Protective association of aspirin/NSAIDs and esophageal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 124(1):47–56
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, YX., Chen, Y., Sun, Hh. et al. Effects of Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitors on Gastrointestinal Malignancies: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Indian J Surg Oncol 13, 348–355 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13193-022-01547-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13193-022-01547-1