Abstract
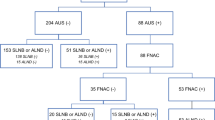
This study evaluates the combined role of axillary ultrasound, fine needle aspiration cytology and sentinel lymph node biopsy in clinically N0 axilla. Between January 2014 and June 2015, 150 women with early breast cancer underwent axillary ultrasound as a first investigation for nodal status. Suspicious nodes were subjected to image guided fine needle aspiration cytology. Non-suspicious and fine needle aspiration cytology negative axillary nodes proceeded to sentinel lymph node biopsy at time of primary breast surgery. All confirmed positive (cytology and frozen) cases proceeded to axillary lymph node dissection. 52 women had positive axillary nodes at final histology. Axillary ultrasound with fine needle aspiration cytology identified 27 patients with positive axillary nodal status and had a sensitivity of 84.36 % (27/32) and specificity of 87.5 % (14/16). Intraoperative frozen analysis identified a further 13 cases with sensitivity of 56.52 % (13/23) and specificity of 97.56 % (80/82). Overall 76.92 % (40/52) patients with positive axillary metastasis were identified peri-operatively using combination of axillary ultrasound, cytology and sentinel lymph node biopsy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cianfrocca M, Goldstein LJ (2004) Prognostic and predictive factors in early-stage breast cancer. Oncologist 9(6):606–616
Fisher ER, Anderson S, Redmond C, Fisher B. Pathologic findings from the National Surgical Adjuvant Breast Project protocol B-06.10-year pathologic and clinical prognostic discriminants. Cancer 1993 Apr 15; 71(8): 2507–2514.
Swinson C, Ravichandran D, Nayagam M, Allen S. Ultrasound and fine needle aspiration cytology of the axilla in the pre-operative identification of axillary nodal involvement in breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 2009 Nov. 35(11): 1152–1157.
Perez-Sanchez VM, Vela-Chavez TA, Villarreal-colin P, Bargallo-Rocha E, Ramirez-ugalde MT, Munoz-Gonzalez D, Zeichner-Granc I. Intra-operative touch imprint cytology of sentinel lymph nodes in breast cancer: experience at a tertiary care center in Mexico. Med Oncol 2010 Jun; 27(2): 233–236.
Khanna R, Bhadani S, Khanna S, Pandey M, Kumar M. Touch imprint cytology evaluation of sentinel lymph node in breast cancer. World J Surg 2011 Jun; 35(6): 1254–1259.
Ecanow JS, Abe H, Newstead GM, Ecanow DB, Jeske JM. Axillary staging of breast cancer: what the radiologist should know. Radiographics 2013 Oct. 33(6): 1589–1612.
Bedi DG, Krishnamurthy R, Krishnamurthy S, Edeiken BS, Le-Petross H, Fornage BD, Bassett RL Jr, Hunt KK. Cortical morphologic features of axillary lymph nodes as a predictor of metastasis in breast cancer: in vitro sonographic study. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2008 Sep; 191(3): 646–652.
Alvarez S, Anorbe E, Alcorta P, Lopez F, Alonso I, Cortes J. Role of sonography in the diagnosis of axillary lymph node metastases in breast cancer: a systematic review. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2006 May; 186(5): 1342–1348.
Abe H, Schmidt RA, Kulkarni K, Sennett CA, Mueller JS, Newstead GM. Axillary lymph nodes suspicious for breast cancer metastasis: sampling with US-guided 14-gauge core-needle biopsy—clinical experience in 100 patients. Radiology 2009 Jan. 250 (1): 41–49.
Rattay T, Muttalib M, Khalifa E, Duncan A, Parker SJ. Clinical utility of routine pre-operative axillary ultrasound and fine needle aspiration cytology in patient selection for sentinel lymph node biopsy. Breast 2012 Apr. 21(2): 210–214.
Lee MC, Eatrides J, Chau A, Han G, Kiuk JV, Khakpour N, Cox CE, Carter WB, Laronga C. Consequences of axillary ultrasound in patients with T2 or greater invasive breast cancers. Ann Surg Oncol 2011 Jan. 18(1): 72–77.
Fernandez AG, Fraile M, Gimenez N, Rene A, Torras M, Canales L, Torres J, Barco I, Gonzalez C, Cirera L, Pessarrodona A. Use of axillary ultrasound, ultrasound-fine needle aspiration biopsy and magnetic resonance imaging in the preoperative triage of breast cancer patients considered for sentinel node biopsy. Ultrasound Med Biol 2011 Jan. 37(1): 16–22.
Park SH, Kim MJ, Park BW, Moon HJ, Kwak JY, Kim EK (2011 Mar) Impact of preoperative ultrasonography and fine-needle aspiration of axillary lymph nodes on surgical management of primary breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 18(3):738–744
Baruah BP, Goyal A, Young P, Douglas-Jones AG, Mansel RE. Axillary node staging by ultrasonography and fine-needle aspiration cytology in patients with breast cancer. Br J Surg 2010 May; 97(5): 680–683.
Carroll PA, O’Mahony D, McDermott R, Boyle T, Dunne B, Kennedy MJ, Connolly EM. Perioperative diagnosis of the positive axilla in breast cancer: a safe, time efficient algorithm. Eur J Surg Oncol 2011 Mar; 37(3): 205–210.
Valente SA, Levine GM, Silverstein MJ, Rayhanbad JA, Weng-Grumley JG, Ji L, Holmes DR, Sposto R, Sener SF. Accuracy of predicting axillary lymph node positivity by physical examination, mammography, ultrasonography, and magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Surg Oncol 2012 Jun; 19(6): 1825–1830.
Leenders MWH, Broeders M, Croese C, Richir MC, Go HL, Langenhorst BL, Meijer S, Schreurs WH. Ultrasound and fine needle aspiration cytology of axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer. To do or not to do? Breast 2012 Aug. 21(4): 578–583.
Acknowledgments
I would like to acknowledge the support of Mr. Unnikrishnan UG who helped me with the statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Ethical approval was taken from institutional ethical committee.
Funding
No funding source.
Conflict of Interest Statement
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goel, G., Janaki, P.D., Smitha, N.V. et al. Role of Axillary Ultrasound, Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology and Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in clinically N0 Breast Cancer. Indian J Surg Oncol 7, 407–412 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13193-016-0520-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13193-016-0520-6