Abstract
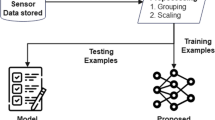
One of the important issues related to road safety is the continuous monitoring of road conditions with the aim of preserving and maintaining the quality of roads. Considering the increasing use of smart phones, a practical solution based on smart phone sensors is proposed in this article to control the safety status of roads. This solution includes the implementation of a centralized traffic information system that monitors the dynamic behavior of vehicles while moving on the roads and collects trip-related information for further processing. To evaluate the system, a 42-kilometer route on a highway in Iran was monitored. A total of 7 parameters comprising speed, three-dimensional instantaneous acceleration and acceleration changes were examined. An event classification approach was adopted to detect accident-black spots based on the pattern of those parameter changes. The classified dataset was trained and modeled using two types of neural network models namely, Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) and Radial Basis Function (RBF). These two neural networks models were trained, tested and validated using MATLAB software and the collected dataset. The predicted error rate was obtained for 700 samples for each output. The mean square error index for RBF and MLP neural networks was obtained as 0.0066 and 0.1399, respectively, indicating acceptable prediction accuracy.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data collected and used in this research would be available to other researchers by request.
References
Fasih-Ramandi, F., Andishe, S., Mehri, F., Karimi, A.: Blood parameters of drivers and road accidents: a study of heavy vehicle drivers in Tehran, Iran, 2018. J. Occup. Health Epidemiol. 11(3), 198–208 (2022)
Piro, G., Cianci, I., Grieco, L.A., Boggia, G., Camarda, P.: Information centric services in smart cities. J. Syst. Softw. 88, 169–188 (2014)
Cui, M., Han, D., Wang, J.: An efficient and safe road condition monitoring authentication scheme based on fog computing. IEEE Internet Things J. 6(5), 9076–9084 (2019)
Kerimov, M., Evtiukov, S., Marusin, A.: Model of multi-level system managing automated traffic enforcement facilities recording traffic violations. Transp. Res. Procedia 50, 242–252 (2020)
Yazdani, M., Rassafi, A.A.: Evaluation of drivers’ affectability and satisfaction with black spots warning application. Civil Eng. J. 5(3), 576–586 (2019)
Kaivo-oja, J., Lauraeus, T., Knudsen, M.S.: Picking the ICT technology winners-longitudinal analysis of 21st century technologies based on the Gartner hype cycle 2008–2017: Trends, tendencies, and weak signals. Int. J. Web. Eng. Technol. 15(3), 216–264 (2020)
Thompson, C.J.B.: Using smartphones to detect Car Accidents and provide situational awareness to emergency responders. Mobilware J. 48, 29–42 (2010)
Zaldivar, J.C.: Providing accident detection in vehicular networks through OBD-II devices and android-based smartphones. In: 5th IEEE Workshop On User Mobility and Vehicular Networks (pp. 1–6). Bonn (2011)
Guidoa, G., Vitalea, A.: Estimation of safety performance measures from smartphone sensors. In: Proceedings of the 15th meeting of the EURO Working Group on Transportation (2012)
Bhoraskar, R.: Wolverine: traffic and road condition estimation using smartphone sensors. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay (2011)
Caballero-Gil, P., Caballero-Gil, C., Molina-Gil, J.: How to build vehicular ad-hoc networks on smartphones. J. Syst. Architect. 59(10), 996–1004 (2013)
Strazdins, G.A., Mednis, A., Kanonirs, G., Zviedris, R., Selavo, L.: Towards vehicular sensor networks with android smartphones for road surface monitoring. Second International Workshop on Networks of Cooperating Objects (CONET) (2011)
Eriksson, J., Girod, L., Madden, S.: Using a mobile sensor network for road surface monitoring. In: Proceedings of the 6th Annual International conference on Mobile Systems (pp. 1–13). Breckenridge, U.S.A. (2008)
Cartel: (n.d.). Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Retrieved from MIT-CarTEL: http://cartel.csail.mit.edu/doku.php. Accessed 03/10/2022
Ma, H., Zhao, D., Dan, P.: Opportunities in mobile crowd sensing. IEEE Commun. Mag. 52(8), 29–35 (2014)
Lane, N.D., Miluzzo, E., Lu, H., Peebles, D., Choudhury, T.: A survey of mobile phone sensing. IEEE Commun. Mag. 48(9), 140–150 (2010)
Ahmadinejad, M., Zargari, S.A., Jalalkamali, R.: Are deceleration numbers a suitable index for road safety? In: Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Transport, vol. 171, no. 5, pp. 247–252. Thomas Telford Ltd (2018)
Haykin, S.: Neural networks and learning machines, 3rd edn. Pearson Education Inc, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada (2009)
Mohanta, B.K., Jena, D., Mohapatra, N., Ramasubbareddy, S., Rawal, B.S.: Machine learning based Accident prediction in secure iot enable transportation system. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 42(2), 713–725 (2022)
Liu, Q., Sun, P., Fu, X., Zhang, J., Yang, H., Gao, H., Li, Y.: Comparative analysis of BP neural network and RBF neural network in seismic performance evaluation of pier columns. Mech. Syst. Signal Process 141, 106707 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Afshari, A., Fallah Tafti, M. Identification of Traffic Accident Black Spots on Suburban Highways Based on Smartphone Sensors of Drivers. Int. J. ITS Res. 22, 108–116 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13177-023-00381-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13177-023-00381-1