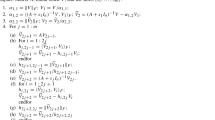Abstract
Computing the matrix exponential for large sparse matrices is essential for solving evolution equations numerically. Conventionally, the shift-invert Arnoldi method is used to compute a matrix exponential and a vector product. This method transforms the original matrix using a shift, and generates the Krylov subspace of the transformed matrix for approximation. The transformation makes the approximation converge faster. In this paper, a new method called the double-shift-invert Arnoldi method is explored. This method uses two shifts for transforming the matrix, and this transformation results in a faster convergence than the shift-invert Arnoldi method.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson, J.E.: Approximation of \(e^{-x}\) by rational functions with concentrated negative poles. J. Approx. Theory 32, 85–95 (1981)
Beckermann, B., Reichel, L.: Error estimates and evaluation of matrix functions via the faber transform. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47, 3849–3883 (2009)
Berljafa, M., Güttel, S.: Parallelization of the rational Arnoldi algorithm. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 39, S197–S221 (2017)
Gallopoulos, E., Saad, Y.: Efficient Solution of parabolic equations by Krylov approximation methods. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. 13, 1236–1264 (1992)
Göckler, T., Grimm, V.: Uniform approximation of \(\varphi \)-functions in exponential integrators by a rational Krylov subspace method with simple poles. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 35, 1467–1489 (2014)
Güttel, S.: Rational Krylov Methods for Operator Functions. Ph.D. thesis. Technischen Universität Bergakademie Freiberg. (2010)
Hashimoto, Y., Nodera, T.: Inexact shift-invert Arnoldi method for evolution equations. ANZIAM J. 58, E1–E27 (2016)
Higham, N.J.: The scaling and squaring method for the matrix exponential revisited. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 26, 1179–1193 (2005)
Hochbruck, M., Lubich, C.: On Krylov subspace approximations to the matrix exponential operator. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 34, 1911–1925 (1997)
Isaacson, S.A.: The reaction-diffusion master equation as an asymptotic approximation of diffusion to a small target. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 70, 77–111 (2009)
Moler, C., Van Loan, C.F.: Nineteen dubious ways to compute the exponential of a matrix. Twenty-five years later. SIAM Rev. 4, 49–53 (2003)
Moret, I., Novati, P.: RD-rational approximations of the matrix exponential. BIT Numer. Math. 44, 595–615 (2004)
Ruhe, A.: Rational Krylov sequence methods for eigenvalue computation. Linear Algebra Appl. 58, 391–405 (1984)
Saad, Y., Schultz, M.H.: GMRES: a generalized minimal residual algorithm for solving nonsymmetric linear systems. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput. 7, 856–869 (1983)
Spijker, M.N.: Numerical ranges and stability estimates. Appl. Numer. Math. 13, 241–249 (1993)
Svoboda, Z.: The convective-diffusion equation and its use in building physics. Int. J. Arch. Sci. 1, 68–79 (2000)
Van den Eshof, J., Hochbruck, M.: Preconditioning lanczos approximations to the matrix exponential. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 27, 1438–1457 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Hashimoto, Y., Nodera, T. Double-shift-invert Arnoldi method for computing the matrix exponential. Japan J. Indust. Appl. Math. 35, 727–738 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13160-018-0309-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13160-018-0309-9