Abstract
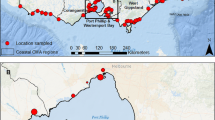
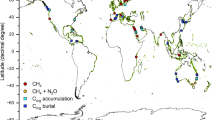
Total organic carbon (TOC) sediment stocks as a CO2 mitigation service require exclusion of allochthonous black (BC) and particulate inorganic carbon corrected for water–atmospheric equilibrium (PICeq). For the first time, we address this bias for a temperate salt marsh and a coastal tropical seagrass in BC hotspots that represent two different blue carbon ecosystems of Malaysia and Australia. Seagrass TOC stocks were similar to the salt marshes with soil depths < 1 m (59.3 ± 11.3 and 74.9 ± 18.9 MgC ha− 1, CI 95 % respectively). Both ecosystems showed larger BC constraints than did their pristine counterparts. However, the seagrass meadows’ mitigation services were largely constrained by both higher BC/TOC and PICeq/TOC fractions (38.0 % ± 6.6 and 43.4 % ± 5.9 %, CI 95 %) and salt marshes around a third (22 % ± 10.2 and 6.0 % ± 3.1 % CI 95 %). The results provide useful data from underrepresented regions, and, reiterates the need to consider both BC and PIC for more reliable blue carbon mitigation assessments to ensure that greenhouse gas emitters do not exceed the ecosystems’ capacity.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
References
Asadpour R, San LH, Alashloo MM and Moussavi SY (2012) A statistical model for mapping spatial distribution of total suspended solid from THEOS satellite imagery over Penang Island, Malaysia. J Appl Sci Res 8(1):271–276
Attiwill PM, Adams MA (2013) Mega-fires, inquiries and politics in the eucalypt forests of Victoria, south-eastern Australia. Forest Ecology and Management 294:45–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2012.09.015
Bindoff NL, Cheung WWL, Kairo JG, Arístegui J, Guinder VA, Hallberg R, Hilmi N, Jiao N, Karim MS, Levin L, O’Donoghue S, Purca Cuicapusa SR, Rinkevich B, Suga T, Tagliabue A and W. P (2019) Changing ocean, marine ecosystems, and dependent communities. In: Pörtner HO, Roberts DC, Masson-Delmotte V, Zhai P, Tignor M, Poloczanska E, Mintenbeck K, Alegría A, Nicolai M, Okem A, Petzold J, Rama B, WNM (eds) IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate
Binh Thanh N, Lehmann J, Hockaday WC, Joseph S, Masiello CA (2010) Temperature Sensitivity of Black Carbon Decomposition and Oxidation. Environmental Science Technology 44:3324–3331. https://doi.org/10.1021/es903016y
Bird MI, Wynn JG, Saiz G, Wurster CM, McBeath A (2015) The pyrogenic carbon cycle. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences 43:273–298. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-earth-060614-105038
Borowitzka MA, Larkum AWD (1987) Calcification in algae: Mechanisms and the role of metabolism. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences 6:1–45. https://doi.org/10.1080/07352688709382246
Burdige DJ (2007) Preservation of organic matter in marine sediments: Controls, mechanisms, and an imbalance in sediment organic carbon budgets? Chemical Reviews 107:467–485
Callaway JC, Borgnis EL, Turner RE, Milan CS (2012) Carbon sequestration and sediment accretion in San Francisco Bay tidal wetlands. Estuaries and Coasts 35:1163–1181
Chee SY, Othman AG, Sim YK, Mat Adam AN, Firth LB (2017) Land reclamation and artificial islands: Walking the tightrope between development and conservation. Global Ecology and Conservation 12:80–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gecco.2017.08.005
Chew ST, Gallagher JB (2018) Accounting for black carbon lowers estimates of blue carbon storage services. Scientific Reports 8:2553. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20644-2
Chuan CH, Gallagher JB, Chew ST, Norlaila Binti MZ (2020) Blue carbon sequestration dynamics within tropical seagrass sediments: long-term incubations for changes over climatic scales. Marine and Freshwater Research 71:892–904. https://doi.org/10.1071/mf19119
Coppola AI, Ziolkowski LA, Masiello CA, Druffel ERM (2014) Aged black carbon in marine sediments and sinking particles. Geophysical Research Letters 41:2427–2433. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013GL059068
Dittmar T and Koch BP (2006) Thermogenic organic matter dissolved in the abyssal ocean. Marine Chem 102:208–217
Dittmar T, Paeng J, Gihring TM, Suryaputra IGNA, Huettel M (2012) Discharge of dissolved black carbon from a fire-affected intertidal system. Limnology and Oceanography 57:1171–1181. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2012.57.4.1171
Doerr SH, Santín C (2016) Global trends in wildfire and its impacts: perceptions versus realities in a changing world. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, BiologicalSciences 371:20150345. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2015.0345
Elmquist M, Gustafsson Ö, Andersson P (2004) Quantification of sedimentary black carbon using the chemothermal oxidation method: An evaluation of ex situ pretreatments and standard additions approaches. Limnology and Oceanography: Methods 2:417–424. https://doi.org/10.4319/lom.2004.2.417
Enriquez S, Schubert N (2014) Direct contribution of the seagrass Thalassia testudinum to lime mud production. Nature Communications 5:3835. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4835
Eyre BD, Andersson AJ, Cyronak T (2014) Benthic coral reef calcium carbonate dissolution in an acidifying ocean. Nature Climate Change 4:969. https://doi.org/10.1038/nclimate2380
Forest Fire Management Victoria (2020) Past bush fire maps. https://www.ffm.vic.gov.au/history-and-incidents/past-bushfires/past-bushfire-maps#navigation. Accessed 6 Jan 2021
Gallagher JB (2014) Explicit and implicit assumptions within the blue carbon conceptual model: A critique. In: Mustaffa S (ed) International Conference on Marine Science and Aquaculture 2014: Ecosystem perspectives in sustainable development Universiti Malaysia Sabah, Kota Kinabalu, p 26–40
Gallagher JB (2017) Taking stock of mangrove and seagrass blue carbon ecosystems: A perspective for future carbon trading. Borneo Journal of Marine Science Aquaculture 1:71–74
Gallagher JB, Ross DJ (2017) Sediment geochronology for bar-built estuaries subject to flood deposition and erosion: A robust multiproxy approach across an estuarine zone. The Holocene 28:341–353. https://doi.org/10.1177/0959683617729441
Gallagher JB, Chuan CH, Yap TK, Fredelina Dona WF (2019) Carbon stocks of coastal seagrass in Southeast Asia may be far lower than anticipated when accounting for black carbon. Biology Letters 15:20180745
Gallagher JB, Chew S-T, Madin J, Thorhaug A (2020) Valuing carbon stocks across a tropical lagoon after accounting for black and inorganic carbon: bulk density proxies for monitoring. Journal of Coastal Research 36:1029–1039. https://doi.org/10.2112/JCOASTRES-D-19-00127.1
Gaveau DLA, Salim MA, Hergoualc’h K et al (2014) Major atmospheric emissions from peat fires in Southeast Asia during non-drought years: evidence from the 2013 Sumatran fires. Scientific Reports 4:6112. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06112
Gehrels WR, Callard SL, Moss PT, Marshall WA, Blaauw M, Hunter J, Milton JA, Garnett MH (2012) Nineteenth and twentieth century sea-level changes in Tasmania and New Zealand. Earth Planetary Science Letters 315–316:94–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2011.08.046
Gustafsson O, Krusa M, Zencak Z, Sheesley RJ, Granat L, Engstrom E, Praveen PS, Rao PS, Leck C and Rodhe H (2009) Brown clouds over South Asia: biomass or fossil fuel combustion? Science 323:495–498
Habeeb RL, Johnson CR, Wotherspoon S, Mumby PJ (2007) Optimal scales to observe habitat dynamics: A coral reef example. Ecological Applications 17:641–647. https://doi.org/10.1890/06-0348
Hammes K, Schmidt MWI, Smernik RJ et al (2007) Comparison of quantification methods to measure fire-derived (black/elemental) carbon in soils and sediments using reference materials from soil, water, sediment and the atmosphere. Global Biogeochem Cycles 21. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006gb002914
Heiri O, Lotter AF, Lemcke G (2001) Loss on ignition as a method for estimating organic and carbonate content in sediments: reproducibility and comparability of results. Journal of Paleolimnology 25:101–110. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1008119611481
Howard JL, Creed JC, Aguiar MVP, Fourqurean JW (2018) CO2 released by carbonate sediment production in some coastal areas may offset the benefits of seagrass “Blue Carbon” storage. Limnology and Oceanography 63:160–172. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.10621
Hyde M (2013) 2013 Tasmanian bushfires inquiry. Tasmanian State Government D. o. P. a. Cabinet. http://stors.tas.gov.au/1230590. Accessed 26 June 2020
Johannessen SC, Macdonald RW (2016) Geoengineering with seagrasses: is credit due where credit is given? Environmental Research Letters 11:113001
Koweek DA, Zimmerman RC, Hewett KM, Gaylord B, Giddings SN, Nickols KJ, Ruesink JL, Stachowicz JJ, Takeshita Y and Caldeira K (2018) Expected limits on the ocean acidification buffering potential of a temperate seagrass meadow. Ecol Appl 28:1694–1714
Krause-Jensen D, Marbà N, Sanz-Martin M, Hendriks IE, Thyrring J, Carstensen J, Sejr MK and Duarte CM (2016) Long photoperiods sustain high pH in Arctic kelp forests. Sci Adv 2:e1501938–e1501938
Krull E, Bray S, Harms B, Baxter N, Bol R, Farquhar G (2007) Development of a stable isotope index to assess decadal-scale vegetation change and application to woodlands of the Burdekin catchment, Australia. Global Change Biology 13:1455-1468. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2007.01376.x
Kuzyakov Y, Bogomolova I, Glaser B (2014) Biochar stability in soil: Decomposition during eight years and transformation as assessed by compound-specific 14 C analysis. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 70:229–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.12.021
Lavelle JW, Massoth GJ, Crecelius EA (1986) Accumulation rates of Recent sediments in Puget Sound. Washington Marine Geology 72:59–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/0025-3227(86)90099-x
Leorri E, Zimmerman AR, Mitra S, Christian RR, Fatela F, Mallinson DJ (2018) Refractory organic matter in coastal salt marshes-effect on C sequestration calculations. Science of the Total Environment 633:391–398
Lim HS, MatJafri MZ, Abdullah K, Alias AN, Wong CJ, Mustapha-Rosli MR, Mohd Saleh N (2009) Water quality mapping using Landsat TM imagery. SPIE. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.820308
Macreadie PI, Ollivier QR, Kelleway JJ et al (2017) Carbon sequestration by Australian tidal marshes. Scientific Reports 7:44071. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep44071
Macreadie PI, Anton A, Raven JA et al (2019) The future of Blue Carbon science. Nature Communications 10:3998. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11693-w
Maher DT, Call M, Santos IR and Sanders CJ (2018) Beyond burial: lateral exchange is a significant atmospheric carbon sink in mangrove forests. Biol Lett 14(7):20180200
Mucci A, Sundby B, Gehlen M, Arakaki T, Zhong S, Silverberg N (2000) The fate of carbon in continental shelf sediments of eastern Canada: a case study. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography 47:733–760. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0967-0645(99)00124-1
Needelman BA, Emmer IM, Emmett-Mattox S, Crooks S, Megonigal JP, Myers D, Oreska MP and McGlathery K (2018) The science and policy of the verified carbon standard methodology for tidal wetland and seagrass restoration. Estuar Coasts 41(8):2159–2171
Nellemann C, Corcoran E, D. C. M (2009) A rapid response assessment. Blue carbon. GRID-Arenda; United Nations Environment Programme. ISBN: 978-82-7701-060-1
Nyman JA, Chabreck RH (1995) Fire in coastal marshes: history and recent concerns. In: Cerulean SI, Todd RE (eds) Fire in wetlands: a management perspective. Proceedings of the Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference. Tall Timbers Research Station, Tallahassee, p 134–141
O’Haver T (2020) A Pragmatic* Introduction to signal processing. Kindle Direct Publishing. https://terpconnect.umd.edu/~toh/spectrum/index.html. Accessed June 2020
Ouyang X, Lee SY (2013) Carbon accumulation rates in salt marsh sediments suggest high carbon storage capacity. Biogeosciences Discussions 19155–19188. https://doi.org/10.5194/bgd-10-19155-2013
Pendleton L, Donato DC, Murray BC, Crooks S, Jenkins WA, Sifleet S, Craft C, Fourqurean JW, Kauffman JB, Marba N, Megonigal P, Pidgeon E, Herr D, Gordon D, Baldera A (2012) Estimating global “blue carbon” emissions from conversion and degradation of vegetated coastal ecosystems. PLoS One 7:e43542. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0043542
Permadi DA, Kim Oanh NT, Vautard R (2018) Integrated emission inventory and modeling to assess distribution of particulate matter mass and black carbon composition in Southeast Asia. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics 18:2725–2747. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-18-2725-2018
Perry CT, Salter MA, Morgan KM, Harborne AR (2019) Census estimates of algal and epiphytic carbonate production highlight tropical seagrass meadows as sediment production hotspots. Frontiers in Marine Science 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2019.00120
Prahalad V, Kirkpatrick JB, Aalders J, Carver S, Ellison J, Harrison-Day V, McQuillan P, Morrison B, Richardson A, Woehler E (2020) Conservation ecology of Tasmanian coastal saltmarshes, south-east Australia – a review. Pacific Conservation Biology 26:105–129. https://doi.org/10.1071/PC19016
Rillig MC (2018) Microplastic disguising as soil carbon storage. Environmental Science Technology 52:6079–6080. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b02338
Rozaimi Jamaludin M, Roslan MFA, Hakimi T, Hamdan N, Omar R, Ali M, Tahirin S (2017) Carbon stores from a tropical seagrass meadow in the midst of anthropogenic disturbance. Marine Pollution Bulletin 119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2017.03.073
Saderne V, Cusack M, Almahasheer H, Serrano O, Masqué P, Arias-Ortiz A, Krishnakumar PK, Rabaoui L, Qurban MA, Duarte CM (2018) Accumulation of carbonates contributes to coastal vegetated ecosystems keeping pace with sea level rise in an Arid Region (Arabian Peninsula). Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences 123:1498–1510. https://doi.org/10.1029/2017JG004288
Saderne VNR, Geraldi PI, Macreadie DT, Maher JJ, Middelburg O, Serrano H, Almahasheer A, Arias-Ortiz M, Cusack BD, Eyre JW, Fourqurean H, Kennedy D, Krause-Jensen T, Kuwae PS, Lavery CE, Lovelock N, Marba P, Masque MA, Mateo I, Mazarrasa KJ, McGlathery MP, Oreska J, Sanders CJ, Santos IR, Smoak JM, Tanaya T, Watanabe K and Duarte CM (2019) Role of carbonate burial in Blue Carbon budgets. Nat Commun 10:1106
Shau Hwai A, Bt. Abdul Karim N-najmi, Yasin Z (2007) Diversity of mollusc communities in the seagrass bed in Pulau Gazumbo, Penang, Malaysia. Marine Research in Indonesia 32:123–127. https://doi.org/10.14203/mri.v32i2.445
Stevenson J, Haberle S (2005) Macro charcoal analysis: a modified technique used by the Department of Archaeology and Natural History. http://hdl.handle.net/1885/144170. Accessed June 2019
Sulpis O, Boudreau BP, Mucci A, Jenkins C, Trossman DS, Arbic BK, Key RM (2018) Current CaCO3 dissolution at the seafloor caused by anthropogenic CO2. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 115:11700–11705. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1804250115
Sun X, Peng PA, Song J, Zhang G and Hu J (2008) Sedimentary record of black carbon in the Pearl River estuary and adjacent northern South China Sea. Appl Geochem 23:3464–3472
Tasmania (1967) The bush fire disaster of 7th February, 1967: report and summary of evidence (excluding appendices), G. Pr, Hobart. http://worldcat.org/title/bush-fire-disaster-of-7th-february-1967-report-and-summary-of-evidence-excluding-appendices/oclc/220580392. Accessed June 2020
Tolhurst TJ, Underwood AJ, Perkins RG, Chapman MG (2005) Content versus concentration: Effects of units on measuring the biogeochemical properties of soft sediments. Estuarine Coastal Shelf Science 63:665–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2005.01.010
Ware JR, Smith SV, Reaka-Kudla ML (1992) Coral reefs: sources or sinks of atmospheric CO2? Coral Reefs 11:127–130. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00255465
Zhao Y, Sayer CD, Birks HH, Hughes M, Peglar SM (2006) Spatial representation of aquatic vegetation by macrofossils and pollen in a small and shallow lake. Journal of Paleolimnology 35:335–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-005-1336-5
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the support of Jeff D Ross of the Institute of Marine and Antarctic Studies, University of Tasmania for facilitating the authors’ (JBG) position of Adjunct Researcher, and the support of the Centre of Marine and Coastal Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia.
Funding
This study was partly funded by Living Wetlands (Tasmania, Australia)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JBG: Conceptualization Validation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing - original draft, Writing - review & editing, Visualization, Resources. VP: Visualisation, Resources, Writing - original draft, Writing - review & editing, Funding acquisition. JA: Investigation, Resources, Writing - review. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable, no animal or plant materials were disturbed or manipulated during sampling or analysis.
Guidelines on ethical review or waiver.
Malaysia:http://www.nccr.gov.my/index.cfm?menuid=26&parentid=17 (accessed 22 February 2021).
Australia: https://www.arc.gov.au/policies-strategies/policy/codes-and-guidelines (accessed 22 February 2021).
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest/Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gallagher, J.B., Prahalad, V. & Aalders, J. Inorganic and Black Carbon Hotspots Constrain Blue Carbon Mitigation Services Across Tropical Seagrass and Temperate Tidal Marshes. Wetlands 41, 65 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-021-01460-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13157-021-01460-3