Abstract
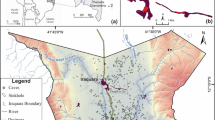
The regularity of karst collapse distribution in Xuzhou city is based on the study of karst collapse development characteristics and key control factors in this region. Several findings are noted. (1) Karst collapse distribution is controlled by the fault zone of the ancient Yellow River; the karst develops stronger while located near the fault zone of the ancient Yellow River, and the karst develops weaker while far away from the fault zone of the ancient Yellow River. (2) The collapse is located in strong development section of shallow karstification level. Collapse karst is mainly located in Ordovician System limestone with a small part of which is located in the Cambrian system limestone. (3) The collapse concentration is within the ancient channel. Most collapse happens in the sand soil monolayer and some small part of the collapse happens in the sand-clay double layer. (4) All collapse is in the cone of depression due to the extraction of karst water. The results of this study provide scientific basis for prevention of karst collapse hazards in Xuzhou in the future.

(Modified from Lu 2003)

(Modified from Xu 1997)

(Modified from Xuzhou Area Karst Collapse Survey Projects, China Geological Survey No.12120114022001)




(Modified from Xuzhou Area Karst Collapse Survey Projects)






(Modified from Wei et al. 2015)




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen GL, Chen YH, Tan HZ, Zhang JH (1990) Research on mechanism, prediction and countermeasure for land-collapse in karst area. Chin J Geol Hazard Control 1(3):41–50 (in Chinese)
Cooper AH (2001) The development of a national Geographic Information System (GIS) for British karst geohazards and risk assessment. In: Proceedings of 8th Multidisciplinary conference on sinkholes and the Engineering and Environmental Impacts of Karst. Louisville, Kentucky
Han BP, Liu XK, Zhu XQ, Feng QY, Sun XF (2006) Environmental effects of groundwater development in xuzhou city, china. J China Univ Min Technol 16(1):13–16
Hu RL, Wang SJ, Lee CF, Xiang JX (2001) Regional risk assessment on Karst collapse in Tangshan city, China. Chin J Rock Mechan Eng 20(2):180–189
Hua XQ, Huang JJ, Miao SX, Zhang L, Wu X (2015) Distribution and causes of geo-hazards in Xuzhou. J Geol Hazards Environ Preserv 26(2):74–80 (in Chinese)
Jiang XZ (1998) The Experimental Study of Karst Collapse Condition. Chin J Geol Hazard Control 9(S):187–191
Jiang XZ, Lei MT, Li Y, Dai JL, Meng Y (2005) Model experiment of rockfill subgrade stability under Karst water impact. Carsologica Sin 24(2):96–102 (in Chinese)
Kang YR (1992) Collapse-causing model in Karstic collapse process. Hydrogeol and Eng Geol 19(4):31–34 (in Chinese)
Lei MT, Jiang XZ, Li Y (2002) Study on the simulation assessment and management method of karst collapse. J Geol Hazards Environ Preserv 13(1):18–22 (in Chinese)
Lu YR (2003) Ecological environment and the sustainable development. Hohai University Press, Hangzhou (in Chinese)
Ma JR, Han BP (1996) Strata characteristics and collapse mechanism of collapse areas in Xuzhou city. Chin J Geol Hazard Control 7(2):51–56 (in Chinese)
Mu WJ, Lei MT, Liang JL (2005) Status quo of the study on subgrade and the treatment techniques in karst area. Carsologica Sin 24(2):89–94 (in Chinese)
Raghu D (1984) Sinkhole risk analysis for a selected area in Warren County. New Jersey. In: Proceedings of the first Multidisciplinary conference on sinkholes and the Environmental Impacts of Karst. Orlando, Florida
Richard C, Benson (1987) Assessment and long term monitoring of localized subsidence using ground penetrating radar. In: Proceedings of the Second Multidisciplinary conference on sinkholes and the Environmental Impacts of Karst. Orlando, Florida
Wang B, He KQ (2006) Study on limit equilibrium height expression of critical soil cave of karst collapse, Yantu Lixue. Rock Soil Mech 27(3):458–462
Wei YY, Sun SL, Huang JJ, Jiang S, Miao SX (2015) Spatial-temporal distribution and causes of karst collapse in the Xuzhou area. Carsologica Sin 34(1):52–57 (in Chinese)
Xing X, Zhou D, Luo Y (2014) Study on geological disasters of karst collapse in Xuzhou and its protection measures. Chin J Geol Hazard Control 25(4):51–58 (in Chinese)
Xiong CX, Liu YX (2014) Relation of surface collapse and karst water exploitation in urban area of Xuzhou City. Chin J Geol Hazard Control2 5(4):51–58 (in Chinese)
Xu XS (1997) Stratigraphy (Lithostratic) of Jiangsu Province. China University of Geosciences Press, Nanjing (in Chinese)
Xu WG, Zhao GR (1981) The implication of suction action for ground subsidence in karst mining areas. Geol Rev 27(2):174–180 (in Chinese)
Zhou DL (2006) Study on transport of karst groundwater of Xuzhou. J Geol Hazards Environ Preserv 17(4):65–69 (in Chinese)
Zhu YW (2000) The influence on groundwork by old disused watercourse alluvia deposit in Xuzhou City. J Pengcheng Vocational Univ 15(2):97–99 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the data support provided by the Xuzhou City Geology Survey and Xuzhou Area Karst Collapse Survey Projects (China Geological Survey No. 12120114022001). Thanks to Prof. Lei Mingtang, Karst Research Institute of Gunlin, for supporting the authors with the valuable materials.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Y., Sun, S., Huang, J. et al. A study on karst development characteristics and key control factors of collapse in Xuzhou, eastern China. Carbonates Evaporites 33, 359–373 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-017-0346-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13146-017-0346-5