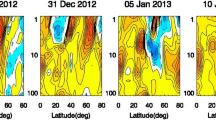
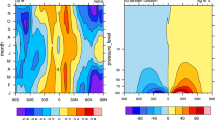
Abstract
Changes in the Brewer-Dobson circulation (BDC) during the 30 years 1980–2009 are investigated using Modern Era Retrospective-analysis for Research and Applications (MERRA) reanalysis data. The mass streamfunction that is induced by wave forcings in the transformed Eulerian-mean (TEM) equation through the downward-control principle is used as a proxy for the BDC. The changes in the BDC are investigated using two aspects: the wave propagation conditions in the stratosphere and the wave activity in the upper troposphere. They are compared in the first (P1) and second (P2) 15-year periods. The resolved wave forcing, expressed by the Eliassen-Palm (EP) flux divergence (EPD), is significantly enhanced during the December-January-February (DJF) season in P2 in both the Northern Hemisphere (NH) high latitudes and the Southern Hemisphere (SH) mid- and high latitudes. The increased zonal mean zonal wind at high latitudes in the SH, caused by ozone depletion, leads to an upward shift of the Rossby-wave critical layer and this allows more transient planetary waves to propagate into the stratosphere. In the NH, the enhanced EPD in DJF leads to an increase in the frequency of Sudden Stratospheric Warming (SSW) events. The gravity wave drag (GWD) is smaller than the EPD and the change in it between the two time periods is insignificant. The residual term in the TEM equation is similar to the GWD in the two periods, but its change between the two periods is as large as the change in the EPD. Among the four components of the EP flux at 250 hPa, the meridional heat flux played a dominant role in the enhancement of the BDC in P2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, M. J., and Coauthors, 2010: Recent developments in gravity-wave effects in climate models and the global distribution of gravity-wave momentum flux from observations and models. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 136, 1103–1124, doi:10.1002/qj.637.
Andrews, D. G., J. R. Holton, and C. B. Leovy, 1987: Middle Atmosphere Dynamics. Academic Press, 489 pp.
Birner, T., and H. Bonisch, 2011: Residual circulation trajectories and transit times into the extratropical lowermost stratosphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 11, 817–827, doi:10.5194/acp-11-817-2011.
Brewer, A. W., 1949: Evidence for a world circulation provided by the measurements of helium and water vapor distribution in the stratosphere. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 75, 351–363, doi:10.1002/qj.49707532603.
Butchart, N., and A. A. Scaife, 2001: Removal of chlorofluorocarbons by increased mass exchange between the stratosphere and troposphere in a changing climate. Nature, 410, 799–802, doi:10.1038/35071047.
Butchart, N., and Coauthors, 2006: Simulations of anthropogenic change in the strength of the Brewer-Dobson circulation. Clim. Dynam., 27, 727–741, doi:10.1007/s00382-006-0162-4.
Butchart, N., and Coauthors, 2010: Chemistry-climate model simulations of twenty-first century stratospheric climate and circulation changes. J. Climate, 23, 5349–5374, doi:10.1175/2010JCLI3404.1.
Cagnazzo, C., C. Claud, and S. Hare, 2006: Aspects of stratospheric long-term changes induced by ozone depletion. Clim. Dynam., 27, 101–111, doi:10.1007/s00382-006-0120-1.
Chun, H.-Y., Y.-H. Kim, H.-J. Choi, and J.-Y. Kim, 2011: Influence of gravity waves in the tropical upwelling: WACCM simulations. J. Atmos. Sci., 68, 2599–2612.
Diallo M., B. Legras, and A. Cheìdin, 2012: Age of stratospheric air in the ERA-Interim. Atmos. Chem. Phys., 12, 12133–12154, doi:10.5194/acp-12-12133-2012.
Dobson, G. M. B., 1956: Origin and distribution of the polyatomic molecules in the atmosphere. Proc. Roy. Soc. London, A235, 187–193.
Engel A., and Coauthors, 2008: Age of stratospheric air unchanged within uncertainties over the past 30 years. Nat. Geosci., 2, 28–31, doi: 10.1038/NGEO388.
Ern, M., P. Preusse, M. J. Alexander, and C. D. Warner, 2004: Absolute values of gravity wave momentum flux derived from satellite data. J. Geophys. Res., 109, D20103, doi:10.1029/2004JD004752.
Fomichev, V. I., A. I. Jonsson, J. de Grandpre, S. R. Beagley, C. McLandress, K. Semeniuk, and T. G. Shepherd, 2007: Response of the middle atmosphere to CO2 doubling: Results from the Canadian middle atmosphere model. J. Climate, 20, 1121–1144.
Garcia, R. R., and B. A. Boville, 1994: Downward control of the mean meridional circulation and temperature distribution of the polar winter stratosphere. J. Atmos. Sci., 51, 2238–2245.
Garcia, R. R., and W. J. Randel, 2008: Acceleration of the Brewer-Dobson circulation due to increases in greenhouse gases, J. Atmos. Sci., 65, 2731–2739, doi:10.1175/2008JAS2712.1.
Haynes, P. H., M. E. McIntyre, T. G. Shepherd, C. J. Marks, and K. P. Shine, 1991: On the “downward control” of extratropical diabatic circulations by eddy-induced mean zonal flow. J. Atmos. Sci., 48, 651–678.
Holton, J. R., 1990: On the global exchange of mass between the stratosphere and troposphere. J. Atmos. Sci., 47, 392–395.
Holton, J. R., P. H. Haynes, M. E. McIntyre, A. R. Douglass, R. B. Rood, and L. Pfister, 1995: Stratosphere-troposphere exchange. Rev. Geophys., 33, 403–439, doi:10.1029/95RG02097.
Hu, Y., and K. K. Tung, 2002: Interannual and decadal variations of planetary-wave activity, stratospheric cooling, and Northern Hemisphere annular mode. J. Climate, 15, 1659–1673.
Iwasaki, T., H. Hamada, and K. Miyazaki, 2009: Comparisons of Brewer-Dobson circulations diagnosed from reanalyses. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan., 87, 997–1006, doi:10.2151/jmsj.87.997.
Kerr-Munslow, A. M., and W. A. Norton, 2006: Tropical wave driving of the annual cycle in tropical tropopause temperatures. Part I: ECMWF analyses. J. Atmos. Sci., 63, 1410–1419.
Kim, Y.-J., S. E. Eckermann, and H.-Y. Chun, 2003: An overview of the past, present and future of gravity-wave drag parameterization for numerical climate and weather prediction models. Atmos.-Ocean, 41, 65–98.
Krishnamurthy, V., and B. P. Kirtman, 2009: Relation between Indian Monsoon variability and SST. J. Climate, 22, 4437–4458.
Li, F., J. Austin, and R. J. Wilson, 2008: The strength of the Brewer-Dobson circulation in a changing climate: Coupled chemistry-climate model simulations. J. Climate, 21, 40–57.
McFarlane, N. A., 1987: The effect of orographically excited gravity wave drag on the general circulation of the lower stratosphere and troposphere. J. Atmos. Sci., 44, 1775–1800.
McInturff, R., 1978: Stratospheric warmings: Synoptic, dynamic and general circulation aspects. NASA Ref. Publ. 1017.
McLandress, C., and T. G. Shepherd, 2009: Simulated anthropogenic changes in the Brewer-Dobson circulation, including its extension to high latitudes. J. Climate, 22, 1516–1540, doi:10.1175/2008JCLI2979.1.
Nakicenovic, N., and R. Swart, Eds., 2000: Special Report on Emissions Scenarios. Cambridge University Press, 570 pp.
Okamoto, K., K. Sato, and H. Akiyoshi, 2011: A study on the formation and trend of the Brewer-Dobson circulation. J. Geophys. Res., 116, D10117, doi:10.1029/2010JD014953.
Plumb, R. A., 2002: Stratospheric transport. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 80, 793–809.
Plumb, R. A., and J. Eluszkiewicz, 1999: The Brewer-Dobson circulation: Dynamics of the tropical upwelling. J. Atmos. Sci., 56, 868–890.
Randel, W. J., and I. M. Held, 1991: Phase speed spectra of transient eddy fluxes and critical layer absorption. J. Atmos. Sci., 48, 688–697.
Rienecker, M. R., and Coauthors, 2011: MERRA-NASA’s Modern-Era Retrospective analysis for research and applications. J. Climate, 24, 3624–3648, doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00015.1.
Salby, M., E. Titova, and L. Deschamps, 2011: Rebound of Antarctic ozone. Geophys. Res. Lett., 38, L09702, doi:10.1029/2011GL047266.
Semeniuk, K., and T. G. Shepherd, 2001: Mechanisms for tropical upwelling in the stratosphere. J. Atmos. Sci., 58, 3097–3115.
Seviour W. J. M., N. Butchart, and S. C. Hardiman, 2012: The Brewer-Dobson circulation inferred from ERA-Interim. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor., Soc., 138, 878–888, doi:10.1002/qj.966.
Shepherd, T. G., 2002: Issues in stratosphere-troposphere coupling. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 80, 769–792, doi:10.2151/jmsj.80.769.
Shepherd, T. G., 2007: Transport in the middle atmosphere. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 85B, 165–191.
Shepherd, T. G., and C. McLandress, 2011: A robust mechanism for strengthening of the Brewer-Dobson circulation in response to climate change: critical-layer control of subtropical wave breaking. J. Atmos. Sci., 68, 784–797.
Solomon, S., K. Rosenlof, R. Portmann, J. Daniel, S. Davis, T. Sanford, and G.K. Plattner, 2010: Contributions of stratospheric water vapor to decadal changes in the rate of global warming. Sci. Express, 327, 1219–1223.
Thompson, D. W. J., and S. Solomon, 2009: Understanding recent stratospheric climate change. J. Climate, 22, 1934–1943, doi:10.1175/2008JCLI2482.1.
Tung, K. K., and R. S. Lindzen, 1979: A theory of stationary long waves. Part II: Resonant Rossby waves in the presence of realistic vertical shears. Mon. Wea. Rev., 107, 735–750.
Wilks, D. S., 2006: Statistical Methods in the Atmospheric Sciences. Academic, San Diego, Calif.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JY., Chun, HY. & Kang, MJ. Changes in the Brewer-Dobson circulation for 1980–2009 revealed in MERRA reanalysis data. Asia-Pacific J Atmos Sci 50 (Suppl 1), 625–644 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-014-0051-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-014-0051-4