Abstract
Objectives
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the correlation between pretreatment planning technetium-99m (99mTc) macroaggregated albumin (MAA) SPECT images and posttreatment transarterial radioembolization (TARE) yttirum-90 (90Y) PET/CT images by comparing the ratios of tumor-to-normal liver counts.
Methods
Fifty-two patients with advanced hepatic malignancy who underwent 90Y microsphere radioembolization from January 2010 to December 2012 were retrospectively reviewed. Patients had undergone 99mTc MAA intraarterial injection SPECT for a pretreatment evaluation of microsphere distribution and therapy planning. After the administration of 90Y microspheres, the patients underwent posttreatment 90Y PET/CT within 24 h. For semiquantitative analysis, the tumor-to-normal uptake ratios in 90Y PET/CT (TNR-yp) and 99mTc MAA SPECT (TNR-ms) as well as the tumor volumes measured in angiographic CT were obtained and analyzed. The relationship of TNR-yp and TNR-ms was evaluated by Spearman's rank correlation and Wilcoxon's matched pairs test.
Results
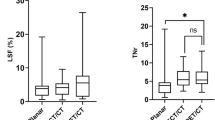
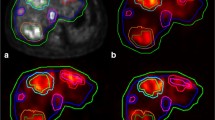
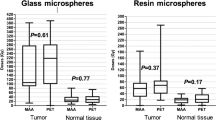
In a total of 79 lesions of 52 patients, the distribution of microspheres was well demonstrated in both the SPECT and PET/CT images. A good correlation was observed of between TNR-ms and TNR-yp (rho value = 0.648, p < 0.001). The TNR-yp (median 2.78, interquartile range 2.43) tend to show significantly higher values than TNR-ms (median 2.49, interquartile range of 1.55) (p = 0.012). The TNR-yp showed weak correlation with tumor volume (rho = 0.230, p = 0.041).
Conclusions
The 99mTc MAA SPECT showed a good correlation with 90Y PET/CT in TNR values, suggesting that 99mTc MAA can be used as an adequate pretreatment evaluation method. However, the 99mTc MAA SPECT image consistently shows lower TNR values compared to 90Y PET/CT, which means the possibility of underestimation of tumorous uptake in the partition dosimetry model using 99mTc MAA SPECT. Considering that 99mTc MAA is the only clinically available surrogate marker for distribution of microsphere, we recommend measurement of tumorous uptake using 90Y PET/CT should be included routinely in the posttherapeutic evaluation.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kulik LM, Atassi B, Van Holsbeeck L, Souman T, Lewandowski RJ, Mulcahy MF, et al. Yttrium-90 microspheres (TheraSphere®) treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: downstaging to resection, RFA and bridge to transplantation. J Surg Oncol. 2006;94:572–86.
Cosimelli M, Golfieri R, Cagol PP, Carpanese L, Sciuto R, Maini CL, et al. Multi-centre phase II clinical trial of yttrium-90 resin microspheres alone in unresectable, chemotherapy refractory colorectal liver metastases. Br J Cancer. 2010;103:324–31.
Hendlisz A, Van Den Eynde M, Peeters M, Maleux G, Lambert B, Vannoote J, et al. Phase III trial comparing protracted intravenous fluorouracil infusion alone or with yttrium-90 resin microspheres radioembolization for liver-limited metastatic colorectal cancer refractory to standard chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:3687–94.
Gulec SA, Pennington K, Wheeler J, Barot TC, Suthar RR, Hall M, et al. Yttrium-90 microsphere-selective internal radiation therapy with chemotherapy (chemo-SIRT) for colorectal cancer liver metastases. Am J Clin Oncol. 2013;36:455–60.
Ozkan ZG, Poyanli A, Ucar A, Kuyumcu S, Akyuz F, Keskin S, et al. Favorable survival time provided with radioembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma patients with and without portal vein thrombosis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2015;30:132–8.
Burton MA, Gray BN, Jones C, Coletti A. Intraoperative dosimetry of 90Y in liver tissue. Int J Rad Appl Instrum B. 1989;16:495–8.
Burton MA, Gray BN, Klemp PF, Kelleher DK, Hardy N. Selective internal radiation therapy: distribution of radiation in the liver. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1989;25:1487–91.
Burton MA, Gray BN, Kelleher DK, Klemp PF. Selective internal radiation therapy: validation of intraoperative dosimetry. Radiology. 1990;175:253–5.
Ho S, Lau WY, Leung TW, Chan M, Ngar YK, Johnson PJ, et al. Partition model for estimating radiation doses from yttrium-90 microspheres in treating hepatic tumours. Eur J Nucl Med. 1996;23:947–52.
Ho S, Lau WY, Leung TWT, Chan M, Johnson PJ, Li AKC. Clinical evaluation of the partition model for estimating radiation doses from yttrium-90 microspheres in the treatment of hepatic cancer. Eur J Nucl Med. 1997;24:293–8.
Ho S, Lau WY, Leung TWT, Chan M, Chan KW, Lee WY, et al. Tumour-to-normal uptake ratio of 90Y microspheres in hepatic cancer assessed with 99TCm macroaggregated albumin. Br J Radiol. 1997;70:823–8.
Knesaurek K, Machac J, Muzinic M, DaCosta M, Zhang Z, Heiba S. Quantitative comparison of yttrium-90 (90Y)-microspheres and technetium-99m (99mTc)-macroaggregated albumin SPECT images for planning 90Y therapy of liver cancer. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2010;9:253–62.
Minarik D, Sjögreen Gleisner K, Ljungberg M. Evaluation of quantitative (90)Y SPECT based on experimental phantom studies. Phys Med Biol. 2008;53:5689–703.
Fabbri C, Sarti G, Cremonesi M, Ferrari M, Di Dia A, Agostini M, et al. Quantitative analysis of 90Y Bremsstrahlung SPECT-CT images for application to 3D patient-specific dosimetry. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2009;24:145–54.
Padia SA, Alessio A, Kwan SW, Lewis DH, Vaidya S, Minoshima S. Comparison of positron emission tomography and bremsstrahlung imaging to detect particle distribution in patients undergoing yttrium-90 radioembolization for large hepatocellular carcinomas or associated portal vein thrombosis. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2013;24:1147–53.
Eaton BR, Kim HS, Schreibmann E, Schuster DM, Galt JR, Barron B, et al. Quantitative dosimetry for yttrium-90 radionuclide therapy: tumor dose predicts fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography response in hepatic metastatic melanoma. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2014;25:288–95.
Lhommel R, van Elmbt L, Goffette P, Van den Eynde M, Jamar F, Pauwels S, et al. Feasibility of 90Y TOF PET-based dosimetry in liver metastasis therapy using SIR-Spheres. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37:1654–62.
Gates VL, Esmail AAH, Marshall K, Spies S, Salem R. Internal pair production of 90Y permits hepatic localization of microspheres using routine PET: proof of concept. J Nucl Med. 2011;52:72–6.
Wissmeyer M, Heinzer S, Majno P, Buchegger F, Zaidi H, Garibotto V, et al. 90Y Time-of-flight PET/MR on a hybrid scanner following liver radioembolisation (SIRT). Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011;38:1744–5.
Jiang M, Fischman A, Nowakowski FS. Segmental perfusion differences on paired Tc-99m macroaggregated albumin (MAA) hepatic perfusion imaging and yttrium-90 (Y-90) bremsstrahlung imaging studies in SIR-sphere radioembolization: associations with angiography. J Nucl Med Radiat Ther. 2012;03:1–5.
Van de Wiele C, Maes A, Brugman E, D’Asseler Y, De Spiegeleer B, Mees G, et al. SIRT of liver metastases: physiological and pathophysiological considerations. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012;39:1646–55.
Moerlin S, Colombetti LG, Patel G. Comparison of pharmaceutical quality of laboratory made macroaggregated albumin with commercially available products. Radiobiol Radiother (Berl). 1977;18:45–51.
Lau WY, Leung TWT, Ho S, Chan M, Leung NWY, Lin J, et al. Diagnostic pharmaco-scintigraphy with hepatic intra arterial technetium-99m macroaggregated albumin in the determination of tumour to non-tumour uptake ratio in hepatocellular carcinoma. Br J Radiol. 1994;67:136–9.
Garin E, Lenoir L, Rolland Y, Edeline J, Mesbah H, Laffont S, et al. Dosimetry based on 99mTc-macroaggregated albumin SPECT/CT accurately predicts tumor response and survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with 90Y-loaded glass microspheres: preliminary results. J Nucl Med. 2012;53:255–63.
Ahmadzadehfar H, Muckle M, Sabet A, Wilhelm K, Kuhl C, Biermann K, et al. The significance of bremsstrahlung SPECT/CT after yttrium-90 radioembolization treatment in the prediction of extrahepatic side effects. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012;39:309–15.
Elschot M, Vermolen BJ, Lam MGEH, de Keizer B, van den Bosch M a a J, de Jong HW a M. Quantitative comparison of PET and bremsstrahlung SPECT for imaging the in vivo yttrium-90 microsphere distribution after liver radioembolization. PLoS One. 2013;8:e55742.
Kim YC, Kim YH, Um SH, Seo YS, Park EK, Oh SY, et al. Usefulness of bremsstrahlung images after intra-arterial Y-90 resin microphere radioembolization for hepatic tumors. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;45:59–67.
Sangro B, Iñarrairaegui M, Bilbao JI. Radioembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012;56:464–73.
Wondergem M, Smits MLJ, Elschot M, de Jong HWAM, Verkooijen HM, van den Bosch MAAJ, et al. 99mTc-macroaggregated albumin poorly predicts the intrahepatic distribution of 90Y resin microspheres in hepatic radioembolization. J Nucl Med. 2013;54:1294–301.
Ng SC, Lee VH, Law MW, Liu RK, Ma VW, Tso WK, et al. Patient dosimetry for 90Y selective internal radiation treatment based on 90Y PET imaging. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2013;14:212–21.
Gulec SA, Mesoloras G, Dezarn WA, McNeillie P, Kennedy AS. Safety and efficacy of Y-90 microsphere treatment in patients with primary and metastatic liver cancer: the tumor selectivity of the treatment as a function of tumor to liver flow ratio. J Transl Med. 2007;5:15.
Lee MY, Chuang VP, Wei CJ, Cheng TY, Cherng MT. Histopathologic correlation of hepatocellular carcinoma after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization with polyvinyl alcohol particle of various sizes. Eur J Radiol. 2012;81:1976–9.
Acknowledgments
This study was partly supported by a research grant for R & D for Clinical and Translational Research, HI13C1611, Korea Health Industry Development Institute, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea.
Conflicts of Interest
Seunghong Rhee, Sungeun Kim, Jaehyuk Cho, Jukyung Park, Jae Seon Eo, Soyeon Park, Eunsub Lee, Yun Hwan Kim, and Jae-Gol Choe declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical Statement
The manuscript contains a statement that the study was approved by an institutional review board or equivalent and has been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. All subjects in the study gave written informed consent or the institutional review board waived the need to obtain informed consent.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This manuscript has not been published before and is not under consideration for publication anywhere else and has been approved by all coauthors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rhee, S., Kim, S., Cho, J. et al. Semi-Quantitative Analysis of Post-Transarterial Radioembolization 90Y Microsphere Positron Emission Tomography Combined with Computed Tomography (PET/CT) Images in Advanced Liver Malignancy: Comparison With 99mTc Macroaggregated Albumin (MAA) Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT). Nucl Med Mol Imaging 50, 63–69 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13139-015-0366-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13139-015-0366-9