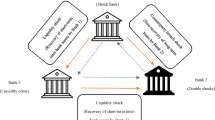
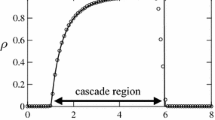
Abstract
The banking industry, as a cornerstone of the economy, plays a pivotal role in the efficient allocation of funds. However, it is not immune to the peril of systemic risk, a threat that can trigger a domino effect, jeopardizing the entire financial system. This research paper delves into the complexities of systemic risk within the banking sector, focusing on the transmission mechanisms through interbank networks and market liquidity. By conducting an empirical analysis based on the 2011 EU-wide stress test, the study reveals the significant roles that network and market liquidity channels play in the dissemination of systemic risk. The paper highlights how the market liquidity channel potentially has a more substantial impact on contagion compared to the network channel, challenging pre-existing beliefs that have predominantly emphasized network structures in systemic risk propagation. The study meticulously analyzes the interplay between financial institutions, interbank lending, borrowing, and the impacts of leverage and market liquidity, offering a comprehensive view of the systemic risk landscape in banking. It provides insights into the complexities of risk dynamics, leveraging the methodology proposed by Chen et al. (Oper. Res. 64(5):1089–1108, 2016) for a detailed balance sheet examination and network modeling. The findings underscore the importance of understanding and controlling risk channels, notably the network and market liquidity channels, to maintain the stability and resilience of the banking system. Policy implications are profound, suggesting that regulators and policymakers need to focus on enhancing market liquidity during economic strains and adopt targeted regulatory approaches to mitigate vulnerabilities stemming from interconnectedness and leverage. The study also emphasizes the need for ongoing monitoring and proactive management of systemic risk channels, recommending regular stress tests and the development of flexible regulatory measures that adapt to changing systemic risk factors. This research contributes significantly to the ongoing discussion on systemic risk in the financial sector, filling gaps in the literature by integrating various elements like network topologies and market liquidity in a comprehensive framework. It provides a novel perspective on the complex relationship between network interconnectedness and liquidity dynamics and offers practical guidance for optimizing banking structures for enhanced efficiency and resilience.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Acemoglu, D., Ozdaglar, A., & Tahbaz-Salehi, A. (2015). Systemic risk and stability in financial networks. American Economic Review, 105(2), 564–608.
Acharya, V. V., & Ryan, S. G. (2016). Banks’ financial reporting and financial system stability. Journal of Accounting Research, 54(2), 277–340.
Anderson, N., Webber, L., Noss, J., Beale, D., & Crowley-Reidy, L. (2018). The resilience of financial market liquidity. Bank of England.
Arner, D. W., Avgouleas, E., Busch, D., & Schwarcz, S. L. (Eds.). (2019). Systemic risk in the financial sector: Ten years after the great crash. McGill-Queen’s Press-MQUP.
Avgouleas, E. (2015). Bank leverage ratios and financial stability: A micro-and macroprudential perspective. Levy Economics Institute Working Paper No. 849. Annandale-on-Hudson, NY: Levy Economics Institute of Bard College. Available at SSRN: http://papers.ssrn.com/abstract=2682675, 2015.
Babu, D. G. S. (2018). Role of financial system in economic development of a country. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Development, 5(8), 100–107.
Besar, D., Booth, P., Chan, K. K., Milne, A. K., & Pickles, J. (2011). Systemic risk in financial services. British Actuarial Journal, 16(2), 195–300.
Bisias, D., Flood, M., Lo, A. W., & Valavanis, S. (2012). A survey of systemic risk analytics. Annual Review of Financial Economics, 4(1), 255–296.
Black, L., Correa, R., Huang, X., & Zhou, H. (2016). The systemic risk of European banks during the financial and sovereign debt crises. Journal of Banking & Finance, 63, 107–125.
Bluhm, M., & Krahnen, J. P. (2014). Systemic risk in an interconnected banking system with endogenous asset markets. Journal of Financial Stability, 13, 75–94.
Chen, N., Liu, X., & Yao, D. D. (2014). Modeling financial systemic risk—The network effect and the market liquidity effect. Available at SSRN: http://papers.ssrn.com/abstract=2463545, 2014.
Chen, N., Liu, X., & Yao, D. D. (2016). An optimization view of financial systemic risk modeling: Network effect and market liquidity effect. Operations Research, 64(5), 1089–1108.
Chinazzi, M., & Fagiolo, G. (2015). Systemic risk, contagion, and financial networks: A survey. In Banking integration and financial crisis: Some recent developments. Fundacion BBVA.
Cont, R., & Moussa, A. (2010). Network structure and systemic risk in banking systems. Available at SSRN: http://papers.ssrn.com/abstract=1733528, 2010.
Cont, R., & Wagalath, L. (2016). Fire sales forensics: Measuring endogenous risk. Mathematical Finance, 26(4), 835–866.
Demange, G. (2018). Contagion in financial networks: A threat index. Management Science, 64(2), 955–970.
Duarte, F., & Eisenbach, T. M. (2021). Fire-sale spillovers and systemic risk. The Journal of Finance, 76(3), 1251–1294.
Dungey, M., & Gajurel, D. (2015). Contagion and banking crisis–International evidence for 2007–2009. Journal of Banking & Finance, 60, 271–283.
Eboli, M. (2019). A flow network analysis of direct balance-sheet contagion in financial networks. Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control, 103, 205–233.
Elliott, M., & Golub, B. (2022). Networks and economic fragility. Annual Review of Economics, 14, 665–696.
Elsinger, H., Lehar, A., & Summer, M. (2013). Network models and systemic risk assessment. Handbook on Systemic Risk, 1(1), 287–305.
Falato, A., Hortacsu, A., Li, D., & Shin, C. (2021). Fire-sale spillovers in debt markets. The Journal of Finance, 76(6), 3055–3102.
Glasserman, P., & Young, H. P. (2016). Contagion in financial networks. Journal of Economic Literature, 54(3), 779–831.
Greenwood, R., Landier, A., & Thesmar, D. (2015). Vulnerable banks. Journal of Financial Economics, 115(3), 471–485.
Haldane, A. G., & May, R. M. (2011). Systemic risk in banking ecosystems. Nature, 469(7330), 351–355.
He, Q. M. (2014). Fundamentals of matrix-analytic methods (Vol. 365). Springer.
He, Z., & Wei, W. (2023). China’s financial system and economy: A review. Annual Review of Economics, 15, 451–483.
Hellwig, M. F. (2009). Systemic risk in the financial sector: An analysis of the subprime-mortgage financial crisis. De Economist, 157, 129–207.
Homar, T., Kick, H., & Salleo, C. (2016). Making sense of the EU wide stress test: A comparison with the SRISK approach. ECB Working Paper, No. 1920, ISBN 978-92-899-2168-8, European Central Bank (ECB), Frankfurt, https://doi.org/10.2866/10852.
Hurd, T. R. (2016). Contagion!: Systemic risk in financial networks (Vol. 42). Springer.
Hüser, A. C. (2015). Too interconnected to fail: A survey of the interbank networks literature. SAFE Working Paper, No. 91, Goethe University Frankfurt, SAFE - Sustainable Architecture for Finance in Europe, Frankfurt, https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2577241.
Joshi, M., Cahill, D., Sidhu, J., & Kansal, M. (2013). Intellectual capital and financial performance: An evaluation of the Australian financial sector. Journal of Intellectual Capital, 14(2), 264–285.
Kidwell, D. S., Blackwell, D. W., & Whidbee, D. A. (2016). Financial institutions, markets, and money. John Wiley & Sons.
Krause, A., & Giansante, S. (2012). Interbank lending and the spread of bank failures: A network model of systemic risk. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization, 83(3), 583–608.
Lai, Y., & Hu, Y. (2021). A study of systemic risk of global stock markets under COVID-19 based on complex financial networks. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 566, 125613.
Lenz, R. (2016). Peer-to-peer lending: Opportunities and risks. European Journal of Risk Regulation, 7(4), 688–700.
Li, F., & Perez-Saiz, H. (2018). Measuring systemic risk across financial market infrastructures. Journal of Financial Stability, 34, 1–11.
Li, W., Hommel, U., & Paterlini, S. (2018a). Network topology and systemic risk: Evidence from the Euro Stoxx market. Finance Research Letters, 27, 105–112.
Li, Y., Hao, A., Zhang, X., & Xiong, X. (2018b). Network topology and systemic risk in peer-to-peer lending market. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 508, 118–130.
Lorenz, J., & Battiston, S. (2008). Systemic risk in a network fragility model analyzed with probability density evolution of persistent random walks. Networks and Heterogeneous Media, 3(2), 185.
Lucas, I., Schomberg, N., & Couturier, F. A. (2013). Impact of liquidity crunch on interbank network. International Journal of Economics and Management Engineering, 7(10), 2733–2738.
Milne, A., & Parboteeah, P. (2016). The business models and economics of peer-to-peer lending. European Credit Research Institute.
Moloney, N. (2023). EU securities and financial markets regulation. Oxford University Press.
Monnet, E., Riva, A., & Ungaro, S. (2021). The real effects of bank runs. Evidence from the French Great Depression (1930–1931). Available at SSRN: http://papers.ssrn.com/abstract=3846142, 2021.
Morrison, W. M. (2019). China’s economic rise: History, trends, challenges, and implications for the United States. Current Politics and Economics of Northern and Western Asia, 28(2/3), 189–242.
Nasini, S., & Erdemlioglu, D. (2019). Multiple channels of financial contagion: An empirical analysis of stock price dynamics. Finance, 40(1), 87–133.
Neveu, A. R. (2018). A survey of network-based analysis and systemic risk measurement. Journal of Economic Interaction and Coordination, 13, 241–281.
Nguyen, T. N. M. (2014). Competition, liquidity and stability: International evidence at the bank and systemic levels (Doctoral dissertation,. Monash University).
Nowicki, J. P. (2015). Mortgage crisis: Exploring incentives prevalent during the boom and bust of the 2001-2007 mortgage market (Doctoral dissertation,. University of Denver).
Paltalidis, N., Gounopoulos, D., Kizys, R., & Koutelidakis, Y. (2015). Transmission channels of systemic risk and contagion in the European financial network. Journal of Banking & Finance, 61, S36–S52.
Rostásy, C. (2019). European integration and cross-border financial governance in the aftermath of the global financial crisis: Challenges and prospects of post-crisis policy responses to systemic risk in the European Union (Doctoral dissertation,. Zeppelin Universität).
Smaga, P. (2014). The concept of systemic risk. In Systemic Risk Centre Special Paper, (5). The London School of Economics and Political Science.
Somarakis, C., Siami, M., & Motee, N. (2016). Interplays between systemic risk and network topology in consensus networks. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 49(22), 333–338.
Stiglitz, J. E. (2010). Risk and global economic architecture: Why full financial integration may be undesirable. American Economic Review, 100(2), 388–392.
Summer, M. (2013). Financial contagion and network analysis. Annual Review of Financial Economics, 5(1), 277–297.
Upper, C., & Worms, A. (2004). Estimating bilateral exposures in the German interbank market: Is there a danger of contagion? European Economic Review, 48(4), 827–849.
Wang, Z., Gao, X., Huang, S., Sun, Q., Chen, Z., Tang, R., & Di, Z. (2022). Measuring systemic risk contribution of global stock markets: A dynamic tail risk network approach. International Review of Financial Analysis, 84, 102361.
Weber, S., & Weske, K. (2017). The joint impact of bankruptcy costs, fire sales and cross-holdings on systemic risk in financial networks. Probability, Uncertainty and Quantitative Risk, 2, 1–38.
Wu, F., Zhang, D., & Ji, Q. (2021). Systemic risk and financial contagion across top global energy companies. Energy Economics, 97, 105221.
Yarovaya, L., Brzeszczyński, J., Goodell, J. W., Lucey, B., & Lau, C. K. M. (2022). Rethinking financial contagion: Information transmission mechanism during the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of International Financial Markets Institutions and Money, 79, 101589.
Funding
This article was supported by the Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China Humanities and Social Sciences Youth Foundation grant number (20YJC630089); and Philosophy and Social Science Fund of Education Department of Jiangsu Province grant number (2019SJA1807).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X. Unraveling Systemic Risk Transmission: An Empirical Exploration of Network Dynamics and Market Liquidity in the Financial Sector. J Knowl Econ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-024-01861-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-024-01861-9