Abstract
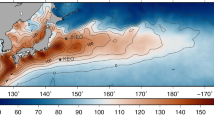
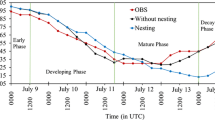
Air–sea exchange plays a vital role in the development and maintenance of tropical cyclones (TCs). Although studies have suggested the dependence of air–sea fluxes on surface waves and sea spray, how these processes modify those fluxes under TC conditions have not been sufficiently investigated based on in-situ observations. Using continuous meteorological and surface wave data from a moored buoy in the northern South China Sea, this study examines the effects of surface waves and sea spray on air–sea fluxes during the passage of Typhoon Hagupit. The mooring was within about 40 km of the center of Hagupit. Surface waves could increase momentum flux to the ocean by about 15%, and sea spray enhanced both sensible and latent heat fluxes to the atmosphere, causing Hagupit to absorb 500 W/m2 more heat flux from the ocean. These results have powerful implications for understanding TC–ocean interaction and improving TC intensity forecasting.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreas E L, Emanuel K A. 2001. Effects of sea spray on tropical cyclone intensity. J Atmos Sci, 58(24): 3741–3751
Andreas E L, Persson P O G, Hare J E. 2008. A bulk turbulent airsea flux algorithm for high-wind, spray conditions. J Phys Oceanogr, 38(7): 1581–1596
Bao J W, Wilczak J M, Choi J K, et al. 2000. Numerical simulations of air-sea interaction under high wind conditions using a coupled model: A study of hurricane development. Mon Weather Rev, 128(7): 2190–2210
Charnock H. 1955. Wind stress on a water surface. Q J Roy Meteor Soc, 81(350): 639–640
Drennan W M, Graber H C, Collins III C O, et al. 2014. EASI: An airsea interaction buoy for high winds. J Atmos Ocean Technol, 31(6): 1397–1409
Drennan W M, Graber H C, Hauser D, et al. 2003. On the wave age dependence of wind stress over pure wind seas. J Geophys Res, 108(C3): 8062
Donelan M A, Haus B K, Reul N, et al. 2004. On the limiting aerodynamic roughness of the ocean in very strong winds. Geophys Res Lett, 31(18): L18306
Drennan W M, Taylor P K, Yelland M J. 2005. Parameterizing the sea surface roughness. J Phys Oceanogr, 35(5): 835–848
Drennan W M, Zhang J A, French J R, et al. 2007. Turbulent fluxes in the hurricane boundary layer: Part II. Latent heat flux. J Atmos Sci, 64(4): 1103–1115
Emanuel K A. 1988. The maximum intensity of hurricanes. J Atmos Sci, 45(7): 1143–1155
Emanuel K A. 1995. Sensitivity of tropical cyclones to surface exchange coefficients and a revised steady-state model incorporating eye dynamics. J Atmos Sci, 52(22): 3969–3976
Fairall C W, Bradley E F, Hare J E, et al. 2003. Bulk parameterization of air-sea fluxes: updates and verification for the COARE algorithm. J Climate, 16(4): 571–591
Fairall C W, Bradley E F, Rogers D P, et al. 1996. Bulk parameterization of air-sea fluxes in TOGA COARE. J Geophys Res, 101(C2): 3747–3764
French J R, Drennan W M, Zhang J A, et al. 2007. Turbulent fluxes in the Hurricane boundary layer: Part I. Momentum flux. J Atmos Sci, 64(4): 1089–1102
Gerbi G P, Trowbridge J H, Edson J B, et al. 2008. Measurements of momentum and heat transfer across the air-sea interface. J Phys Oceanogr, 38(5): 1054–1072
Hara T, Belcher S E. 2004. Wind profile and drag coefficient over mature ocean surface wave spectra. J Phys Oceanogr, 34(11): 2345–2358
He Hailun, Chen Dake. 2011. Effects of surface wave breaking on the oceanic boundary layer. Geophys Res Lett, 38(7): L07604
Hilburn K A, Wentz F J. 2008. Intercalibrated passive microwave rain products from the unified microwave ocean retrieval algorithm (UMORA). J Appl Meteor Clim, 47(3): 778–794
Hwang P A. 2011. A note on the ocean surface roughness spectrum. J Atmos Oceanic Technol, 28(3): 436–443
Jarosz E, Mitchell D A, Wang D W T, et al. 2007. Bottom-up determination of air-sea momentum exchange under a major tropical cyclone. Science, 315(5819): 1707–1709
Kukulka T, Hara T. 2008a. The effect of breaking waves on a coupled model of wind and ocean surface waves: Part I. Mature seas. J Phys Oceanogr, 38(10): 2145–2163
Kukulka T, Hara T. 2008b. The effect of breaking waves on a coupled model of wind and ocean surface waves: Part II. Growing seas. J Phys Oceanogr, 38(10): 2164–2184
Large W G, Pond S. 1981. Open ocean momentum flux measurements in moderate to strong winds. J Phys Oceanogr, 11(3): 324–336
Large W G, Pond S. 1982. Sensible and latent heat flux measurements over the ocean. J Phys Oceanogr, 12(5): 464–482
Li Shuang, Li Ming, Gerbi G P, et al. 2013. Roles of breaking waves and Langmuir circulation in the surface boundary layer of a coastal ocean. J Geophys Res, 118(10): 5173–5187
Li Funing, Song Jinbao, He Hailun, et al. 2016. Assessment of surface drag coefficient parametrizations based on observations and simulations using the weather research and forecasting model. Atmos Oceanic Sci Lett, 9(4): 327–336
Liu Bin, Guan Changlong, Xie Li’an, et al. 2012. An investigation of the effects of wave state and sea spray on an idealized typhoon using an air-sea coupled modeling system. Adv Atmos Sci, 29(2): 391–406
Liu Bin, Liu Huiqing, Xie Lian, et al. 2011. A coupled atmospherewave-ocean modeling system: simulation of the intensity of an idealized tropical cyclone. Mon Weather Rev, 139(1): 132–152
Montoya R D, Arias O A, Royero O J C, et al. 2013. A wave parameters and directional spectrum analysis for extreme winds. Ocean Eng, 67: 100–118
Moon I J, Ginis I, Hara T. 2004. Effect of surface waves on Charnock coefficient under tropical cyclones. Geophys Res Lett, 31(20): L20302
Oost W A, Komen G J, Jacobs C M J, et al. 2002. New evidence for a relation between wind stress and wave age from measurements during ASGAMAGE. Bound-Layer Meteor, 103(3): 409–438
Pedreros R, Dardier G, Dupuis H, et al. 2003. Momentum and heat fluxes via the eddy correlation method on the R/V L'Atalante and an ASIS buoy. J Geophys Res, 108(C11): 3339
Potter H, Graber H C, Williams N J, et al. 2015. In situ measurements of momentum fluxes in typhoons. J Atmos Sci, 72(1): 104–118
Powell M D, Vickery P J, Reinhold T A. 2003. Reduced drag coefficient for high wind speeds in tropical cyclones. Nature, 422(6929): 279–283
Price J F. 1981. Upper ocean response to a hurricane. J Phys Oceanogr, 11(2): 153–175
Rastigejev Y, Suslov S A. 2014. E-ε model of spray-laden near-sea atmospheric layer in high wind conditions. J Phys Oceanogr, 44(2): 742–763
Rastigejev Y, Suslov S A, Lin Y L. 2011. Effect of ocean spray on vertical momentum transport under high-wind conditions. Bound-Layer Meteor, 141(1): 1–20
Smith S D. 1988. Coefficients for sea surface wind stress, heat flux, and wind profiles as a function of wind speed and temperature. J Geophys Res, 93(C12): 15467–15472
Song Jinbao, Fan Wei, Li Shuang, et al. 2015. Impact of surface waves on the steady near-surface wind profiles over the ocean. Bound-Layer Meteor, 155(1): 111–127
Taylor P K, Yelland M A. 2001. The dependence of sea surface roughness on the height and steepness of the waves. J Phys Oceanogr, 31(2): 572–590
Walsh K J E, Sandery P, Brassington G B, et al. 2010. Constraints on drag and exchange coefficients at extreme wind speeds. J Geophys Res, 115(C9): C09007
Wang Juanjuan, Song Jinbao, Huang Yansong, et al. 2013. Application of the Hilbert-Huang Transform to the estimation of airsea turbulent fluxes. Bound-Layer Meteor, 147(3): 553–568
Wu Lichuan, Rutgersson A, Sahlée E, et al. 2015. The impact of waves and sea spray on modelling storm track and development. Tellus A, 67(1): 27967
Xu Yao, He Hailun, Song Jinbao, et al. 2017. Observations and modeling of typhoon waves in the South China Sea. J Phys Oceanogr, 47(6): 1307–1324
Xu Fumin, Perrie W, Toulany B, et al. 2007. Wind-generated waves in hurricane Juan. Ocean Modell, 16(3–4): 188–205
Zhang J A, Black P G, French J R, et al. 2008. First direct measurements of enthalpy flux in the hurricane boundary layer: The CBLAST results. Geophys Res Lett, 35(14): L14813
Zhang Ting, Song Jinbao. 2018. Effects of sea-surface waves and ocean spray on air-sea momentum fluxes. Adv Atmos Sci, 35(4): 469–478, doi: 10.1007/s00376-017-7101-7
Zhang Ting, Song Jinbao, Li Shuang, et al. 2016. The effects of winddriven waves and ocean spray on the drag coefficient and nearsurface wind profiles over the ocean. Acta Oceanol Sin, 35(11): 79–85
Zhao Dongliang, Toba Y, Suzuki Y, et al. 2003. Effect of wind waves on air-sea gas exchange: Proposal of an overall CO2 transfer velocity formula as a function of breaking-wave parameter. Tellus B, 55(2): 478–487
Zhao Dongliang, Xie Lian. 2010. A practical bi-parameter formula of gas transfer velocity depending on wave states. J Oceanogr, 66(5): 663–671
Acknowledgements
The AMSR data are produced by Remote Sensing Systems and sponsored by the NASA Earth Science MEaSUREs DISCOVER Project and the NASA AMSR-E Science Team (www.remss.com). The NCEP Reanalysis data are provided by the NOAA/OAR/ESRL PSD (http://www.esrl.noaa.gov/psd/). The sea spray code is from Dr. E. L. Andreas (http://www.nwra.com/resumes/andreas/).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China under contract No. LR15D060001; the National Program on Global Change and Air-Sea Interactions under contract No. GASI-IPOVAI-04; the National Natural Science Foundation of China under contract Nos 41476021, 41706034 and 41321004.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, H., Wu, Q., Chen, D. et al. Effects of surface waves and sea spray on air–sea fluxes during the passage of Typhoon Hagupit. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 37, 1–7 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-018-1208-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-018-1208-2