Abstract
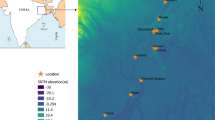
Oxygen and carbon isotope ratios (δ 18O and δ 13C) in otoliths were used to identify the stock structure of small yellow croaker, Larimichthys polyactis. Otoliths were collected from fish at five locations across the Yellow Sea and the Bohai Sea representing most of their distributional range and fisheries areas. The significant differences in the isotopic signatures showed that the five locations could be chemically distinguished and clearly separated, indicating stock subdivision. Correlation of δ 18O and δ 13C values suggested that population of L. polyactis could be divided into the Bohai Sea group, the southern Yellow Sea group and the central Yellow Sea group. Discriminant analysis of δ 18O and δ 13C values demonstrated a high significant difference with 85.7% classification accuracy. The spatial separation of L. polyactis indicated a complex stock structure across the Yellow Sea and the Bohai Sea. These results indicate that optimal fisheries management may require a comprehensive consideration on the current spatial arrangements. This study has provided further evidence that measurement of the stable isotopes ratios in otolith can be a valuable tool in the delineation of fishery management units.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almany G R, Berumen M L, Thorrold S R, et al. 2007. Local replenishment of coral reef fish populations in a marine reserve. Science, 316(5825): 742–744
Begg G A, Friedland K D, Pearce J B. 1999. Stock identification and its role in stock assessment and fisheries management: an overview. Fisheries Research, 43(1–3): 1–8
Campana S E. 1999. Chemistry and composition of fish otoliths: pathways, mechanisms and applications. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 188: 263–297
Correia A T, Barros F, Sial A N. 2011. Stock discrimination of European conger eel (Conger conger L.) using otolith stable isotope ratios. Fisheries Research, 108(1): 88–94
Devereux I. 1967. Temperature measurements from oxygen isotope ratios of fish otoliths. Science, 155(3770): 1684–1685
Edmonds J S, Fletcher W J. 1997. Stock discrimination of pilchards Sardinops sagax by stable isotope ratio analysis of otolith carbonate. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 152: 241–247
Epstein S, Buchsbaum R, Lowenstam H A, et al. 1953. Revised carbonate-water isotopic temperature scale. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 64(11): 1315–1326
Gao Y W, Beamish R J. 1999. Isotopic composition of otoliths as a chemical tracer in population identification of sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka). Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 56(11): 2062–2068
Gao Y W, Joner S H, Bargmann G G. 2001. Stable isotopic composition of otoliths in identification of spawning stocks of Pacific herring (Clupea pallasi) in Puget Sound. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 58(11): 2113–2120
Han Zhiqiang, Lin Longshan, Shui Bonan, et al. 2009. Genetic diversity of small yellow croaker Larimichthys polyactis revealed by AFLP markers. African Journal of Agricultural Research, 4(7): 605–610
Li Yuan, Han Zhen, Song Na, et al. 2013. New evidence to genetic analysis of small yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis) with continuous distribution in China. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology, 50: 331–338
Lin Longshan, Cheng Jiahua, Ren Yiping, et al. 2004. Analysis of population biology of small yellow croaker Pseudosciaena polyactis in the East China Sea region. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China (in Chinese), 11(4): 333–338
Lin Xinzhuo, Deng Siming, Huang Zhengyi, et al. 1965. Biometrics study of small yellow croaker. In: The paper Collection of Marine Fishery Resources (in Chinese). Beijing: Agriculture Press, 84–108
Liu Xiaoshun. 1990. Small yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena ployactis Bleeker). In: Fishery Bureau of Ministry of Agriculture, ed. Investigation and Division of Fisheries Resource of the Bohai and Yellow Sea (in Chinese). Beijing: China Ocean Press, 191–200
Meng Zining, Zhuang Zhimeng, Jin Xianshi, et al. 2003. Genetic diversity in small yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena polyactis) by RAPD analysis. Biodiversity Science (in Chinese), 11(3): 197–203
Newman S J, Pember M B, Rome B M, et al. 2011. Stock structure of blue threadfin Eleutheronema tetradactylum across northern Australia as inferred from stable isotopes in sagittal otolith carbonate. Fisheries Management and Ecology, 18(3): 246–257
Newman S J, Steckis R A, Edmonds J S, et al. 2000. Stock structure of the goldband snapper Pristipomoides multidens (Pisces: Lutjanidae) from the waters of northern and western Australia by stable isotope ratio analysis of sagittal otolith carbonate. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 198: 239–247
Newman S J, Wright I W, Rome B M, et al. 2010. Stock structure of Grey Mackerel, Scomberomorus semifasciatus (Pisces: Scombridae) across northern Australia, based on otolith stable isotope chemistry. Environmental Biology of Fishes, 89(3–4): 357–367
Perkins M J, McDonald R A, van Veen F J F, et al. 2014. Application of nitrogen and carbon stable isotopes (δ 15N and δ 13C) to quantify food chain length and trophic structure. PLoS One, 9(3): e93281
Schwarcz H P, Gao Y, Campana S, et al. 1998. Stable carbon isotope variations in otoliths of Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 55(8): 1798–1806
Stephenson P C, Edmons J S, Moran M J, et al. 2001. Analysis of stable isotope ratios to investigate stock structure of red emperor and Rankin cod in northern Western Australia. Journal of Fish Biology, 58(1): 126–144
Tohse H, Mugiya Y. 2008. Sources of otolith carbonate: experimental determination of carbon incorporation rates from water and metabolic CO2, and their diel variations. Aquatic Biology, 1(3): 259–268
Xiao Yongshuang, Zhang Yan, Gao Tianxiang, et al. 2009. Genetic diversity in the mtDNA control region and population structure in the small yellow croaker Larimichthys polyactis. Environmental Biology of Fishes, 85(4): 303–314
Xu Guangping, Zhong Xiaming, Ding Yyaping, et al. 2005. The research on genetic diversity of Pseudosciaena polyactis population from the southern part of the Yellow Sea. Marine Sciences (in Chinese), 29(11): 34–38
Xu Zhaoli, Chen Jiajie. 2010. Population division of Larimichthys polyactis in China Sea. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology (in Chinese), 21(11): 2856–2864
Zhang Chi, Ye Zhenjiang, Wan Rong, et al. 2014. Investigating the population structure of small yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis) using internal and external features of otoliths. Fisheries Research, 153: 41–47
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The National Basic Research Program (973 Program) of China under contract Nos 2015CB453300 and 2010CB428900.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Huang, J., Tang, X. et al. Stable isotopic composition of otoliths in identification of stock structure of small yellow croaker (Larimichthys polyactis) in China. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 35, 29–33 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-016-0868-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-016-0868-z