Abstract
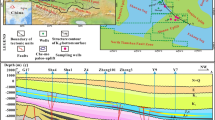
Over the past several years, a number of hydrocarbon reservoirs have been discovered in the deepwater area of Qiongdongnan Basin, northwestern South China Sea. These oil/gas fields demonstrate that the evolution of the deepwater sedimentary environment are controlling the formation and distribution of large-scale clastic reservoirs. Integration between seismic and borehole data were necessary to best clarify the distribution and quality of these deepwater reservoirs. Geochemical and paleobiological evidence from discrete samples was also applied to document specific information regarding the sedimentary environment. Results show that the Qiongdongnan Basin has existed as a thriving marine environment since Oligocene, when several rifting depressions developed throughout the entire Qiongdongnan Basin. Triggered by the faults activities, several distinct provenances supplied the coarse sediments, transporting and depositing them in deep parts of the rifting depressions. A fan delta system then formed nearby the source in the deeper area of these rifting depressions. The sedimentary environment of Qiongdongnan gradiationally became deepwater since early Miocene. Consequently, abundances of sediments were transported from Hainan Island and Southern Uplift, and then sunk into the basin center. The submarine fans revealed by many boreholes in this area verified them as good reservoir. Because the area reached its lowest sea level at late Miocene and the Southern Uplift subsidenced under sea level, not providing any sediment, so that the carbonate mesa and biorhythms characteristic of this area also developed during this period. In the west part of Qiongdongnan Basin, sediments transported from Vietnam increased in response to the Tibetan Uplift. Consequently, a central canyon developed along the center of Qiongdongnan Basin, which has been confirmed by several boreholes as a favorable hydrocarbon reservoir. The clarification of the deepwater sedimentary environment’s evolution is potentially highly beneficial to future hydrocarbon exploration in the deepwater area of Qiongdongnan Basin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Briais A, Patriat P, Tapponnier P. 1993. Updated interpretation of magnetic anomalies and seafloor spreading stages in the South China Sea: Implications for the Tertiary tectonics of Southeast Asia. Journal of Geophysical Research, 98(B4): 6299–6328
Cao Licheng, Jiang Tao, Wang Zhenfeng, et al. 2015. Provenance of Upper Miocene sediments in the Yinggehai and Qiongdongnan basins, northwestern South China Sea: Evidence from REE, heavy minerals and zircon U-Pb ages. Marine Geology, 361: 136–146
Chen P P H, Chen Zhiyong, Zhang Qiming. 1993. Sequence stratigraphy and continental margin development of the northwestern shelf of the South China Sea. AAPG Bulletin, 77(5): 842–862
Clift P D, Sun Zhen. 2006. The sedimentary and tectonic evolution of the Yinggehai-Song Hong basin and the southern Hainan margin, South China Sea: Implications for Tibetan uplift and monsoon intensification. Journal of Geophysical Research, 111(B6): B6405, doi: 10.1029/2005JB004048
Cullen A, Reemst P, Henstra G, et al. 2010. Rifting of the South China Sea: new perspectives. Petroleum Geoscience, 16(3): 273–282
Flower M F J, Russo R M, Tamaki K, et al. 2001. Mantle contamination and the Izu-Bonin-Mariana (IBM) ‘high-tide mark’: evidence for mantle extrusion caused by Tethyan closure. Tectonophysics, 333(1–2): 9–34
Hall R. 2002. Cenozoic geological and plate tectonic evolution of SE Asia and the SW Pacific: computer-based reconstructions, model and animations. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 20(4): 353–431
Hao Fang, Li Sitian, Sun Yongchuan, et al. 1998. Geology, compositional heterogeneities, and geochemical origin of the Yacheng gas field, Qiongdongnan basin, South China Sea. American Associate Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 82(7): 1372–1384
Hayes D E, Nissen S S. 2005. The South China Sea margins: implications for rifting contrasts. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 237(3–4): 601–616
He Yunlong, Xie Xinong, Kneller B C, et al. 2013. Architecture and controlling factors of canyon fills on the shelf margin in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 41: 264–276
Holloway N H. 1982. North Palawan Block, Philippines: its relation to Asian mainland and role in evolution of South China Sea. AAPG Bull, 66(9): 1355–1383
Hori K, Tanabe S, Saito Y, et al. 2004. Delta initiation and Holocene sea-level change: Example from the Song Hong (Red River) delta, Vietnam. Sedimentary Geology, 164(3–4): 237–249
Hutchison C S. 2004. Marginal basin evolution: the southern South China Sea. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 21(9): 1129–1148
Jiang Tao, Tang Sulin, Xie Xinong, et al. 2014. Numerical simulation on sedimentary processes of turbidity current and its applications on reservoir prediction in Qiongdongnan basin, northern South China Sea. In: Yang Jianwen, ed. Basins: Methods of Formation, Ongoing Developments and Emerging Challenges. New York: Nova Science Publishers Inc, 27–48
Jiang Tao, Xie Xinong, Tang Suling, et al. 2007. Numerical simulation on the evolution of sediment waves caused by turbidity currents. Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(17): 2429–2434
Jiang Tao, Xie Xinong, Wang Zhenfeng, et al. 2013. Seismic features and origin of sediment waves in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea. Marine Geophysical Research, 34(3–4): 281–294
Lallemand S, Jolivet L. 1986. Japan Sea: a pull-apart basin?. Earth Planet and Science Letter, 76(3–4): 375–389
Leloup P H, Arnaud N, Lacassin R, et al. 2001. New constraints on the structure, thermochronology, and timing of the Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone, SE Asia. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 106(B4): 6683–6732
Li Xiangquan, Fairweather L, Wu Shiguo, et al. 2013. Morphology, sedimentary features and evolution of a large palaeo submarine canyon in Qiongdongnan basin, Northern South China Sea. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 62: 685–696
Liu Zhifei, Coline C, Huang Wei, et al. 2007. Climatic and tectonic controls on weathering in South China and Indochina Peninsula: Clay mineralogical and geochemical investigations from the Pearl, Red, and Mekong drainage basins. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 8(5): doi: 10.1029/2006GC001490
Lu Xixi, Chen Xiqing. 2008. Larger Asian rivers and their interactions with estuaries and coasts. Quaternary International, 186(1): 1–3
Lüdmann T, Wong H K, Wang Pinxian. 2001. Plio-Quaternary sedimentation processes and neotectonics of the northern continental margin of the South China Sea. Marine Geology, 172(3–4): 331–358
Schärer U, Tapponnier P, Lacassin R, et al. 1990. Intraplate tectonics in Asia: a precise age for large-scale Miocene movement along the Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone, China. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 97(1–2): 65–77
Song Guangzeng, Wang Hua, Gan Huajun, et al. 2014. Paleogene tectonic evolution controls on sequence stratigraphic patterns in the central part of deepwater area of Qiongdongnan basin, northern South China Sea. Journal of Earth Science, 25(2): 275–288
Su Ming, Xie Xinong, Xie Yuhong, et al. 2014. The segmentations and the significances of the Central Canyon System in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 79(Part A): 552–563
Tapponnier P, Lacassin R, Leloup P H, et al. 1990. The Ailao Shan/Red River metamorphic belt: Tertiary left-lateral shear between Indochina and South China. Nature, 343(6257): 431–437
Tapponnier P, Peltzer G, Le Dain A Y, et al. 1982. Propagating extrusion tectonics in Asia: new insights from simple experiments with plasticine. Geology, 10(12): 611–616
Tapponnier P, Xu Zhiqin, Roger F, et al. 2001. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet Plateau. Science, 294(5547): 1671–1677
Taylor B, Hayes D E. 1983. Origin and history of the South China Sea basin. In: Hayes D E, ed. The Tectonic and Geologic Evolution of Southeast Asian Seas and Islands: Part 2. American Geophysical Union, Geophysical Monographs Series. Washington, DC: American Geophysical Union, 27: 23–56
Vail P R, Mitchum R M Jr, Thompson S III. 1977. Seismic stratigraphy and global changes of sea level, part 4: Global cycles of relative changes of sea level. In: Payton C E, ed. Seismic Stratigraphy: Applications to Hydrocarbon Exploration. AAPG Memoir, 26. 7th ed. Tulsa, OK: American Association of Petroleum Geologists, 99–116
Van Wagoner J C, Mitchum R M, Campion K M, et al. 1990. Siliciclastic Sequence Stratigraphy in Well Logs, Cores, and Outcrops. American Association of Petroleum Geologist Methods in Exploration Series 7. Tulsa, OK: American Association of Petroleum Geologists, 55
Wang Yingmin, Xu Qiang, Li Dong, et al. 2011. Late Miocene Red River submarine fan, northwestern South China Sea. Chinese Science Bulletin, 56(14): 1488–1494
Xie Xinong, Müller D R, Li Sitian, et al. 2006. Origin of anomalous subsidence along the northern South China Sea margin and its relationship to dynamic topography. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 23(7): 745–765
Xie Xinong, Müller Dietmar, Ren Jianye, et al. 2008. Stratigraphic architecture and evolution of the continental slope system in offshore Hainan, northern South China Sea. Marine Geology, 247(3–4): 129–144
Xu Yigang, Wei Jingxian, Qiu Huaning, et al. 2012. Opening and evolution of the South China Sea constrained by studies on volcanic rocks: preliminary results and a research design. Chinese Science Bulletin, 57(24): 3150–3164
Yuan Shengqiang, Lü Fuliang, Wu Shiguo, et al. 2009. Seismic stratigraphy of the Qiongdongnan deep sea channel system, northwest South China Sea. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 27(2): 250–259
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: The National Science and Technology Major Project of China under contract No. 2011ZX05025-002-02; the National Natural Science Foundation of China under contract Nos 41476032 and 41372112.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Jiang, T., Zhang, D. et al. Evolution of deepwater sedimentary environments and its implication for hydrocarbon exploration in Qiongdongnan Basin, northwestern South China Sea. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 34, 1–10 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-015-0645-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-015-0645-4